Abstract
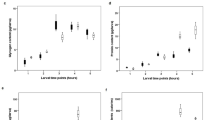
Esterases are known to play essential role in metabolism, reproductive physiology and behaviour of Drosophila. Esterases are highly polymorphic enzymes in Drosophila, but the polymorphism of these enzymes is not well studied in Drosophila ananassae. Recent studies on esterase polymorphism in D. ananassae revealed that Est-4 locus comprises Est-4 active and Est-4 null alleles depending on enzymatic activity. For the in vivo functional characterization of this locus, homozygous lines of genotypes Est-4 active and Est-4 null were derived from the flies collected from Gangtok, Sikkim, in 2006. Mating propensity, mating pattern, fecundity, fertility and productivity of female, life span and triglycerides level were investigated in the flies bearing either Est-4 active or Est-4 null genotypes. Results showed that mating occurred randomly with nonsignificant difference in mating propensity between Est-4 active and Est-4 null flies. However, a significant difference in fecundity and strong dependency between genotypes and the rate of fertility was found. The median values of progeny produced per female were 24 and 20 for Est-4 active and Est-4 null genotypes, respectively. The life span assay showed a significant difference in the survivorship between the two genotypes. Triglycerides level was higher in Esterase-4 active larval haemolymph as well as in mature flies’ homogenate than that of Esterase-4 null. Thus, Esterase-4 locus of D. ananassae has its role in fecundity, fertility and productivity of female, life span control and lipid metabolism.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aslund S.-E. and Rasmuson M. 1978 Mating behaviour as a fitness component involved in maintaining allozyme polymorphism in Drosophila melanogaster III. The amount of variation among allozyme genotypes in the Est-6 and Lap-A allozyme systems. Hereditas 89, 29–35.
Ayala F. J., Mourao C. A., Perez-Salas S., Richmond R. and Dobzhansky T. 1970 Enzyme variability in the Drosophila willistoni group I. Genetic differentiation among sibling species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 67, 225–232.
Bell G. and Koufopanou V. 1986 The cost of reproduction. Oxford Surv. Evol. Biol. 3, 83–131.
Beller M., Riedel D., Jansch L., Dieterich G., Wehland J., Jackle H. et al. 2006 Characterization of the Drosophila lipid droplet subproteome. Mol. Cell Proteomics 5, 1082–1094.
Birley A. J. and Beardmore J. A. 1977 Genetical composition, temperature, density and selection in an enzyme polymorphism. Heredity 39, 133–144.
Birner-Gruenberger R., Bickmeyer I., Lange J., Hehlert P., Hermetter A., Kollroser M. et al. 2012 Functional fat body proteomics and gene targeting reveal in vivo functions of Drosophila melanogaster \(\alpha \)-Esterase-7. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 42, 220–229.
Campbell P. M., de Q Robin G. C., Court L. N., Court N., Dorrian S. J., Russell R. J. et al. 2003 Developmental expression and gene/enzyme identifications in the alpha esterase gene cluster of Drosophila melanogaster. Insect Mol. Biol. 12, 459–471.
Carvajal-Rodriguez A. and Rolan-Alvarez E. 2006 JMATING: a software for the analysis of sexual selection and sexual isolation effects from mating frequency data. BMC Evol. Biol. 6, 40.
Chertemps T., Francois A., Durand N., Rosell G., Dekker T., Lucas P. et al. 2012 A carboxylesterase, Esterase-6, modulates sensory physiological and behavioral response dynamics to pheromone in Drosophila. BMC Biol. 10, 56.
Chintapalli V. R., Wang J. and Dow J. A. T. 2007 Using FlyAtlas to identify better Drosophila melanogaster models of human disease. Nat. Genet. 39, 715–720.
Chippindale A. K., Leroi A. M., Kim S. B. and Rose M. R. 1993 Phenotypic plasticity and selection in Drosophila life history evolution. I. Nutrition and the cost of reproduction. J. Evol. Biol. 6, 171–193.
Coyne J. A., Elwyn S. and Rolan-Alvarez E. 2005 Impact of experimental design on drosophila sexual isolation studies: direct effects and comparison to field hybridization data. Evolution 59, 2588–2601.
Dierick H. A. and Greenspan R. J. 2006 Molecular analysis of flies selected for aggressive behavior. Nat. Genet. 38, 1023–1031.
Elens A. A. and Wattiaux J. M. 1964 Direct observations of sexual isolation. Dros. Inf. Serv. 39, 118–119.
Ellis L. L. and Carney G. E. 2010 Mating alters gene expression patterns in Drosophila melanogaster male heads. BMC Genomics 11, 558.
Gems D., Sutton A. J., Sundermeyer M. L., Albert P. S., King K. V., Edgley M. L. et al. 1998 Two pleiotropic classes of daf-2 mutation affect larval arrest, adult behavior, reproduction and longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 150, 129–155.
Gilbert D. G. and Richmond R. C. 1981 Studies of esterase 6 in Drosophila melanogaster. VI. Ejaculate competitive abilities of males having null or active alleles. Genetics 97, 85–94.
Gilbert D. G. and Richmond R. C. 1982 Esterase 6 in Drosophila melanogaster: reproductive function of active and null males at low temperature. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79, 2962–2966.
