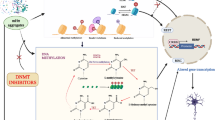
Abstract
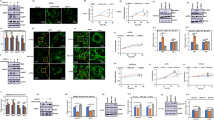
Background: Chemobrain is widespread in breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy. However, the exact mechanism, especially the associated signalling pathway, is not currently clear. This study was to evaluate the behavioural changes in breast cancer mice after chemotherapy and to further explore the role of Wnt3a/glycogen synthase kinase (GSK3β)/β-catenin signalling in chemobrain. Methods: MMTV-PyMT(+) breast cancer mice were injected intraperitoneally with doxorubicin (4 mg/kg) once a week for three weeks to establish a chemobrain model. The Morris water maze (MWM) and novel object recognition (NOR) tests were performed to assess the learning and memory ability. Electron microscopy was used to observe the structural changes in the hippocampal CA1 region. The brain tissue of breast cancer mice after chemotherapy was taken out for mRNA-seq detection. Then, the expression levels and phosphorylation of key proteins in the Wnt3a/GSK3 β/β-catenin signalling pathway were evaluated through Western blotting (WB) and immunofluorescence. Results: Doxorubicin-induced spatial and short-term memory impairment was observed in breast cancer mice, and obvious neuronal damage could be seen in the hippocampal CA1 region. Immunofluorescence staining for GSK3β was increased. Wnt signalling pathway is highly enriched from mRNA-seq analysis, with GSK3β genes at important nodes. The relative protein levels of p-PI3K, p-AKT, p-GSK3 β, Wnt3a and TCF-1 were decreased significantly, while the p-β-catenin level was increased. After injection of the GSK3β inhibitor sb216763 (1 ng/0.5 µl/side), hippocampal neuronal injury was alleviated to some extent, and the changes in the expression of proteins upstream and downstream of this signalling pathway were reversed. Conclusion: Wnt3a/GSK3 β/β-catenin signalling is likely involved in doxorubicin-induced memory impairment. This result provides basic evidence for the further study of chemobrain in breast cancer.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data supporting the findings of this article are available in the article and in its online supplementary material.
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A (2023) Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin 73(1):17–48. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21763
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2021) Global Cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Koevoets EW, Schagen SB, de Ruiter MB, Geerlings MI, Witlox L, van der Wall E, Stuiver MM, Sonke GS, Velthuis MJ, Jobsen JJ, Menke-Pluijmers MBE, Goker E, van der Pol CC, Bos M, Tick LW, van Holsteijn NA, van der Palen J, May AM, Monninkhof EM, group PAMs (2022) Effect of physical exercise on cognitive function after chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer: a randomized controlled trial (PAM study). Breast Cancer Res 24(1):36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-022-01530-2
Juan Z, Chen J, Ding B, Yongping L, Liu K, Wang L, Le Y, Liao Q, Shi J, Huang J, Wu Y, Ma D, Ouyang W, Tong J (2022) Probiotic supplement attenuates chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment in patients with breast cancer: a randomised, double-blind, and placebo-controlled trial. Eur J Cancer 161:10–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2021.11.006
Salerno EA, Culakova E, Kleckner AS, Heckler CE, Lin PJ, Matthews CE, Conlin A, Weiselberg L, Mitchell J, Mustian KM, Janelsins MC (2021) Physical activity patterns and relationships with cognitive function in patients with breast Cancer before, during, and after chemotherapy in a prospective, nationwide study. J Clin Oncol 39(29):3283–3292. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.20.03514
Syed Alwi SM, Narayanan V, Mohd Taib NA, Che Din N (2021) Chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment (CRCI) among early-stage breast cancer survivors in Malaysia. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 43(5):534–545. https://doi.org/10.1080/13803395.2021.1945539
Denduluri N, Somerfield MR, Chavez-MacGregor M, Comander AH, Dayao Z, Eisen A, Freedman RA, Gopalakrishnan R, Graff SL, Hassett MJ, King TA, Lyman GH, Maupin GR, Nunes R, Perkins CL, Telli ML, Trudeau ME, Wolff AC, Giordano SH (2021) Selection of optimal adjuvant chemotherapy and targeted therapy for early breast Cancer: ASCO Guideline Update. J Clin Oncol 39(6):685–693. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.20.02510
