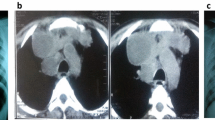
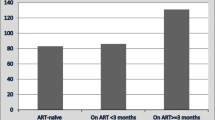
Abstract
The global impact of the converging dual epidemics of tuberculosis (TB) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is one of the major public health challenges of our time. The World Health Organization (WHO) reports 9.2 million new cases of TB in 2006 of whom 7.7% were HIV-infected. Tuberculosis is the most common opportunistic infection in HIV-infected patients as well as the leading cause of death. Further, there has been an increase in rates of drug resistant tuberculosis, including multi-drug (MDRTB) and extensively drug resistant TB (XDRTB), which are difficult to treat and contribute to increased mortality. The diagnosis of TB is based on sputum smear microscopy, a 100-year old technique and chest radiography, which has problems of specificity. Extra-pulmonary, disseminated and sputum smear negative manifestations are more common in patients with advanced immunosuppression. Newer diagnostic tests are urgently required that are not only sensitive and specific but easy to use in remote and resource-poor settings. Treatment of HIV-TB co-infection is complex and associated with high pill burden, overlapping drug toxicities, risk of immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS) and challenges related to adherence. From a programmatic point of view, screening of all HIV-infected persons for tuberculosis and vice-versa will help identify co-infected patients who require treatment for both infections. This requires good coordination and communication between the TB and AIDS control programs, in India.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DMC:
-
designated microscopy centre
- HIV:
-
human immunodeficiency virus
- ICTC:
-
integrated counseling and testing centre
- IRIS:
-
immune reconstitution inflammatrory syndrome
- NRTIs:
-
nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
- NSAID:
-
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
- PCP:
-
Pneumocystis Jiroveci pneumonia
- PGL:
-
persistent generalized lymphadenopathy
- PI:
-
protease inhibitor
- RNTCP:
-
Revised National TB Control Program
- TB:
-
tuberculosis
References
Ackah A N, Coulibaly D, Digbeu H, Diallo K, Vetter K M, Coulibaly I M, Greenberg A E, De Cock K M 1995 Response to treatment, mortality and CD4 lymphocyte counts in HIV infected persons with tuberculosis in Abidjan, Cote d’Ivoire; Lancet 345 607–610
Agarwal S P and Chauhan L S 2005 Tuberculosis control in India (Elsevier, a division of Reed Elsevier India Private Limited)
Ahmad Z and Shameem M 2005 Manifestations of Tuberculosis in HIV Infected Patients; JIACM 6 302–305
Andrews J R, Shah N S, Gandhi N, Moll T, Friedland G; Tugela Ferry Care and Research (TF CARES) Collaboration 2007 Multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis: implications for the HIV epidemic and antiretroviral therapy rollout in South Africa; J. Infect. Dis. (Suppl. 3) 196 S482–S490
Antonucci G, Girardi E, Raviglione M C, Ippolito G 1995 Risk factors for tuberculosis in HIV-infected persons: A prospective cohort study; JAMA 274 143–148
Arora V K and Kumar S V 1999 Pattern of opportunistic pulmonary infections in HIV sero-positive subjects: observations from Pondicherry, India; Indian J. Chest Dis. Allied Sci. 41 135–144
Burman W J and Jones B E 2001 Treatment of HIV-related Tuberculosis in the Era of Effective Antiretroviral Therapy; Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 164 7–12
Cohen K, van Cutsem G, Boulle A, McIlleron H, Goemaere E, Smith P J and Maartens G 2008 Effect of rifampicin-based antitubercular therapy on nevirapine plasma concentrations in South African adults with HIV-associated tuberculosis; J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 61 389–393
