Abstract
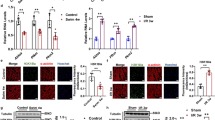
It has recently been accepted that long-term high-fat diet (HFD) intake is a significant possible cause for prediabetes and cognitive and brain dysfunction through the disruption of brain mitochondrial function and dynamic balance. Although modulation of mitochondrial dynamics by inhibiting fission and promoting fusion has been shown to reduce the morbidity and mortality associated with a variety of chronic diseases, the impact of either pharmacological inhibition of mitochondrial fission (Mdivi-1) or stimulation of fusion (M1) on brain function in HFD-induced prediabetic models has never been studied. Thirty-two male Wistar rats were separated into 2 groups and fed either a normal diet (ND, n = 8) or HFD (n = 24) for 14 weeks. At week 12, HFD-fed rats were divided into 3 subgroups (n = 8/subgroup) and given an intraperitoneal injection of either saline, Mdivi-1 (1.2 mg/kg/day), or M1 (2 mg/kg/day) for 2 weeks. Cognitive function and metabolic parameters were determined toward the end of the protocol. The rats then were euthanized, and the brain was immediately removed in order to evaluate brain mitochondrial function and mitochondrial dynamics. HFD-fed rats experienced prediabetes, evidenced by elevated plasma insulin and the HOMA index, impaired mitochondrial function in the brain, altered dynamic regulation, and cognitive impairment were also found. Mdivi-1 and M1 treatment exerted neuroprotection to a similar extent by improving metabolic parameters, balancing mitochondrial dynamics, and reducing mitochondrial dysfunction, resulting in a gradual increase in cognitive function. Therefore, pharmacological targeting of mitochondrial fission and fusion protected the brain against chronic HFD-induced prediabetes.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Malik VS, Willet WC, Hu FB (2020) Nearly a decade on — trends, risk factors and policy implications in global obesity. Nat Rev Endocrinol 16(11):615–616. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-020-00411-y
Haththotuwa RN, Wijeyaratne CN, Senarath U (2020) Chapter 1 - worldwide epidemic of obesity. In: Mahmood TA, Arulkumaran S, Chervenak FA (eds) Obesity and Obstetrics (Second Edition). Elsevier, pp 3–8.:https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-817921-5.00001-1
Riccardi G, Giacco R, Rivellese AA (2004) Dietary fat, insulin sensitivity and the metabolic syndrome. Clin Nutr 23(4):447–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2004.02.006
Apaijai N, Pintana H, Chattipakorn SC, Chattipakorn N (2012) Cardioprotective effects of metformin and vildagliptin in adult rats with insulin resistance induced by a high-fat diet. Endocrinology 153(8):3878–3885. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2012-1262
Pipatpiboon N, Pratchayasakul W, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC (2012) PPARgamma agonist improves neuronal insulin receptor function in hippocampus and brain mitochondria function in rats with insulin resistance induced by long term high-fat diets. Endocrinology 153 (1):329-338.:https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2011-1502
Pratchayasakul W, Kerdphoo S, Petsophonsakul P, Pongchaidecha A, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC (2011) Effects of high-fat diet on insulin receptor function in rat hippocampus and the level of neuronal corticosterone. Life Sci 88 (13–14):619–627.:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2011.02.003
Petersen KF, Befroy D, Dufour S, Dziura J, Ariyan C, Rothman DL, DiPietro L, Cline GW, Shulman GI (2003) Mitochondrial dysfunction in the elderly: possible role in insulin resistance. Science 300(5622):1140–1142. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1082889
Maneechote C, Palee S, Kerdphoo S, Jaiwongkam T, Chattipakorn SC, Chattipakorn N (2021) Modulating mitochondrial dynamics attenuates cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury in prediabetic rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin.:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-021-00626-3
Maneechote C, Palee S, Kerdphoo S, Jaiwongkam T, Chattipakorn SC, Chattipakorn N (2020) Pharmacological inhibition of mitochondrial fission attenuates cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury in pre-diabetic rats. Biochem Pharmacol 182:114295.:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114295
Maneechote C, Palee S, Apaijai N, Kerdphoo S, Jaiwongkam T, Chattipakorn SC, Chattipakorn N (2019) Mitochondrial dynamic modulation exerts cardiometabolic protection in obese insulin-resistant rats. Clin Sci (Lond) 133(24):2431–2447. https://doi.org/10.1042/cs20190960
