Abstract
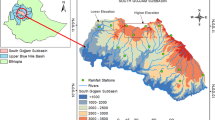
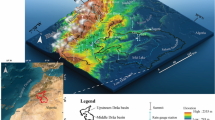
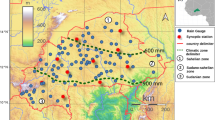
This study aims to assess the accuracy of three satellite-derived products (IMERG-F, CHIRPS and PERSIANN CDR) in quantifying the erosivity of rainfall. A network of 14 gauge stations is utilized to estimate the R-factor in west-central Morocco between 2001 and 2020. This evaluation is conducted at the basin, and the pixel scale is based on five statistical metrics. The present research showed that rainfall intensity and the topographic characteristic of terrain could highly affect the performance of SPPs in estimating the R-factor; the results show that the estimations become less accurate either in high altitudes or in high rainfall intensities. Furthermore, the findings indicate that CHIRPS outperforms the other datasets, particularly at the basin scale where the relative bias is close to 0, with a minimum error and a Nash coefficient of about 0.62, followed by the IMERG-F product, while PERSIANN CDR has the lowest performance. Overall, this study’s outcome yields valuable insights into the applicability of CHIRPS product in estimating rainfall erosivity factor in scarcely gauged areas characterized by a complex climate and topography.
Research highlights
-
The rainfall erosivity factor was calculated using three satellite precipitation products.
-
CHIRPS product exhibited the best performance in estimating rainfall erosivity in Tensift watershed.
-
The performance of SPPs in estimating R factor is highly affected by the altitudes and the climatic caracteristics of the study area.
-
The vulnerability maps were created to identify regions threatened by water erosion according to the three products.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alijanian M, Rakhshandehrooc G R, Mishra A and Dehghani M 2019 Evaluation of remotely sensed precipitation estimates using PERSIANN-CDR and MSWEP for spatio-temporal drought assessment over Iran; J. Hydrol. 579 124189, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124189.
Alsumaiti T S, Hussein K, Ghebreyesus D T and Sharif H O 2020 Performance of the CMORPH and GPM IMERG products over the United Arab Emirates; Remote Sens. 12(9), https://doi.org/10.3390/RS12091426.
Arnoldus H M 1977 Methodology used to determine the maximum potential average annual soil loss due to sheet and rill erosion in Morocco. Assessing soil degradation; FAO Soil Bulletin 34 39–51.
Ayele Almaw F, Hiroshi Y, Katsuyuki S, Nigussie H, Takayuki K, Dagnenet S, Kindiye E and Ashebir Sewale B 2017 Spatial distribution and temporal trends of rainfall and erosivity in the Eastern Africa region; Hydrol. Process. 31(25) 4555–4567, https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.11378.
Camici S, Massari C, Ciabatta L, Marchesini I and Brocca L 2020 Which rainfall score is more informative about the performance in river discharge simulation? A comprehensive assessment on 1318 basins over Europe; Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 24 4869–4885, https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-24-4869-2020.
Chai T and Draxler R R 2014 Root mean square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE)? – Arguments against avoiding RMSE in the literature; Geosci. Model Dev. 7 1247–1250, https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-7-1247-2014.
Chang Y, Lei H, Zhou F and Yang D 2022 Spatial and temporal variations of rainfall erosivity in the middle Yellow River Basin based on hourly rainfall data; Catena 216 106406, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2022.106406.
Chen J, Wang Z, Wu X, Chen X, Lai C, Zeng A and Li J 2019 Accuracy evaluation of GPM multi-satellite precipitation products in the hydrological application over alpine and gorge regions with sparse rain gauge network; Hydrol. Res. 50(6) 1710–1729, https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.2019.133.
Chen Y, Xu M, Wang Z, Gao P and Lai C 2021 Applicability of two satellite-based precipitation products for assessing rainfall erosivity in China; Sci. Total Environ. 757 143975, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143975.
Chris C F, Peterson J P, Landsfeld M F, Pedreros D H, Verdin J, Rowland J D, Romero B E, Husak G J, Michaelsen J C and Verdin A P 2014 A quasi-global precipitation time series for drought monitoring; US Geol. Surv. Data Ser. 832 4p.
Das S, Kumar M and Gupta V 2022 A step towards mapping rainfall erosivity for India using high-resolution GPM satellite rainfall products; Catena 212 106067, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2022.106067.
Dash C J, Das N K and Adhikary P P 2019 Rainfall erosivity and erosivity density in Eastern Ghats; Nat. Hazards 97(2) 727–746, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-019-03670-9.