Gilbert D. G., Richmond R. C. and Sheehan K. B. 1981 Studies on esterase 6 in Drosophila melanogaster. V. Progeny production and sperm use in females inseminated by males having active or null alleles. Evolution 35, 21–37.
Hansen M., Flatt T. and Aguilaniu H. 2013 Reproduction, fat metabolism, and life span: what is the connection? Cell Metabol. 17, 10–19.
Harshman L. G. and Hoffmann A. A. 2000 Laboratory selection experiments using Drosophila: what do they really tell us? Trends Ecol. Evol. 15, 32–36.
Healy M. J., Dumancic M. M. and Oakeshott J. G. 1991 Biochemical and physiological studies of soluble esterases from Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem. Genet. 29, 365–388.
Judd E. T., Wessels F. J., Drewry M. D., Grove M., Wright K., Hahn D. A. et al. 2011 Ovariectomy in grasshoppers increases somatic storage, but proportional allocation of ingested nutrients to somatic tissues is unchanged. Aging Cell 10, 972–979.
Kojima K. and Yarbrough K. M. 1967 Frequency dependent selection at the esterase 6 locus in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 57, 645–649.
Krishnamoorti K. and Singh A. K. 2013 Esterase-4 locus comprises active and null alleles in Drosophila ananassae. Dros. Inf. Serv. 96, 54–55.
Kumar S. and Singh A. K. 2014 Complete absence of linkage disequilibrium between enzyme loci in natural populations of Drosophila ananassae. Genetika 46, 227–234.
Langely C. H., Voelker R. A., Leigh-Brown A. J., Ohnishi S., Dickson B. and Montgomeri E. 1981 Null allele frequencies at allozyme loci in natural populations of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 99, 151–156.
Lewontin R. C. and Hubby J. L. 1966 A molecular approach to the study of genic heterozygosity in natural populations. II. Amount of variation and degree of heterozygosity in natural populations of Drosophila pseudoobscura. Genetics 54, 595–609.
Mackay T. F. C., Roshina N. V., Leips J. W. and Pasyukova E. G. 2006 Complex genetic architecture of Drosophila longevity. In Handbook of the biology of aging (ed. E. J. Masaro and S. N. Austad), pp. 181–216. Elsevier Press, Burlington, USA.
Nanda P. and Singh B. N. 2008 No effect of marking procedures and choice situations on the pattern of matings in Drosophila ananassae. Dros. Inf. Serv. 91, 10–13.
Oakeshott J. G., van Papenrecht E. A., Boyce T. M., Healy M. J. and Russell R. J. 1993 Evolutionary genetics of Drosophila esterases. Genetica 90, 239–268.
Paaby A. B. and Schmidt P. S. 2008 Functional significance of allelic variation at methuselah, an aging gene in Drosophila. PLoS One 3, e1987.
Paaby A. B. and Schmidt P. S. 2009 Dissecting the genetics of longevity in Drosophila melanogaster. Fly 3, 1–10.
Partridge L., Gems D. and Withers D. J. 2005 Sex and death: what is the connection? Cell 120, 461–472.
Richmond R. C. and Senior A. 1981 Esterase 6 of Drosophila melanogaster: kinetics of transfer to females, decay in females and male recovery. J. Insect Physiol. 27, 849–853.
Saad M., Game A. Y., Healy M. J. and Oakeshott J. G. 1994 Associations of esterase 6 allozyme and activity variation with reproductive fitness in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetica 94, 43–56.
Singh B. N. 2010 Drosophila ananassae: a good model species for genetical, behavioral and evolutionary studies. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 48, 333–345.
Singh B. N. 2013 Genetic polymorphisms in Drosophila. Curr. Sci. 105, 461–469.
Som A. and Singh B. N. 1998 No effect of marking flies either by nail polish on scutellum or by wing clipping on mating success in Drosophila ananassae. Dros. Inf. Serv. 81, 202–203.
Tatar M., Kopelman A., Epstein D., Tu M. P., Yin C. M. and Garofalo R. S. 2001 A mutant Drosophila insulin receptor homolog that extends life-span and impairs neuroendocrine function. Science 292, 107–110.
Tweedie S., Ashburner M., Falls K., Leyland P., McQuilton P., Marygold S. et al. 2009 FlyBase: enhancing Drosophila gene ontology annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, D555–D559.
Voelkar R. A., Langley C. H., Leigh-Brown A. J., Ohnishi S., Dickson B., Montgomery E. et al. 1980 Enzyme null alleles in natural populations of Drosophila melanogaster: frequencies in a North Carolina population. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77, 1091–1095.
Williams G. C. 1966 Natural selection, the costs of reproduction, and a refinement of Lack’s principle. Am. Nat. 100, 687–690.
Wright T. R. F. 1963 The genetics of an Esterase in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 48, 787–801.
Acknowledgements
KK is grateful to University Grant Commission, New Delhi, for providing the research fellowship. We are thankful to E. Rolan-Alvarez for helping us with JMATING software. We also thank the anonymous reviewers for their comments and suggestions on the original draft of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Corresponding editor: N. G. Prasad.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishnamoorti, K., Singh, A.K. Fitness differences due to allelic variation at Esterase-4 locus in Drosophila ananassae . J Genet 96, 625–631 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-017-0814-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-017-0814-7