Andryszak P, Wilkosc M, Zurawski B, Izdebski P (2018) Verbal memory in breast cancer patients treated with chemotherapy with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl) 27(1). https://doi.org/10.1111/ecc.12749
Li W, Zhang Q, Cai Y, Chen T, Cheng H (2022) The COMT genetic factor regulates chemotherapy-related prospective memory impairment in survivors with HER2-/+ breast Cancer. Front Oncol 12:816923. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.816923
Zhao J, Zuo H, Ding K, Zhang X, Bi Z, Cheng H (2020) Changes in plasma IL-1beta, TNF-alpha and IL-4 levels are involved in chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment in early-stage breast cancer patients. Am J Transl Res 12(6):3046–3056
Cheng H, Li W, Gong L, Xuan H, Huang Z, Zhao H, Wang LS, Wang K (2017) Altered resting-state hippocampal functional networks associated with chemotherapy-induced prospective memory impairment in breast cancer survivors. Sci Rep 7:45135. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep45135
Xuan H, Gan C, Li W, Huang Z, Wang L, Jia Q, Chen Z, Cheng H (2017) Altered network efficiency of functional brain networks in patients with breast cancer after chemotherapy. Oncotarget 8(62):105648–105661. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.22358
Rodriguez Martin B, Fernandez Rodriguez EJ, Rihuete Galve MI, Cruz Hernandez JJ (2020) Study of Chemotherapy-Induced Cognitive impairment in women with breast Cancer. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(23). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17238896
Shokoohinia Y, Hosseinzadeh L, Moieni-Arya M, Mostafaie A, Mohammadi-Motlagh HR (2014) Osthole attenuates doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells through inhibition of mitochondrial dysfunction and ROS production. Biomed Res Int 2014:156848. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/156848
John J, Kinra M, Mudgal J, Viswanatha GL, Nandakumar K (2021) Animal models of chemotherapy-induced cognitive decline in preclinical drug development. Psychopharmacology 238(11):3025–3053. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-021-05977-7
Kitamura Y, Kanemoto E, Sugimoto M, Machida A, Nakamura Y, Naito N, Kanzaki H, Miyazaki I, Asanuma M, Sendo T (2017) Influence of nicotine on doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide combination treatment-induced spatial cognitive impairment and anxiety-like behavior in rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 390(4):369–378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-016-1338-z
Licht T, Sasson E, Bell B, Grunewald M, Kumar S, Kreisel T, Ben-Zvi A, Keshet E (2020) Hippocampal neural stem cells facilitate access from circulation via apical cytoplasmic processes. Elife 9. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.52134
Yue Y, Xue Q, Yang J, Li X, Mi Z, Zhao G, Zhang L (2020) Wnt-activated olfactory ensheathing cells stimulate neural stem cell proliferation and neuronal differentiation. Brain Res 1735:146726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2020.146726
Fortress AM, Schram SL, Tuscher JJ, Frick KM (2013) Canonical wnt signaling is necessary for object recognition memory consolidation. J Neurosci 33(31):12619–12626. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0659-13.2013
Wang Q, Huang X, Su Y, Yin G, Wang S, Yu B, Li H, Qi J, Chen H, Zeng W, Zhang K, Verkhratsky A, Niu J, Yi C (2022) Activation of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway mitigates blood-brain barrier dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 145(12):4474–4488. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awac236
Li W, Gan C, Yu S, Xu J, Tang L, Li Q, Zhu Z, Cheng H (2023) GSK3beta rs3107669 polymorphism implicates chemotherapy-associated retrospective memory deficits in breast cancer survivors. Am J Cancer Res 13(10):4961–4975
Li J, Shi C, Ding Z, Jin W (2020) Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3beta Promotes Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction by Inducing the M1 Polarization and Migration of Microglia. Mediators Inflamm 2020:7860829. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/7860829
Hooper C, Markevich V, Plattner F, Killick R, Schofield E, Engel T, Hernandez F, Anderton B, Rosenblum K, Bliss T, Cooke SF, Avila J, Lucas JJ, Giese KP, Stephenson J, Lovestone S (2007) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibition is integral to long-term potentiation. Eur J Neurosci 25(1):81–86. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.05245.x