Chunchai T, Keawtep P, Arinno A, Saiyasit N, Prus D, Apaijai N, Pratchayasakul W, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC (2019) N-acetyl cysteine, inulin and the two as a combined therapy ameliorate cognitive decline in testosterone-deprived rats. Aging 11(11):3445–3462. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.101989
Pratchayasakul W, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC (2011) Effects of estrogen in preventing neuronal insulin resistance in hippocampus of obese rats are different between genders. Life Sci 89 (19–20):702–707.:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2011.08.011
Pintana H, Pratchayasakul W, Sa-nguanmoo P, Pongkan W, Tawinvisan R, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC (2016) Testosterone deprivation has neither additive nor synergistic effects with obesity on the cognitive impairment in orchiectomized and/or obese male rats. Metabolism 65(2):54–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2015.10.015
Suen DF, Norris KL, Youle RJ (2008) Mitochondrial dynamics and apoptosis. Genes Dev 22(12):1577–1590. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1658508
Chan DC (2006) Mitochondrial fusion and fission in mammals. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 22:79–99. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.cellbio.22.010305.104638
Leduc-Gaudet J-P, Reynaud O, Chabot F, Mercier J, Andrich DE, St-Pierre DH, Gouspillou G (2018) The impact of a short-term high-fat diet on mitochondrial respiration, reactive oxygen species production, and dynamics in oxidative and glycolytic skeletal muscles of young rats. Physiol Rep 6 (4):e13548.:https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.13548
Ong SB, Kalkhoran SB, Hernandez-Resendiz S, Samangouei P, Ong SG, Hausenloy DJ (2017) Mitochondrial-shaping proteins in cardiac health and disease - the long and the short of it! Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 31(1):87–107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-016-6710-1
Scott I, Youle RJ (2010) Mitochondrial fission and fusion. Essays Biochem 47:85–98. https://doi.org/10.1042/bse0470085
Gao AW, Cantó C, Houtkooper RH (2014) Mitochondrial response to nutrient availability and its role in metabolic disease. EMBO Mol Med 6(5):580–589. https://doi.org/10.1002/emmm.201303782
Flippo KH, Strack S (2017) Mitochondrial dynamics in neuronal injury, development and plasticity. J Cell Sci 130(4):671–681. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.171017
Rigotto G, Basso E (2019) Mitochondrial dysfunctions: a thread sewing together Alzheimer's disease, diabetes, and obesity. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:7210892.:https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7210892
Khan MSH, Hegde V (2020) Obesity and diabetes mediated chronic inflammation: a potential biomarker in Alzheimer’s disease. J Pers Med 10(2):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10020042
Zhang X, Huang W, Shao Q, Yang Y, Xu Z, Chen J, Zhang X, Ge X (2020) Drp1, a potential therapeutic target for Parkinson's disease, is involved in olfactory bulb pathological alteration in the rotenone-induced rat model. Toxicol Lett 325:1-13.:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2020.02.009
Zhang Y, Rui T, Luo C, Li Q (2021) Mdivi-1 alleviates brain damage and synaptic dysfunction after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. Exp Brain Res.:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-021-06089-6
Mishra A, Singh S, Tiwari V, Bano S, Shukla S (2020) Dopamine D1 receptor agonism induces dynamin related protein-1 inhibition to improve mitochondrial biogenesis and dopaminergic neurogenesis in rat model of Parkinson's disease. Behav Brain Res 378:112304.:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2019.112304
Surinkaew P, Apaijai N, Sawaddiruk P, Jaiwongkam T, Kerdphoo S, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC (2020) Mitochondrial fusion promoter alleviates brain damage in rats with cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Alzheimers Dis 77(3):993–1003. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-200495
Ruiz A, Alberdi E, Matute C (2018) Mitochondrial division inhibitor 1 (mdivi-1) protects neurons against excitotoxicity through the modulation of mitochondrial function and intracellulAr Ca2+ signaling. Front Mol Neurosci 11 (3).:https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2018.00003
