Abstract
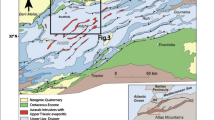
In the present study, two-dimensional (2D) electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) and vertical electrical sounding (VES) techniques were adopted to predict and detect landslides and subsurface voids occurrences in the Tghat-Oued Fez district of Fez city, Morocco. The purpose of this research is to examine the effects of electrical-based applied geophysics methods for data inversion and modelling using open-source algorithms for spatial distribution and shape of sliding and underground cavities as well as fractured zones in the study area. The data acquisition was based on nine ERT profiles using a dipole–dipole electrode array configuration and 72 VES soundings laid out on an area in which underground cavities were expected. 2D electrical sections, derived from electrical resistivity tomography measurements, in terms of electrical resistivity contrast, correctly highlighted the site's well-defined lithology, identified the presence of cavities with variable geometry, and were capable of inferring the sliding surface. VES-based measurements, in conjunction with the ERT technique, mapped the potential presence of near-surface voids inside a conductive marly formation caused by high electrical resistivity anomalies and delimited the conglomerate roof layer. The joint combination of these two electrical-based geophysical methods along with the numerical modelling and inversion of the data structure and parameters using the useful features of the open-source python-based environment pyGIMLi and BERT, have demonstrated their capability to infer near-surface voids in the study area. The geophysical survey results suggest that the integrated geophysical approach is a reliable and capable geophysical tool and could be effectively used for landslide, and cavity detection and to assess the risk of those subsidence-prone areas. Thus, this approach could be easily applied and reproduced in those areas with similar characteristics.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmamou M, Conrad G and Plaziat J 1989 Réinterprétation des conditions de dépôt des calcaires fluviatiles, lacustres et palustres du bassin ploi-quaternaire ancien sur la bordure nord du bassin du Saiss (Maroc); Méditerranée 2(3) 41–49.
Anaconda.org, Boundless Electrical Resistivity Tomography [online] 2022, https://anaconda.org/gimli/pybert.
Arjwech R, Ruansorn T, Schulmeister M, Everett M E, Thitimakorn T, Pondthai P and Somchat K 2021 Protection of electricity transmission infrastructure from sinkhole hazard based on electrical resistivity tomography; Eng. Geol. 293 106318, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106318.
Balkaya Ç, Göktürkler G, Erhan Z and Ekinci Y L 2012 Exploration for a cave by magnetic and electrical resistivity surveys: Ayvacık Sinkhole example, Bozdağ, İzmir (Western Turkey); Geophysics 77 B135–B146.
Bargach K, Ruano P, Chabli A, Galindo-Zaldivar J, Chalouan A, Jabaloy A, Akil M, Ahmamou M, Sanz De Galdeano C and Benmakhlouf M 2004 Recent Tectonic Deformations and Stresses in the Frontal Part of the Rif Cordillera and the Saïss Basin (Fez and Rabat Regions, Morocco); Pure Appl. Geophys. 161 521–540.
Boualla O, Fadili A, Najib S, Khalid M, Makan A and Zourarah B 2021 Assessment of collapse dolines occurrence using electrical resistivity tomography: Case study of Moul El Bergui area, Western Morocco; J. Appl. Geophys. 191 104366, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2021.104366.
Caleb L and Anthony J W 2022 Underground cavity detection through group dispersion of a GPR signal; Remote Sens. 14 4808.
Carbonel D, Rodríguez-Tribaldos V, Gutiérrez F, Galve J P, Guerrero J, Zarroca M, Roqué C, Linares R, McCalpin J P and Acosta E 2015 Investigating a damaging buried sinkhole cluster in an urban area (Zaragoza city, NE Spain) integrating multiple techniques: Geomorphological surveys, DInSAR, DEMs, GPR, ERT, and trenching; Geomorphology 229 3–16.
Cardarelli E, Cercato M, Cerreto A and Di Filippo G 2010 Electrical resistivity and seismic refraction tomography to detect buried cavities; Geophys. Prospect. 58 685–695.
Charroud M, Cherai B, Benabdelhadi M, Charroud A, El Moutaouakkil N, Falguères C and Lahrach A 2006 Sedimentary evolution of a fore-chain Sais basin during plio-quaternary and modalities of tectonic inversion (Sais basin, Morocco); Geophys. Res. Abst. Eur. Geosci. Union 8 10039.