Deng J, Habib A, Obregon DF, Barger SW, Giunta B, Wang YJ, Hou H, Sawmiller D, Tan J (2015) Soluble amyloid precursor protein alpha inhibits tau phosphorylation through modulation of GSK3beta signaling pathway. J Neurochem 135(3):630–637. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13351
Nusse R, Clevers H (2017) Wnt/beta-Catenin signaling, Disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities. Cell 169(6):985–999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.016
Shimizu T, Kagawa T, Inoue T, Nonaka A, Takada S, Aburatani H, Taga T (2008) Stabilized beta-catenin functions through TCF/LEF proteins and the Notch/RBP-Jkappa complex to promote proliferation and suppress differentiation of neural precursor cells. Mol Cell Biol 28(24):7427–7441. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.01962-07
Alese OO, Ngoupaye GT, Rakgantsho C, Mkhize NV, Zulu S, Mabandla MV (2020) Glutamatergic pathway in depressive-like behavior associated with pentylenetetrazole rat model of epilepsy with history of prolonged febrile seizures. Life Sci 253:117692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117692
Yoshimura T, Kawano Y, Arimura N, Kawabata S, Kikuchi A, Kaibuchi K (2005) GSK-3beta regulates phosphorylation of CRMP-2 and neuronal polarity. Cell 120(1):137–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2004.11.012
Guy CT, Cardiff RD, Muller WJ (1992) Induction of mammary tumors by expression of polyomavirus middle T oncogene: a transgenic mouse model for metastatic disease. Mol Cell Biol 12(3):954–961. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.12.3.954-961.1992
Fremouw T, Fessler CL, Ferguson RJ, Burguete Y (2012) Preserved learning and memory in mice following chemotherapy: 5-Fluorouracil and doxorubicin single agent treatment, doxorubicin-cyclophosphamide combination treatment. Behav Brain Res 226(1):154–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2011.09.013
Salas-Ramirez KY, Bagnall C, Frias L, Abdali SA, Ahles TA, Hubbard K (2015) Doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide induce cognitive dysfunction and activate the ERK and AKT signaling pathways. Behav Brain Res 292:133–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2015.06.028
Aston WJ, Hope DE, Nowak AK, Robinson BW, Lake RA, Lesterhuis WJ (2017) A systematic investigation of the maximum tolerated dose of cytotoxic chemotherapy with and without supportive care in mice. BMC Cancer 17(1):684. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-017-3677-7
Keeney JTR, Ren X, Warrier G, Noel T, Powell DK, Brelsfoard JM, Sultana R, Saatman KE, Clair DKS, Butterfield DA (2018) Doxorubicin-induced elevated oxidative stress and neurochemical alterations in brain and cognitive decline: protection by MESNA and insights into mechanisms of chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment (chemobrain). Oncotarget 9(54):30324–30339. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.25718
Ren X, Keeney JTR, Miriyala S, Noel T, Powell DK, Chaiswing L, Bondada S, St Clair DK, Butterfield DA (2019) The triangle of death of neurons: oxidative damage, mitochondrial dysfunction, and loss of choline-containing biomolecules in brains of mice treated with doxorubicin. Advanced insights into mechanisms of chemotherapy induced cognitive impairment (chemobrain) involving TNF-alpha. Free Radic Biol Med 134:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.12.029
Hua L, Anjum F, Shafie A, Ashour AA, Almalki AA, Alqarni AA, Banjer HJ, Almaghrabi SA, He S, Xu N (2023) Identifying promising GSK3beta inhibitors for cancer management: a computational pipeline combining virtual screening and molecular dynamics simulations. Front Chem 11:1200490. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2023.1200490
Pondugula SR, Majrashi M, Almaghrabi M, Ramesh S, Abbott KL, Govindarajulu M, Gill K, Fahoury E, Narayanan N, Desai D, Ren J, Nadar R, McElroy T, Moore T, Majeed M, Kalyanam N, Dhanasekaran M (2021) Oroxylum Indicum ameliorates chemotherapy induced cognitive impairment. PLoS ONE 16(6):e0252522. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0252522
Guo Y, Zou G, Qi K, Jin J, Yao L, Pan Y, Xiong W (2021) Simvastatin impairs hippocampal synaptic plasticity and cognitive function in mice. Mol Brain 14(1):41. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-021-00758-x