De Brito C S, da Silva R M, Santos C A G, Neto R M B and Coelho V H R 2022 Long-term basin-scale comparison of two high-resolution satellite-based remote sensing datasets for assessing rainfall and erosivity in a basin in the Brazilian semi-arid region; Theor. Appl. Climatol. 147 1049–1064, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-021-03857-w.
Delgado D, Sadaoui M, Ludwig W and Méndez W 2022 Spatio-temporal assessment of rainfall erosivity in Ecuador based on RUSLE using satellite-based high frequency GPM-IMERG precipitation data; Catena 219 106597, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2022.106597.
Diem J E, Hartter J, Ryan S J and Palace M W 2014 Validation of satellite rainfall products for Western Uganda; J. Hydrometeorol. 15(5) 2030–2038, https://doi.org/10.1175/JHM-D-13-0193.1.
Dinku T, Hailemariam K, Maidment R, Tarnavsky E and Connor S 2013 Combined use of satellite estimates and rain gauge observations to generate high-quality historical rainfall time series over Ethiopia; Int. J. Climatol. 34 2489–2504, https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.3855.
El Alaoui El Fels A, Saidi M E and Bin Alam M J 2022 Rainfall frequency analysis using assessed and corrected satellite precipitation products in Moroccan arid areas. The case of Tensift Watershed; Earth Syst. Environ. 6(2) 391–404, https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-021-00290-x.
Emberger L 1964 La Position phytogeographique Du Maroc Dans L’Ensemble Mediterraneen; Al Awamia 12 1–15.
Fels El Alaoui El and A, Saidi M E, Bouiji A and Benrhanem M 2021 Rainfall regionalization and variability of extreme precipitation using artificial neural networks: A case study from western central Morocco; J. Water Clim. Change 12(4) 1107–1122, https://doi.org/10.2166/wcc.2020.217.
Fenta A A, Yasuda H, Shimizu K, Ibaraki Y, Haregeweyn N, Kawai T, Belay A S, Sultan D and Ebabu K 2018 Evaluation of satellite rainfall estimates over the Lake Tana basin at the source region of the Blue Nile River; Atmos. Res. 212 43–53, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2018.05.009.
Funk C, Peterson P, Landsfeld M, Pedreros D, Verdin J, Shukla S, Husak G, Rowland J, Harrison L, Hoell A and Michaelsen J 2015 The climate hazards infrared precipitation with stations – a new environmental record for monitoring extremes; Sci. Data 2 150066, https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2015.66.
Haile A T, Habib E and Rientjes T 2012 Evaluation of the climate prediction center (CPC) morphing technique (CMORPH ) rainfall product on hourly time scales over the source of the Blue Nile River; Hydrol. Process. 27 1829–1839, https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.9330.
Hossain F and Huffman G J 2008 Investigating error metrics for satellite rainfall data at hydrologically relevant scales; J. Hydrometeorol. 9(3) 563–575, https://doi.org/10.1175/2007JHM925.1.
Huang W, Liu P and Hsu J 2021 Multiple timescale assessment of wet season precipitation estimation over Taiwan using the PERSIANN family products; Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 103(88) 102521, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2021.102521.
Huffman G J, Bolvin D T, Braithwaite D, Hsu K L, Joyce R J, Kidd C, Nelkin E J, Sorooshian S, Stocker E F, Tan Wolff D B and Xie P 2020 Integrated multi-satellite retrievals for the global precipitation measurement (GPM) mission (IMERG); Adv. Global Change Res. 67 343–353, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-24568-9_19.
Karmouda N, Kacimi I, Elkharrim M, Brirhet H and Hamidi M 2022 Geo-statistical and hydrological assessment of three satellite precipitation products over Ouergha basin (Northern Morocco); Arab. J. Geosci. 15 235, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-09124-6.
Katiraie-Boroujerdy P, Asanjan A A, Hsu K and Sorooshian S 2017 Intercomparison of PERSIANN-CDR and TRMM-3B42V7 precipitation estimates at monthly and daily time scales; Atmos. Res. 193 36–49, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2017.04.005.
Lai C, Chen X, Wang Z, Wu X, Zhao S, Wu X and Bai W 2016 Spatio-temporal variation in rainfall erosivity during 1960–2012 in the Pearl River Basin, China; Catena 137 382–391, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2015.10.008.
Lai C, Zhong R, Wang Z, Wu X, Chen X, Wang P and Lian Y 2019 Monitoring hydrological drought using long-term satellite-based precipitation data; Sci. Total Environ. 649 1198–1208, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.245.