Charroud M, Cherai B, Benabdelhadi M and Falgueres C 2007 Impact de la néotectonique quaternaire sur la dynamique sédimentaire du Saïs (Maroc): Du bassin d’avant fosse pliocène au plateau continental quaternaire; Quaternaire 18(4) 327–334.
Cherai B, Charroud M, Lahrach A and El Moutaouakil N 2004 Le front sud rifain une expression complexe d’une tectonique tangentielle à la limite du bassin de Sais au Mio-Pliocène et au Quaternaire (Région de Fès, Maroc); Colloque international à la mémoire de Feue A. Faure Muret, Rabat, Maroc, 13.
Cherai B, Charroud M, Julien B, Gourari L and Benabdelhadi M 2007 Impact de la néotectonique et des mouvements verticaux sur le réseau hydrographique du Sebou au Quaternaire; La 4ème Rencontre des Quaternaristes Marocains (RQM4), Du 15 au 17 Novembre 2007, Oujda, Maroc, 36p.
Cherai B, Charroud M, Lahrach A and Babault J 2008 Influence de la tectonique compressive et des mouvements verticaux d’origine mantellique sur l’évolution quaternaire du Saïs entre le Rif et le Moyen Atlas ; Actes RQM4, Oujda, pp. 171–181.
Cook J C 1965 Seismic mapping of underground cavities using reflection amplitudes; Geophysics 30(4) 527–538.
Doyoro Y G, Chang P Y, Puntu J M, Lin D J, Van Huu T, Rahmalia D A and Shie M S 2022 A review of open software resources in python for electrical resistivity modelling; Geosci. Lett. 9(1) 3, https://doi.org/10.1186/s40562-022-00214-1.
Essa K S, Mehanee S, Soliman K and Diab Z E 2020 Gravity profile interpretation using the R-parameter imaging technique with application to ore exploration; Ore Geol. Rev. 126 103695.
Essa K, Mehanee S and Elhussein M 2021 Magnetic data profiles interpretation for mineralized buried structures identification applying the variance analysis method; Pure Appl. Geophys. 178 973–993, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-020-02553-6.
Everett M E 2013 Near-Surface Applied Geophysics; Cambridge University Press, https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781139088435.
Faugères J C 1978 Southern Rifan Ridges. Sedimentological and Structural Evolution of an Atlantico–Mesogean Basin of African Margin; Thesis, University of Bordeaux I, Talence, 480p.
Fu Z, Ren Z, Hua X, Shi Y, Chen H, Chen C, Li Y and Tang J 2020 Identification of underground water-bearing caves in noisy urban environments (Wuhan, China) using 3D electrical resistivity tomography techniques; J. Appl. Geophys. 174 103966, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2020.103966.
Gambetta M, Armadillo E, Carmisciano C, Stefanelli P, Cocchi L and Tontini F C 2011 Determining geophysical properties of a near-surface cave through integrated microgravity vertical gradient and electrical resistivity tomography measurements; J. Cave Karst Stud. 73 11–15.
Gan J, Li H, He Z, Gan Y, Mu J, Liu H and Wang L 2022 Application and significance of geological, geochemical, and geophysical methods in the Nanpo Gold Field in Laos; Minerals 12 96, https://doi.org/10.3390/min12010096.
Gibson P J, Lyle P and George D M 2004 Application of resistivity and magnetometry geophysical techniques for near-surface investigations in karstic terranes in Ireland; J. Cave Karst Stud. 66(2) 35–38.
Göktürkler G, Balkaya C and Erhan Z 2008 Geophysical investigation of a landslides: The Altindag landslide site, Izmir (western Turkey); J. Appl. Geophys. 65(2) 84–96, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2008.05.008.
Gómez-Ortiz D and Martín-Crespo T 2012 Assessing the risk of subsidence of a sinkhole collapse using ground penetrating radar and electrical resistivity tomography; Eng. Geol. 149–150 1–12, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.07.022.
Grandjean G 2006 Imaging sub-surface objects by seismic P-wave tomography: Numerical and experimental validations; Near Surf. Geophys. 4 279–287.
Griffiths D H and Barker R D 1993 Two dimensional resistivity imaging and modelling in areas of complex geology; J. Appl. Geophys. 29 211–226.
Günter T, Martin T and Rücker C 2016 Spectral inversion of SIP field data using pyGIMLi/BERT; In: Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop on Induced Polarization, Aarhus (Denmark), June 6–8, 2016.