De Cock K M, Soro B, Coulibaly I M and Lucas S B 1992 Tuberculosis and HIV infection in sub-Saharan Africa; JAMA 268 1581–1587
de Jong B C, Israelski D M, Corbett E L and Small P M 2004 Clinical management of tuberculosis in the context of HIV infection; Annu. Rev. Med. 55 283–301
Deivanayagam C N, Rajasekaran S, Senthilnathan V, Krishnarajasekhar R, Raja K, Chandrasekar C, Palanisamy S, Samuel Dinesh A, Jothivel G and Elango S V 2001 Clinicoradiological spectrum of tuberculosis among HIV sero-positives - a Tambaram study; Indian J. Tuber. 48 123–127
Driver C R, Munsiff S S, Li J, Kundamal N and Osahan S S 2001 Relapse in persons treated for drug susceptible tuberculosis in a population with high co-infection with Human Immunodeficiency virus in New York City; Clin. Infect. Dis. 33 1762–1769
Emergence of XDR-TB WHO concern over extensive drug resistant TB strains that are virtually untreatable 2006; accessed from http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/notes/2006/np23/en/print.html on 25/05/08
Fee M J, Oo M M, Gabayan A E, Radin D R and Barnes P F 1995 Abdominal tuberculosis in patients infected with the human immunodeficiency virus; Clin. Infect. Dis. 20 938–944
Finlay A F, Walt M V, Holtz T H, Thorpe L E, Wells C D and Weyer K 2004 Treatment outcome of patients with multidrug resistant tuberculosis in south Africa using a standardized regimen, 1999–2000 (abstract 584); in Program and abstracts of the infectious diseases (Society of America 2004 Annual Meeting Alexandria, VA: infectious Disease society of America) p. 155
Gil-Setas A, Torroba L, Fernandez J L, Martinez-Artola V and Olite J 2004 Evaluation of the MB/BacT system compared with Middlebrook 7H11 and Lowenstein-Jensen media for detection and recovery of mycobacteria from clinical specimens; Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 10 224–228
Harries A D, Hargreaves N J, Jindani A, Enarson D A, Meher D and Salaniponi F M 2001 Deaths from tuberculosis in Sub-Saharan African countries with a high prevalence of HIV -1; Lancet 357 1519–1523
Havlir D V and Barnes P F 1999 Tuberculosis in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection; N. Engl. J. Med. 340 367–373
Jindani A, Nunn A J and Enarson D A 2004 Two 8-month regimens of chemotherapy for treatment of newly diagnosed pulmonary tuberculosis: international multicentre randomized trial; Lancet 364 1244–1251
Kejariwal D, Sarkar N, Chakraborti S K, Agarwal V and Roy S 2001 Pyrexia of unknown origin: a prospective study of 100 cases; J. Postgrad. Med. 47 104–107
Kumarasamy N, Vallabhaneni S, Flanigan T P, Mayer K H and Solomon S 2005 Clinical profile of HIV in India; Indian J. Med. Res. 121 377–394
Lawn S D, Bekker L G and Miller R F 2005 Immune reconstitution disease associated with mycobacterial infections in HIV-infected individuals receiving antiretrovirals; Lancet Infect. Dis. 5 361–373
Lawn S D, Butera S B and Shinnick T M 2002 Tuberculosis unleashed: the impact of HIV infection on the host granulomatous response to mycobacterium tuberculosis; Microbes Infection 4 635–646
Lawn S D, Myer L, Bekker L G and Wood R 2007 Tuberculosis-associated immune reconstitution disease: incidence, risk factors and impact in an antiretroviral treatment service in South Africa; AIDS 21 335–341
Lawn S, Myer L, Bekker L G and Wood R 2007 Early mortality among patients with HIV associated TB in Africa: Implications for the time to initiate ART (Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections: Abstract 81)
Lee J J, Suo J, Lin C B, Wang J D, Lin T Y and Tsai Y C 2003 Comparative evaluation of the BACTEC MGIT 960 system with solid medium for isolation of mycobacteria; Int. J. Tuber. Lung Dis. 7 569–574