Cassidy-Stone A, Chipuk JE, Ingerman E, Song C, Yoo C, Kuwana T, Kurth MJ, Shaw JT et al (2008) Chemical inhibition of the mitochondrial division dynamin reveals its role in Bax/Bak-dependent mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization. Dev Cell 14(2):193–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2007.11.019
Zhang N, Wang S, Li Y, Che L, Zhao Q (2013) A selective inhibitor of Drp1, mdivi-1, acts against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via an anti-apoptotic pathway in rats. Neurosci Lett 535(104):109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2012.12.049
Li Y, Wang P, Wei J, Fan R, Zuo Y, Shi M, Wu H, Zhou M et al (2015) Inhibition of Drp1 by Mdivi-1 attenuates cerebral ischemic injury via inhibition of the mitochondria-dependent apoptotic pathway after cardiac arrest. Neuroscience 311(67):74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.10.020
Apaiajai N, Chunchai T, Jaiwongkam T, Kerdphoo S, Chattipakorn SC, Chattipakorn N (2018) Testosterone deprivation aggravates left-ventricular dysfunction in male obese insulin-resistant rats via impairing cardiac mitochondrial function and dynamics proteins. Gerontol 64(4):333–343. https://doi.org/10.1159/000487188
Tunapong W, Apaijai N, Yasom S, Tanajak P, Wanchai K, Chunchai T, Kerdphoo S, Eaimworawuthikul S et al (2017) Chronic treatment with prebiotics, probiotics and synbiotics attenuated cardiac dysfunction by improving cardiac mitochondrial dysfunction in male obese insulin-resistant rats. Eur J Nutr.:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-017-1482-3
Shwe T, Bo-Htay C, Ongnok B, Chunchai T, Jaiwongkam T, Kerdphoo S, Kumfu S, Pratchayasakul W et al (2021) Hyperbaric oxygen therapy restores cognitive function and hippocampal pathologies in both aging and aging-obese rats. Mech Ageing Dev 195:111465.:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2021.111465
Jinawong K, Apaijai N, Wongsuchai S, Pratchayasakul W, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC (2020) Necrostatin-1 mitigates cognitive dysfunction in prediabetic rats with no alteration in insulin sensitivity. Diabetes 69(7):1411. https://doi.org/10.2337/db19-1128
Jinawong K, Apaijai N, Wongsuchai S, Pratchayasakul W, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC (2020) Necrostatin-1 mitigates cognitive dysfunction in prediabetic rats with no alteration in insulin sensitivity. Diabetes 69(7):1411–1423. https://doi.org/10.2337/db19-1128
Clewer AG, Scarisbrick DH (2001) practical statistics and experimental design for plant and crop science. In, 2001
Saiyasit N, Chunchai T, Prus D, Suparan K, Pittayapong P, Apaijai N, Pratchayasakul W, Sripetchwandee J et al (2020) Gut dysbiosis develops before metabolic disturbance and cognitive decline in high-fat diet-induced obese condition. Nutrition 69:110576.:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2019.110576
Sa-Nguanmoo P, Tanajak P, Kerdphoo S, Jaiwongkam T, Pratchayasakul W, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC (2017) SGLT2-inhibitor and DPP-4 inhibitor improve brain function via attenuating mitochondrial dysfunction, insulin resistance, inflammation, and apoptosis in HFD-induced obese rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 333(43):50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2017.08.005
Chunchai T, Thunapong W, Yasom S, Wanchai K, Eaimworawuthikul S, Metzler G, Lungkaphin A, Pongchaidecha A et al (2018) Decreased microglial activation through gut-brain axis by prebiotics, probiotics, or synbiotics effectively restored cognitive function in obese-insulin resistant rats. J Neuroinflammation 15(1):11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-018-1055-2
Pratchayasakul W, Thongnak LO, Chattipakorn K, Lungaphin A, Pongchaidecha A, Satjaritanun P, Jaiwongkam T, Kerdphoo S et al (2018) Atorvastatin and insulin equally mitigate brain pathology in diabetic rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 342(79):85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2018.01.021
Putti R, Sica R, Migliaccio V, Lionetti L (2015) Diet impact on mitochondrial bioenergetics and dynamics. Front Physiol 6:109. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2015.00109
Jheng HF, Tsai PJ, Guo SM, Kuo LH, Chang CS, Su IJ, Chang CR, Tsai YS (2012) Mitochondrial fission contributes to mitochondrial dysfunction and insulin resistance in skeletal muscle. Mol Cell Biol 32(2):309–319. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.05603-11
Sartorius T, Peter A, Schulz N, Drescher A, Bergheim I, Machann J, Schick F, Siegel-Axel D et al (2014) Cinnamon extract improves insulin sensitivity in the brain and lowers liver fat in mouse models of obesity. PLoS One 9 (3):e92358.:https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0092358