Deshpande D, Chhugani K, Chang Y, Karlsberg A, Loeffler C, Zhang J, Muszynska A, Munteanu V, Yang H, Rotman J, Tao L, Balliu B, Tseng E, Eskin E, Zhao F, Mohammadi P, Mangul PPL S (2023) RNA-seq data science: from raw data to effective interpretation. Front Genet 14:997383. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2023.997383
Ballouz S, Dobin A, Gingeras TR, Gillis J (2018) The fractured landscape of RNA-seq alignment: the default in our STARs. Nucleic Acids Res 46(10):5125–5138. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky325
Dietrich J, Prust M, Kaiser J (2015) Chemotherapy, cognitive impairment and hippocampal toxicity. Neuroscience 309:224–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.06.016
Ahn J, Lee D, Jung YC, Kim KR (2022) Structural and functional brain alterations associated with cancer-associated cognitive decline in gastric cancer patients: a preliminary longitudinal neuroimaging study. Brain Behav 12(1):e2437. https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.2437
Vaquero L, Rodriguez-Fornells A, Pera-Jambrina MA, Bruna J, Simo M (2021) Plasticity in bilateral hippocampi after a 3-month physical activity programme in lung cancer patients. Eur J Neurol 28(4):1324–1333. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.14670
Tacar O, Sriamornsak P, Dass CR (2013) Doxorubicin: an update on anticancer molecular action, toxicity and novel drug delivery systems. J Pharm Pharmacol 65(2):157–170. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2042-7158.2012.01567.x
Eide S, Feng ZP (2020) Doxorubicin chemotherapy-induced chemo-brain: Meta-analysis. Eur J Pharmacol 881:173078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173078
Li W, Gan C, Lv Y, Wang S, Cheng H (2017) Chemotherapy-induced prospective memory impairment in breast cancer patients with different hormone receptor expression. Med (Baltim) 96(13):e6514. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000006514
Tangpong J, Miriyala S, Noel T, Sinthupibulyakit C, Jungsuwadee P, St Clair DK (2011) Doxorubicin-induced central nervous system toxicity and protection by xanthone derivative of Garcinia mangostana. Neuroscience 175:292–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.11.007
Butterfield DA (2014) The 2013 SFRBM discovery award: selected discoveries from the butterfield laboratory of oxidative stress and its sequela in brain in cognitive disorders exemplified by Alzheimer disease and chemotherapy induced cognitive impairment. Free Radic Biol Med 74:157–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.06.006
Park HS, Kim CJ, Kwak HB, No MH, Heo JW, Kim TW (2018) Physical exercise prevents cognitive impairment by enhancing hippocampal neuroplasticity and mitochondrial function in doxorubicin-induced chemobrain. Neuropharmacology 133:451–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.02.013
Moruno-Manchon JF, Uzor NE, Kesler SR, Wefel JS, Townley DM, Nagaraja AS, Pradeep S, Mangala LS, Sood AK, Tsvetkov AS (2016) TFEB ameliorates the impairment of the autophagy-lysosome pathway in neurons induced by doxorubicin. Aging 8(12):3507–3519. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.101144
Lim I, Joung HY, Yu AR, Shim I, Kim JS (2016) PET Evidence of the Effect of Donepezil on Cognitive Performance in an Animal Model of Chemobrain. Biomed Res Int 2016:6945415. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6945415
Chandrasekaran K, Choi J, Arvas MI, Salimian M, Singh S, Xu S, Gullapalli RP, Kristian T, Russell JW (2020) Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Administration prevents Experimental Diabetes-Induced Cognitive Impairment and loss of hippocampal neurons. Int J Mol Sci 21(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21113756
Lauretti E, Dincer O, Pratico D (2020) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1867(5):118664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2020.118664
Yang Q, Huang DD, Li DG, Chen B, Zhang LM, Yuan CL, Huang HH (2019) Tetramethylpyrazine exerts a protective effect against injury from acute myocardial ischemia by regulating the PI3K/Akt/GSK-3beta signaling pathway. Cell Mol Biol Lett 24:17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-019-0141-5
Wang S, He B, Hang W, Wu N, Xia L, Wang X, Zhang Q, Zhou X, Feng Z, Chen Q, Chen J (2018) Berberine alleviates Tau Hyperphosphorylation and Axonopathy-Associated with Diabetic Encephalopathy via restoring PI3K/Akt/GSK3beta pathway. J Alzheimers Dis 65(4):1385–1400. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-180497