Long R, Maycher B, Scalcini M and Manfred J 1991 Chest roentgenogram in pulmonary tuberculosis patients seropositive for HIV type I; Chest 99 123–127
Lucas S B, De Cock K M, Hounnou A, Peacock C, Diomande M, Hondé M, Beaumel A, Kestens L and Kadio A 1994 Contribution of tuberculosis to slim disease in Africa; BMJ 308 1531–1533
Manabe Y C, Campbell J D, Sydnor E and Moore R D 2007 Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome: risk factors and treatment implications; J. Acquir. Immune Defici. Syndr. 46 456–462
Manosuthi W, Mankatitham W, Lueangniyomkul A, Chimsuntorn S and Sungkanuparph S 2008 Standard-dose efavirenz vs. standard-dose nevirapine in antiretroviral regimens among HIV-1 and tuberculosis co-infected patients who received rifampicin; HIV Med. 9 294–299
Manosuthi W, Sungkanuparph S, Thakkinstian A, Rattanasiri S, Chaovavanich A, Prasithsirikul W, Likanonsakul S and Ruxrungtham K 2006 Plasma nevirapine levels and 24-week efficacy in HIV-infected patients receiving nevirapine-based highly active antiretroviral therapy with or without rifampicin; Clin. Infect. Dis. 43 253–255
McIlleron H, Meintjes G, Burman W J and Maartens G 2007 Complications of antiretroviral therapy in patients with tuberculosis: drug interactions, toxicity, and immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome; J. Infect. Dis. (Suppl. 1) 196 S63–S75
Miranda A, Morgan M, Jamal L, Laserson K, Barreira D, Silva G, Santos J, Wells C, Paine P and Garrett D 2007 Impact of antiretroviral therapy on the incidence of tuber-culosis: the Brazilian experience, 1995–2001; PLoS ONE 2 e826
Mohammed A, Myre L, Ehrlich R, Wood R, Cilliers F and Maartens G 2007 Randomised controlled trial of isoniazid preventive therapy in South African adults with advanced HIV disease; Int. J. Tuber. Lung Dis. 11 1114–1120
Nahid P, Gonzalez L C, Rudoy I, De long B C, Unger A and Kawamura L M 2007 Treatment outcomes of patients with HIV and tuberculosis; Am. J. Respire. Crit. Care Med. 175 1196–1206
Narita M, Ashkin D, Hollender E S and Pitchenik A E 1998 Paradoxical worsening of tuberculosis following Antiretroviral therapy in patients with AIDS; Am. Crit. Care 158 157–161
Narita M, Kellman M, Franchini D L, McMillan M E, Hollender E S and Ashkin D 2002 Short course rifampicin and pyrazinamide treatment for latent tuberculosis infection in patients with HIV infection: the 2 year experience of a comprehensive community based programme in Broward county, Florida; Chest 122 1292–1298
National AIDS Control Organization 2007 Antiretroviral therapy guidelines for HIV-infected adults and adolescents including post-exposure prophylaxis (Section A7)
Park M M, Davis A L, Schluger N W, Cohen H and Rom W N 1996 Outcome of MDR -TB patients, 1983–1993: prolonged survival with appropriate therapy; Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 153 317–324
Ramachandran R, Swaminathan S, Somasundaram S, Asgar V N, Paramesh P and Paramasivan C N 2002 Mycobacteremia in tuberculosis patients with HIV infection; Indian J. Tuberc. 50 29–31
Rieder H L 1999 Epidemiological basis of tuberculosis control First edition [International Union against Tuberculosis and Lung Diseases (UNION)] pp 50–52
Rupali P, Abraham O C, Zachariah A, Subramanian S and Mathai D 2003 Aetiology of prolonged fever in antiretroviral-naïve human immunodeficiency virus-infected adults; Natl. Med. J. India 16 193–199
Sahn S A and Neff T A 1974 Miliary tuberculosis; Am. J. Med. 56 494–505
Sharma S K, Mohan A and Kadhiravan T 2005 HIV-TB co-infection: epidemiology, diagnosis & management; Indian J. Med. Res. 121 550–567