Tong M, de la Monte SM (2009) Mechanisms of ceramide-mediated neurodegeneration. J Alzheimers Dis 16(4):705–714. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-2009-0983
Manczak M, Calkins MJ, Reddy PH (2011) Impaired mitochondrial dynamics and abnormal interaction of amyloid beta with mitochondrial protein Drp1 in neurons from patients with Alzheimer’s disease: implications for neuronal damage. Hum Mol Genet 20(13):2495–2509. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddr139
Manczak M, Reddy PH (2012) Abnormal interaction between the mitochondrial fission protein Drp1 and hyperphosphorylated tau in Alzheimer’s disease neurons: implications for mitochondrial dysfunction and neuronal damage. Hum Mol Genet 21(11):2538–2547. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/dds072
Yao J, Du H, Yan S, Fang F, Wang C, Lue LF, Guo L, Chen D et al (2011) Inhibition of amyloid-beta (Abeta) peptide-binding alcohol dehydrogenase-Abeta interaction reduces Abeta accumulation and improves mitochondrial function in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 31(6):2313–2320. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.4717-10.2011
Cha MY, Han SH, Son SM, Hong HS, Choi YJ, Byun J, Mook-Jung I (2012) Mitochondria-specific accumulation of amyloid β induces mitochondrial dysfunction leading to apoptotic cell death. PLoS One 7 (4):e34929.:https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0034929
Baek SH, Park SJ, Jeong JI, Kim SH, Han J, Kyung JW, Baik SH, Choi Y et al (2017) Inhibition of Drp1 ameliorates synaptic depression, Aβ deposition, and cognitive impairment in an Alzheimer’s disease model. J Neurosci 37(20):5099–5110. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.2385-16.2017
Mancini G, Pirruccio K, Yang X, Blüher M, Rodeheffer M, Horvath TL (2019) Mitofusin 2 in mature adipocytes controls adiposity and body weight. Cell Rep 26 (11):2849–2858.e2844.:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.02.039
Calkins MJ, Manczak M, Mao P, Shirendeb U, Reddy PH (2011) Impaired mitochondrial biogenesis, defective axonal transport of mitochondria, abnormal mitochondrial dynamics and synaptic degeneration in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 20(23):4515–4529. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddr381
Wang X, Su B, Lee HG, Li X, Perry G, Smith MA, Zhu X (2009) Impaired balance of mitochondrial fission and fusion in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 29(28):9090–9103. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.1357-09.2009
Jiang S, Nandy P, Wang W, Ma X, Hsia J, Wang C, Wang Z, Niu M et al (2018) Mfn2 ablation causes an oxidative stress response and eventual neuronal death in the hippocampus and cortex. Mol Neurodegener 13(1):5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-018-0238-8
Pysh JJ, Khan T (1972) Variations in mitochondrial structure and content of neurons and neuroglia in rat brain: an electron microscopic study. Brain Res 36(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(72)90762-7
Nürnberger S, Rentenberger C, Thiel K, Schädl B, Grunwald I, Ponomarev I, Marlovits S, Meyer C et al (2017) Giant crystals inside mitochondria of equine chondrocytes. Histochem Cell Biol 147(5):635–649. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-016-1516-6
Farrants GW, Hovmöller S, Stadhouders AM (1988) Two types of mitochondrial crystals in diseased human skeletal muscle fibers. Muscle Nerve 11(1):45–55. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.880110109
Fecher C, Trovò L, Müller SA, Snaidero N, Wettmarshausen J, Heink S, Ortiz O, Wagner I et al (2019) Cell-type-specific profiling of brain mitochondria reveals functional and molecular diversity. Nat Neurosci 22(10):1731–1742. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-019-0479-z
Sripetchwandee J, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC (2018) Links between obesity-induced brain insulin resistance, brain mitochondrial dysfunction, and dementia. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 9:496.:https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00496
Nuzzo D, Picone P, Baldassano S, Caruana L, Messina E, Marino Gammazza A, Cappello F, Mulè F et al (2015) Insulin resistance as common molecular denominator linking obesity to Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 12(8):723–735. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567205012666150710115506
