Abstract
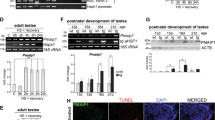
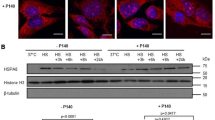
Heat shock response is associated with the synthesis of heat shock proteins (Hsps) which is strictly regulated by different members of heat shock transcription factors (HSFs). We previously reported that a rat histiocytoma, BC-8 failed to synthesize Hsps when subjected to typical heat shock conditions (42°C, 60 min). The lack of Hsp synthesis in these cells was due to a failure in HSF1 DNA binding activity. In the present study we report that BC-8 tumor cells when subjected to heat shock at higher temperature (43°C, 60 min) or incubation for longer time at 42°C, exhibited necrosis characteristics; however, under mild heat shock (42°C, 30 min) conditions cells showed activation of autophagy. Mild heat shock treatment induced proteolysis of HSF1, and under similar conditions we observed an increase in HSF2 expression followed by its enhanced DNA binding activity. Inhibiting HSF1 proteolysis by reversible proteasome inhibition failed to inhibit heat shock induced autophagy. Compromising HSF2 expression but not HSF1 resulted in the inhibition of autophagy, suggesting HSF2 dependent activation of autophagy. We are reporting for the first time that HSF2 is heat inducible and functions in heat shock induced autophagic cell death in BC-8 tumor cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- [(Ca2+)i]:
-
intracellular calcium
- DioC6(3):
-
3′,3′-dihexyloxacarbocyanine iodide
- Hsc70:
-
heat shock cognate protein 70
- Hsp:
-
heat shock protein
- Hsp70:
-
heat shock protein 70
- H2-DCFDA:
-
2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate
- HSE:
-
heat shock element
- HSF:
-
heat shock transcription factor
- lamp2a:
-
lysosomal-associated membrane protein
- MDC:
-
monodansylcadaverine
- Rhod-2:
-
1-[2-Amino-5-(3-dimethylamino-6-dimethylammonio-9-xanthenyl) phenoxy]-2-(2-amino-5-methylphenoxy)ethane-N,N,N′,N′-tetracetic acid chloride
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
References
Bergamini E Cavallini G Donati A and Gori Z 2003 The antiageing effects of caloric restriction may involve stimulation of macroautophagy and lysosomal degradation, and can be intensified pharmacologically; Biomed. Pharmacother. 57 203–208
Feder M F and Hofmann G E 1999 Heat Shock Proteins, Molecular Chaperones, and The Stress Response. Evolutionary and Ecological Physiology; Annu. Rev. Physiol. 61 243–282.
Gonzalez-Polo R Boya P Pauleau A L Jalil A Larochette N Souquere S Eskelinen E L Peirron G Saftig P and Kroemer G 2005 The apoptosis/autophagy paradox:autophagic vaporisation before apoptotic death; J. Cell Sci. 118 3091–3102
Katschinski D M 2004 On heat and cells and proteins; News Physiol. Sci. 19 11–15
Kiffin R Christian C Knecht E and Cuervo A M 2004 Activation of chaperone-mediated autophagy during oxidative stress; Mol. Biol. Cell. 15 4829–4840
Mathew A Mathur S K and Morimoto R I 1998 Heat shock response and protein degradation: regulation of HSF2 by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway; Mol. Cell. Biol. 18 5091–5198
Mathew A Mathur S K Jolly C Fox S G Kim S and Morimoto R I 2001 Stress specific activation and repression of heat shock factors 1 and 2; Mol. Cell. Biol. 21 7163–7171.
Morimoto R I 1998 Regulation of heat shock transcriptional response: cross talk between a family of heat shock factors, molecular chaperones, and negative regulators; Genes Dev. 12 3788–3796
Ohsumi Y and Mizushima N 2004 The ubiquitin-like conjugation systems essential for autophagy; Semin Cell Dev. Biol. 15 231–236
Pirkkala L Nykanen P and Sistonen L 2001 Roles of the heat shock transcription factors in regulation of heat shock response and beyond; FASEB J. 15 1118–1131
Sarge K D Zimarino V Holm K Wu C and Morimoto R I 1991 Cloning and characterization of two mouse heat shock with distinct inducible and DNA-binding activity; Genes Dev. 5 1902–1911
Schett G Steiner C W Groger M Winkler S Graninger W Smolen J Xu Q and Steiner G 1999 activation of Fas inhibits heat induced activation of HSF1 and upregulation of Hsp70; FASEB J. 13 833–842
Sistonen L Sarge K D Phillips B Abravaya K and Morimoto R I 1992 Activation of heat shock factor 2 during hemin induced differentiation of human erythroleukemia cells; Mol. Cell. Biol. 12 4104–4111
Soti C Nagy E Giricz Z Vigh L Csermely P and Ferdinandy P 2005 Heat shock proteins as emerging therapeutic targets; Br. J. Pharmacol. 146 769–780
Sreedhar A S Pardhasaradhi B V V Begum Z Khar A and Srinivas U K 1999 lack of heat shock response triggers programmed cell death in a rat histiocytoma; FEBS Letts. 456 339–342
Sreedhar A S Pardhasaradhi B V V Khar A and Srinivas U K 2000 Heat induced expression of CD95 and its correlation with the activation of apoptosis in a rat histiocytic tumor cell line; FEBS Letts. 472 271–275
Sreedhar A S Pardhasaradhi B V V Khar A and Srinivas U K 2002 A cross talk between cellular signaling and cellular redox state during heat induced apoptosis in a rat histiocytoma; Free Radic. Biol. Med. 32 221–227
Sreedhar A S and Csermely P 2004 Heat shock proteins in the regulation of apoptosis: new strategies in tumor therapy. A comprehensive review; Pharm. Ther. 101 227–257
Sreedhar A S Deepu O Abhishek A and Srinivas U K 2006 Heat shock transcription factors: a comprehensive review; in Stress response: a molecular biology approach (eds) Amere S Sreedhar and Usha K Srinivas (Research Signpost ISBN:81-308-0109-4) (In press)
Sreedhar A S 2006 Pharmacological interventions of Hsps and hyperthermia in anticancer treatments; Jpn. J. Hyperther. Oncol. 22 201–227
Swamynathan S K, Revathi C J and Srinivas U K 1996 Identification and characterization of promoter elements responsible for the induction of albumin gene by heat shock in early embryonic rat liver; DNA Cell Biol. 15 897–905
Tilly K, Spence J and Georgopoulos C 1989 Modulation and stability of the Escherichia coli heat shock regulatory factor sigma; J. Bacteriol. 171 1585–1589
Wu C 1995 Heat shock transcription factors: structure and regulation; Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 11 441–469
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prasad, K.V., Taiyab, A., Jyothi, D. et al. Heat shock transcription factors regulate heat induced cell death in a rat histiocytoma. J Biosci 32, 585–593 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-007-0058-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-007-0058-4