Li J and Heap A D 2011 A review of comparative studies of spatial interpolation methods in environmental sciences: Performance and impact factors; Ecol. Inform. 6(3–4) 228–241, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2010.12.003.
Miao C, Ashouri H, Hsu K L, Sorooshian S and Duan Q 2015 Evaluation of the PERSIANN-CDR daily rainfall estimates in capturing the behavior of extreme precipitation events over China; J. Hydrometeorol. 16 1387–1396, https://doi.org/10.1175/JHM-D-14-0174.1.
Montgomery D R 2007 Soil erosion and agricultural sustainability; Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 104(33) 13,268–13,272, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0611508104.
Morgan R P C, Quinton J N, Smith R E, Govers G, Poesen J W A, Auerswald K, Chisci G, Torri D and Styczen M E 1998 The European soil erosion model (eurosem): A dynamic approach for predicting sediment transport from; Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 544 527–544.
Nash J E and Sutcliffe J V 1970 River flow forcasting through conceptual models Part I – A discussion of principles; J. Hydrol. 10 282–290.
Nawaz M, Iqbal M F and Mahmood I 2021 Validation of CHIRPS satellite-based precipitation dataset over Pakistan; Atmos. Res. 248 105289, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2020.105289.
Panagos P, Ballabio C, Borrelli P and Meusburger K 2016 Spatio-temporal analysis of rainfall erosivity and erosivity density in Greece; Catena 137 161–172, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2015.09.015.
Panagos P, Borrelli P, Meusburger K, Yu B, Klik A, Lim K J, Yang J E, Ni J, Miao C, Chattopadhyay N, Sadeghi S H, Hasbavi Z, Zabihi M, Larionov G A, Krasnov S F, Gorobets A V, Levi Y, Erpul G, Birkel C, Hoyos N, Naipal V, Oliveira P T S, Bonilla C A, Meddi M, Nel W, Al Dashti H, Boni M, Diodato N, Van Oost K, Nearing M and Ballabio C 2017 Global rainfall erosivity assessment based on high-temporal resolution rainfall records; Scientific Reports 7 4175, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-04282-8.
Prakash S 2019 Performance assessment of CHIRPS, MSWEP, SM2RAIN-CCI, and TMPA precipitation products across India; J. Hydrol. 571 50–59, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.01.036.
Rachdane M, El Khalki E, Saidi M E, Nehmadou M, Ahbari A and Tramblay Y 2022 Comparison of high-resolution satellite precipitation products; Water 14(20) 3336, https://doi.org/10.3390/w14203336.
Renard K G, Foster G R, Weesies G A, Mccool D K and Yoder D C 1997 Predicting soil erosion by water: A guide to conservation planning with the revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE); US Departement of Agriculture, Agricultural Handbook 703 404p.
Rompaey A V, Bazzoffi P, Jones R J A and Montanarella L 2005 Modeling sediment yields in Italian catchments; Geomorphology 65 157–169, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2004.08.006.
Saddique N, Muzammil M, Jahangir I, Sarwar A, Ahmed E, Ammar Aslam R and Bernhofer C 2022 Hydrological evaluation of 14 satellite-based, gauge-based and reanalysis precipitation products in a data-scare mountainous catchment; Hydrol. Sci. J. 67 436–450, https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2021.2022152.
Salih W, Chehbouni A and Epule T E 2022 Evaluation of the performance of multi-source satellite products in simulating observed precipitation over the Tensift Basin in Morocco evaluation of the performance of multi-source satellite products in simulating observed precipitation over the Tensift; Remote Sens. 14 1171, https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051171.
Schneider U, Becker A, Finger P, Meyer-Christoffer A, Ziese M and Rudolf B 2014 GPCC’s new land surface precipitation climatology based on quality-controlled in situ data and its role in quantifying the global water cycle; Theor. Appl. Climatol. 115 15–40, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-013-0860-x.
Shen Z, Yong B, Yi L, Wu H and Xu H 2022 From TRMM to GPM, how do improvements of post/near-real-time satellite precipitation estimates manifest?; Atmos. Res. 268 106029, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2022.106029.
Shin J, Kim T, Heo J and Lee J 2019 Spatial and temporal variations in rainfall erosivity and erosivity density in South Korea; Catena 176 125–144, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.01.005.
Tan M L and Santo H 2018 Comparison of GPM IMERG, TMPA 3B42 and PERSIANN-CDR satellite precipitation products over Malaysia; Atmos. Res. 202 63–76, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2017.11.006.