Upadhya D, Hattiangady B, Shetty GA, Zanirati G, Kodali M, Shetty AK (2016) Neural stem cell or Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-derived GABA-ergic Progenitor Cell Grafting in an animal model of chronic temporal lobe Epilepsy. Curr Protoc Stem Cell Biol 38(2D 7 1–2D 7):47. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpsc.9
Dijkshoorn ABC, van Stralen HE, Sloots M, Schagen SB, Visser-Meily JMA, Schepers VPM (2021) Prevalence of cognitive impairment and change in patients with breast cancer: a systematic review of longitudinal studies. Psychooncology 30(5):635–648. https://doi.org/10.1002/pon.5623
Hoeflich KP, Luo J, Rubie EA, Tsao MS, Jin O, Woodgett JR (2000) Requirement for glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in cell survival and NF-kappaB activation. Nature 406(6791):86–90. https://doi.org/10.1038/35017574
Pleen J, Townley R (2022) Alzheimer’s disease clinical trial update 2019–2021. J Neurol 269(2):1038–1051. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-021-10790-5
Ou Z, Kong X, Sun X, He X, Zhang L, Gong Z, Huang J, Xu B, Long D, Li J, Li Q, Xu L, Xuan A (2018) Metformin treatment prevents amyloid plaque deposition and memory impairment in APP/PS1 mice. Brain Behav Immun 69:351–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2017.12.009
Song JX, Malampati S, Zeng Y, Durairajan SSK, Yang CB, Tong BC, Iyaswamy A, Shang WB, Sreenivasmurthy SG, Zhu Z, Cheung KH, Lu JH, Tang C, Xu N, Li M (2020) A small molecule transcription factor EB activator ameliorates beta-amyloid precursor protein and tau pathology in Alzheimer’s disease models. Aging Cell 19(2):e13069. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.13069
Contreras A, Del Rio D, Martinez A, Gil C, Morales L, Ruiz-Gayo M, Del Olmo N (2017) Inhibition of hippocampal long-term potentiation by high-fat diets: is it related to an effect of palmitic acid involving glycogen synthase kinase-3? NeuroReport 28(6):354–359. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNR.0000000000000774
Vallee A, Lecarpentier Y (2016) Alzheimer Disease: crosstalk between the Canonical Wnt/Beta-Catenin pathway and PPARs alpha and Gamma. Front Neurosci 10:459. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2016.00459
Xue R, Wan Y, Sun X, Zhang X, Gao W, Wu W (2019) Nicotinic Mitigation of Neuroinflammation and oxidative stress after chronic sleep deprivation. Front Immunol 10:2546. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02546
Xu ZP, Gan GS, Liu YM, Xiao JS, Liu HX, Mei B, Zhang JJ (2018) Adiponectin attenuates Streptozotocin-Induced tau hyperphosphorylation and cognitive deficits by rescuing PI3K/Akt/GSK-3beta pathway. Neurochem Res 43(2):316–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2426-2
Chen J, Park CS, Tang SJ (2006) Activity-dependent synaptic wnt release regulates hippocampal long term potentiation. J Biol Chem 281(17):11910–11916. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M511920200
Ivanova OY, Dobryakova YV, Salozhin SV, Aniol VA, Onufriev MV, Gulyaeva NV, Markevich VA (2017) Lentiviral modulation of Wnt/beta-Catenin signaling affects in vivo LTP. Cell Mol Neurobiol 37(7):1227–1241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-016-0455-z
Xu N, Zhou WJ, Wang Y, Huang SH, Li X, Chen ZY (2015) Hippocampal Wnt3a is necessary and sufficient for Contextual Fear Memory Acquisition and consolidation. Cereb Cortex 25(11):4062–4075. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhu121
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81872504).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wen Li constructed the model, performed the behavioural tests, conducted the experiments, and wrote the manuscript; Chen Gan, and Sheng Yu performed data collection; Jian Xu arranged the manuscript; Lingxue Tang performed statistical analysis; Huaidong Cheng designed the project. All authors contributed to manuscript editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest related to this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Gan, C., Yu, S. et al. Wnt3a/GSK3β/β-catenin Signalling Modulates Doxorubicin-associated Memory Deficits in Breast Cancer. Mol Neurobiol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-023-03910-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-023-03910-x