Singh S, Gopinath K, Shahdad S, Kaur M, Singh B and Sharma P 2007 Nontuberculous mycobacterial infections in Indian AIDS patients detected by a novel set of ESAT-6 polymerase chain reaction primers; Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 60 14–18
Singh S, Sankar M M and Gopinath K 2007 High rate of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis in Indian AIDS patients; AIDS 21 2345–2347
Steingart K R, Henry M, Ng V, Hopewell P C, Ramsay A, Cunningham J, Urbanczik R, Perkins M, Aziz M A and Pai M 2006 Fluorescence versus conventional sputum smear microscopy for tuberculosis: a systematic review; Lancet Infect. Dis. 6 570–581
Swaminathan S, Deivanayagam C N, Rajasekaran S, Venkatesan P, Padmapriyadarsini C, Menon P A, Ponnuraja C and Dilip M 2008 Long term follow up of HIV-infected patients with tuberculosis treated with 6-month intermittent short course chemotherapy; Natl. Med. J. Indian 21 3–7
Swaminathan S, Narendran G, Menon P A, Padmapriyadarsini C, Arunkumar N, Sudharshanam N M, Ramesh Kumar S and Chandrasekhar S 2007 Impact of HIV infection on radiographic features in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis; Indian J. Chest Dis. Allied Sci. 49 133–136
Swaminathan S, Paramasivan C N, Ponnuraja C, Iliayas S, Rajasekaran S and Narayanan P R 2005 Anti-tuberculosis drug resistance tuberculosis in South India; Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 9 896–900
Swaminathan S, Ramachandran R, Baskaran G, Paramasivan C N, Ramanathan U, Venkatesan P, Prabhakar R and Datta M 2000 Risk of development of tuberculosis in HIV infected patients; Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 4 839–844
Swaminathan S, Subbaraman R, Venkatesan P, Subramanyam S, Ramesh Kumar S, Mayer K H and Narayanan P R 2008 Tuberculin skin test results in HIV-infected patients in India: Implications for latent tuberculosis treatment; Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 12 168–173
TB/HIV, A Clinical Manual, WHO 2004 accessed from http://libdoc.who.int/publications/2004/9241546344.pdf on 25/05/2008
Thomas A, Ramachandran R, Rehaman F, Jaggarajamma K, Santha T, Selvakumar N, Krishnan N, Mohan N S, Sundaram V, Wares F and Narayanan PR 2007 Management of multi drug resistance tuberculosis in the field: Tuberculosis Research Centre experience; Indian J. Tuberc. 54 117–124
Thomas B E, Ramachandran R, Anitha S, Swaminathan S 2007 Feasibility of routine HIV testing among TB patients through a Voluntary, Counseling and Testing Centre (VCTC); Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 11 1296–1301
WHO Smear Negative Algorithm 2006 Improving the diagnosis and treatment of smear-negative pulmonary and extrapulmonary tuberculosis among adults and adolescents; Accessed from http://www.who.int/tb/publications/2006/tbhiv_recommendations.pdf
William R and Stuart G 2004 Tuberculosis (New York: Lippin Cott Williams and Wilkins)
Williams-Bouyer N, Yorke R, Lee H I and Woods G L 2000 Comparison of the BACTEC MGIT 960 and ESP culture system II for growth and detection of mycobacteria; J. Clin. Microbiol. 38 4167–4170
Woldehanna S and Volmink J 2004 Treatment of latent tuberculosis infection in HIV infected persons; Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 1 CD000171
World Health Organization 2006 Initiating First-Line ART in Relationship to Starting Anti-TB Therapy; accessed from http://www.womenchildrenhiv.org/wchiv?page=charts-00-13 on 25/05/2008
World Health Organization 2008. Global tuberculosis control: surveillance, planning, financing. WHO report 2008. WHO/HTM/TB/2008.393. Geneva
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swaminathan, S., Narendran, G. HIV and tuberculosis in India. J Biosci 33, 527–537 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-008-0071-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-008-0071-2