Günther T and Rücker C 2022 Boundless electrical resistivity tomography BERT2 – The User Tutorial; 2019, http://www.resistivity.net/download/bert-tutorial.pdf.
Günther T, Rücker C and Spitzer K 2006 3-d modeling and inversion of DC resistivity data incorporating topography – Part II: Inversion; Geophys. J. Int. 166(2) 506–517.
Hasan M, Shang Y, Jin W and Akhter G 2020 An engineering site investigation using non-invasive geophysical approach; Environ. Earth Sci. 79(11), https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09013-3.
Ivanov J, Miller R D and Peterie S L 2016 Detecting and delineating voids and mines using surface-wave methods in Galena, Kansas; SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2016, https://doi.org/10.1190/segam2016-13967007.1.
Kang M S, Kim N, Im S B, Lee J J and An Y K 2019 3D GPR Image-based UcNet for enhancing underground cavity detectability; Remote Sens. 11 2545, https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11212545.
Karriqi A and Alikaj P 2011 Combination of resistivity “real section” with quantitative interpretation of vertical electrical soundings; Proceedings of GeoAlb 2011 “Mineral Resources and Their Perspective”, Mitrovice, Kosovo, 27–30 September, 2011, pp. 466–469.
Kearey P, Brooks M and Hill I 2013 An introduction to geophysical exploration; 3rd edn, Wiley-Blackwell, Oxford, UK, 272p.
Kumar P, Tiwari P, Singh A, Biswas A and Acharya T 2021 Electrical resistivity and induced polarization signatures to delineate the near-surface aquifers contaminated with seawater invasion in Digha, West-Bengal, India; Catena 207 105596, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2021.105596.
Kumar P, Tiwari P, Biswas A and Acharya T 2022 Geophysical investigation for seawater intrusion in the high-quality coastal aquifers of India: A review; Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24233-9.
Leucci G and De Giorgi L 2010 Microgravimetric and ground penetrating radar geophysical methods to map the shallow karstic cavities network in a coastal area (Marina di Capilungo, Lecce, Italy); Explor. Geophys. 41 178–188.
Loke M H 1999 A practical guide to 2D and 3D surveys; Electrical Imaging Surveys for Environmental and Engineering Studies, pp. 1–10.
Loke M H and Barker R D 1996 Rapid least-squares inversion of apparent resistivity pseudosections using a quasi-Newton method; Geophys. Prospect. 44 131–152.
Martínez-Pagán P, Gómez-Ortiz D, Martín-Crespo T, Manteca J I and Rosique M 2013 The electrical resistivity tomography method in the detection of shallow mining cavities. A case study on the Victoria Cave, Cartagena (SE Spain); Eng. Geol. 156 1–10.
Mehanee S 2022a Simultaneous joint inversion of residual gravity and self potential data measured along profile: Theory, numerical examples and a case study from mineral exploration with cross validation from electromagnetic data; IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 60 1–20, https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2021.3071973.
Mehanee S 2022b A new scheme for gravity data interpretation by a faulted 2-D horizontal thin block: Theory, numerical examples and real data investigation; IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 60 1–14, https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2022.3142628.
Mehanee S and Zhdanov M 1999 Magnetotelluric inversion of blocky geoelectrical structures using the minimum support method; Presented at the 69th International exposition and meeting, Society of Exploration Geophysicists (SEG), Houston, Texas, USA.
Mehanee S and Zhdanov M 2002 Two-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion of blocky geoelectrical structures; J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 107(B4), https://doi.org/10.1029/2001JB000191.
Mehanee S, Golubev N and Zhdanov M 1998 Weighted regularized inversion of magnetotelluric data; Presented at the 68th International and Meeting, Society of Exploration Geophysicists (SEG), New Orleans, Louisiana, USA.
Mehanee S, Essa K S and Diab Z E 2021 Magnetic data interpretation using a new R-parameter imaging method with application to mineral exploration; Nat. Resour. Res. 30(1), https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-020-09690-8.
Metwaly M and Al Fouzan F 2013 Application of 2-D geoelectrical resistivity tomography for subsurface cavity detection in the eastern part of Saudi Arabia; Geosci. Front. 4(4) 469–476.
Mooney H M 1980 Handbook of Engineering Geophysics; Vol. 2, Electrical Resistivity; Bison Instruments, Inc., 81p.
Niculescu B M and Andrei G 2019 Using Vertical electrical soundings to characterize seawater intrusions in the southern area of Romanian Black Sea Coastline; Acta Geophys. 67(6) 1845–1863.