Teng H, Viscarra R A, Shi Z, Behrens T, Chappell A and Bui E 2016 Assimilating satellite imagery and visible-near infrared spectroscopy to model and map soil loss by water erosion in Australia; Environ. Model. Softw. 77 156–167, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2015.11.024.
Teng H, Ma Z, Chappell A, Shi Z, Liang Z and Yu W 2017 Improving rainfall erosivity estimates using merged TRMM and gauge data; Remote Sens. 9 1134, https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9111134.
Tsitsagi M, Berdzenishvili A and Gugeshashvili M 2018 Spatial and temporal variations of rainfall-runoff erosivity (R) factor in Kakheti, Georgia; Ann. Agrar. Sci. 16(2) 226–235, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aasci.2018.03.010.
Vrieling A, Sterk G and De Jong S M 2010 Satellite-based estimation of rainfall erosivity for Africa; J. Hydrol. 395(3–4) 235–241, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.10.035.
Wang Z, Zhong R, Lai C and Chen J 2017 Evaluation of the GPM IMERG satellite-based precipitation products and the hydrological utility; Atmos. Res. 196 151–163, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2017.06.020.
Willmott C J and Matsuura K 2005 Advantages of the mean absolute error (MAE) over the root mean square error (RMSE) in assessing average model performance; Clim. Res. 30 79–82.
Wischmeier W H and Smith D D 1978 Predicting rainfall erosion losses; Fresen. Environ. Bull. 26(12) 7034–7044.
Xie Y, Yin S, Liu B, Nearing M A and Zhao Y 2016 Models for estimating daily rainfall erosivity in China; J. Hydrol. 535 547–558, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.02.020.
Xu Z, Pan B, Han M, Zhu J and Tian L 2019 Spatial-temporal distribution of rainfall erosivity, erosivity density and correlation with El Niño-Southern Oscillation in the Huaihe River Basin, China; Ecol. Inform. 52 14–25, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2019.04.004.
Yin S, Xie Y, Liu B and Nearing M A 2015 Rainfall erosivity estimation based on rainfall data collected over a range of temporal resolutions; Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 19 4113–4126, https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-19-4113-2015.
Zambrano-Bigiarini M, Nauditt A, Birkel C, Verbist K and Ribbe L 2017 Temporal and spatial evaluation of satellite-based rainfall estimates across the complex topographical and climatic gradients of Chile; Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 21(2) 1295–1320, https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-21-1295-2017.
Zeng W, Ding X, Sun W and Mu X 2023 Improvement of satellite-based rainfall product CHIRPS in estimating rainfall erosivity on the Loess Plateau; Land Degrad. Dev. 34(15) 4517–4528, https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.4790.
Zhang L, Gao L, Chen J, Zhao L, Zhao J and Qiao Y 2022a Comprehensive evaluation of mainstream gridded precipitation datasets in the cold season across the Tibetan Plateau; J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 43 101186, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2022.101186.
Zhang Y, Wu C, Yeh P J, Li J, Hu B X, Feng P and Jun C 2022b Evaluation and comparison of precipitation estimates and hydrologic utility of CHIRPS, TRMM 3B42 V7 and PERSIANN-CDR products in various climate regimes; Atmos. Res. 265 105881, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2021.105881.
Zhong R, Chen X, Lai C, Wang Z, Lian Y, Yu H and Wu X 2019 Drought monitoring utility of satellite-based precipitation products across mainland China; J. Hydrol. 568 343–359, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.10.072.
Acknowledgement
Financial support was provided by the Project of National Center for Scientific and Technical Research (CNRST) ‘Domaines Prioritaires de la Recherche Scientifique et du Développement Technologique / Ref. PPR1/2015/63’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Najat Ben Daoud: Conceptualization, methodology, investigation, software, validation, writing – original draft. Lahcen Daoudi: Supervision, methodology, investigation, writing – original draft, review and editing. Mariame Rachdane: Data curation, investigation, writing – original draft, review and editing. Abdelali Gourfi: Investigation, writing – original draft, review and editing. Mohamed Elmehdi Saidi: Data curation, investigation, writing – original draft, review and editing.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by P A Francis
Corresponding editor: P A Francis
Supplementary material pertaining to this article is available on the Journal of Earth System Science website (http://www.ias.ac.in/Journals/Journal_of_Earth_System_Science).
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ben Daoud, N., Daoudi, L., Rachdane, M. et al. Suitability of satellite-based rainfall products for estimating rainfall erosivity in areas with contrasted climate and terrain properties: Example of west-central Morocco. J Earth Syst Sci 133, 78 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-024-02287-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-024-02287-2