Ghavami S, Shojaei S, Yeganeh B, Ande SR, Jangamreddy JR, Mehrpour M, Christoffersson J, Chaabane W et al (2014) Autophagy and apoptosis dysfunction in neurodegenerative disorders. Prog Neurobiol 112:24-49.:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.10.004
Sturman O, Germain PL, Bohacek J (2018) Exploratory rearing: a context- and stress-sensitive behavior recorded in the open-field test. Stress 21(5):443–452. https://doi.org/10.1080/10253890.2018.1438405
Denninger JK, Smith BM, Kirby ED (2018) Novel object recognition and object location behavioral testing in mice on a budget. J Vis Exp (141).:https://doi.org/10.3791/58593
Bartsch T, Wulff P (2015) The hippocampus in aging and disease: from plasticity to vulnerability. Neuroscience 309(1):16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.07.084
Smith BM, Yao X, Chen KS, Kirby ED (2018) A larger social network enhances novel object location memory and reduces hippocampal microgliosis in aged mice. Front Aging Neurosci 10:142. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2018.00142
Garthe A, Roeder I, Kempermann G (2016) Mice in an enriched environment learn more flexibly because of adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Hippocampus 26(2):261–271. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.22520
Chieffi S, Messina G, Villano I, Messina A, Esposito M, Monda V, Valenzano A, Moscatelli F et al (2017) Exercise influence on hippocampal function: possible involvement of orexin-A. Front Physiol 8:85.:https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00085
Saiyasit N, Chunchai T, Apaijai N, Pratchayasakul W, Sripetchwandee J, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC (2020) Chronic high-fat diet consumption induces an alteration in plasma/brain neurotensin signaling, metabolic disturbance, systemic inflammation/oxidative stress, brain apoptosis, and dendritic spine loss. Neuropeptides 82:102047.:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.npep.2020.102047
Cruz-Sanchez A, Dematagoda S, Ahmed R, Mohanathaas S, Odenwald N, Arruda-Carvalho M (2020) Developmental onset distinguishes three types of spontaneous recognition memory in mice. Sci Rep 10(1):10612. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-67619-w
Bordt EA, Clerc P, Roelofs BA, Saladino AJ, Tretter L, Adam-Vizi V, Cherok E, Khalil A et al (2017) The putative Drp1 inhibitor mdivi-1 is a reversible mitochondrial complex I inhibitor that modulates reactive oxygen species. Dev Cell 40 (6):583–594.e586.:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2017.02.020
Aishwarya R, Alam S, Abdullah CS, Morshed M, Nitu SS, Panchatcharam M, Miriyala S, Kevil CG, Bhuiyan MS (2020) Pleiotropic effects of mdivi-1 in altering mitochondrial dynamics, respiration, and autophagy in cardiomyocytes. Redox Biol 36:101660.:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2020.101660
Wang D, Wang J, Bonamy GM, Meeusen S, Brusch RG, Turk C, Yang P, Schultz PG (2012) A small molecule promotes mitochondrial fusion in mammalian cells. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 51(37):9302–9305. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201204589
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Siripong Palee, Thidarat Jaiwongkam, and Sasiwan Kerdphoo for their laboratory assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by the Senior Research Scholar Grant from the National Research Council of Thailand (S.C.C.), the NSTDA Research Chair grant from the National Science and Technology Development Agency Thailand (N.C.), the Chiang Mai University Center of Excellence Award (N.C.), the National Research Council of Thailand, Fundamental Fund 2022, Chiang Mai University (C.M.), and the National Research Council of Thailand (C.M.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.M. performed the experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. T.C., N.A. performed the experiments. N.C. designed the study, contributed to the discussion, and edited the manuscript. S.C.C. designed the study, analyzed the data, contributed to the discussion, and edited and finalized the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Thailand (Permit No. 34/2561) and were performed at the Cardiac Electrophysiology Research and Training Center, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maneechote, C., Chunchai, T., Apaijai, N. et al. Pharmacological Targeting of Mitochondrial Fission and Fusion Alleviates Cognitive Impairment and Brain Pathologies in Pre-diabetic Rats. Mol Neurobiol 59, 3690–3702 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-022-02813-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-022-02813-7