Nuzzo L, Leucci G and Negri S 2007 GPR, VES and refraction seismic surveys in the karstic area ‘spedicaturo’ near Nociglia (Lecce, Italy); Near Surf. Geophys. 5(1) 67–76.
Parasnis D S 1997 Principles of applied geophysics; 5th edn, Chapman and Hall, London, pp. 104–176.
Pazdirek O and Blaha V 1996 Examples of resistivity imaging using ME-100 resistivity field acquisition system; In: EAGE 58th conference and technical exhibition extended abstracts, Amsterdam.
Plank Z and Polgár D 2019 Application of the DC resistivity method in urban geological problems of karstic areas; Near Surf. Geophys. 15(5) 547–561.
Putiska R, Kusnirak D, Dostal I, Lacny A, Mojzes A, Hok J, Pasteka R, Krajnak M and Bosansky M 2014 Integrated geophysical and geological investigations of karst structures in Komberek, Slovakia; J. Cave Karst Stud. 76(3) 155–163.
Ronczka M, Rücker C and Günther T 2015 Numerical study of long-electrode electric resistivity tomography – Accuracy, sensitivity, and resolution; Geophysics 80(6) 317–328.
Rücker C, Günther T and Spitzer K 2006 Three-dimensional modelling and inversion of dc resistivity data incorporating topography – I. Modelling; Geophys. J. Int. 166 495–505, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03011.x.
Rücker C, Günther T and Wagner F M 2017 pyGIMLi: An open-source library for modelling and inversion in geophysics; Comput. Geosci. 109 106–123, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2017.07.011.
Takahashi T and Kawase T 1990 Analysis of apparent resistivity in a multi-layer earth structure; IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 5 604–612.
Taltasse P 1953 Recherches géologiques et hydrogéologiques dans le bassin lacustre de Fès-Meknès; Notes et Mémoires du Service Géologique, Maroc 115 152.
Tarantola A 2005 Inverse problem theory and methods for model parameters estimation; 1st edn, The Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (SIAM), Cambridge University Press, 352p.
Telford W M, Geldart L P and Sheriff R E 1990 Resistivity methods; In: Applied Geophysics; 2nd edn, Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, UK, pp. 353–358.
Tikhonov A N and Arsenin V Y 1977 Solution of ill-posed problems; V.H. Winston and Sons, Washington D.C., John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Van Schoor M 2002 Detection of sinkholes using 2D electrical resistivity imaging; J. Appl. Geophys. 50 393–399.
Ward S H 1990a Geotechnical and environmental geophysics; Vol. II, Environmental and Groundwater; Investigations in Geophysics Series, Society of Exploration Geophysicists, 352p, https://doi.org/10.1190/1.9781560802785.2.
Ward S H 1990b Geotechnical and Environmental Geophysics; Vol. III, Geotechnical Investigations in Geophysics Series, Society of Exploration Geophysicists, 305p, https://doi.org/10.1190/1.9781560802785.3.
Whiteley J S, Chambers J E, Uhlemann S, Wilkinson P B and Kendall J M 2019 Geophysical monitoring of moisture-induced landslides: A review; Rev. Geophys. 57 106–145.
Zhou W, Beck B F and Adams A L 2002 Effective electrode array in mapping karst hazards in electrical resistivity tomography; Environ. Geol. 42 922–928.
Acknowledgements
We would like to take this opportunity to acknowledge the time and effort devoted by two anonymous reviewers for their critical comments that significantly improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, software: Oussama Jabrane, Driss El Azzab, Mohammed Charroud. Inversion software and validation: Pedro Martínez-Pagán and Marcos A Martínez-Segura. Investigation and resources: Oussama Jabrane, Driss El Azzab, Mohammed Charroud, Bouabid El Mansouri, Mahjoub Himi, and Mohammed Elgettafi. Data curation and writing-original draft preparation: Oussama Jabrane. Writing, reviewing and editing: Oussama Jabrane, Pedro Martínez-Pagán and Driss El Azzab. Supervision and project management: Driss El Azzab and Pedro Martínez-Pagán.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Arkoprovo Biswas
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jabrane, O., El Azzab, D., Martínez-Pagán, P. et al. Comparison of the pyGIMLi and BERT packages for landslide and cavity detection: A case study from Tghat-Oued Fez, Morocco. J Earth Syst Sci 132, 107 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-023-02119-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-023-02119-9