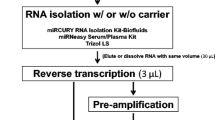
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs that regulate post-transcriptional gene expression. Recent studies have shown that human disease states correlate with measurable differences in the level of circulating miRNAs relative to healthy controls. Thus, there is great interest in developing clinical miRNA assays as diagnostic or prognostic biomarkers for diseases, and as surrogate measures for therapeutic outcomes. Our studies have focused on miRNAs in human cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) as biomarkers for central nervous system (CNS) diseases. Our objective here was to examine factors that may affect the outcome of quantitative PCR (qPCR) studies on CSF miRNAs, in order to guide planning and interpretation of future CSF miRNA TaqMan® low-density array (TLDA) studies. We obtained CSF from neurologically normal (control) donors and used TLDAs to measure miRNA expression. We examined sources of error in the TLDA outcomes due to (1) nonspecific amplification of products in total RNA, (2) variations in RNA isolations performed on different days, (3) miRNA primer probe efficiency, and (4) variations in individual TLDA cards. We also examined the utility of card-to-card TLDA corrections and use of an unchanged “reference standard” to remove batch processing effects in large-scale studies.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stedman TL (2004) The American Heritage Stedman's medical dictionary. Houghton Mifflin Co., Boston
Quinn JF, Patel T, Wong D, Das S, Freedman JE, Laurent LC, Carter BS, Hochberg F et al (2015) Extracellular RNAs: development as biomarkers of human disease. J Extracell Vesicles 4:27495. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v4.27495
Rao P, Benito E, Fischer A (2013) MicroRNAs as biomarkers for CNS disease. Front Mol Neurosci 6:39. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2013.00039
Denk J, Boelmans K, Siegismund C, Lassner D, Arlt S, Jahn H (2015) MicroRNA profiling of CSF reveals potential biomarkers to detect Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 10:e0126423. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0126423
Gui Y, Liu H, Zhang L, Lv W, Hu X (2015) Altered microRNA profiles in cerebrospinal fluid exosome in Parkinson disease and Alzheimer disease. Oncotarget 6:37043–37053. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.6158
Muller M, Jakel L, Bruinsma IB, Claassen JA, Kuiperij HB, Verbeek MM (2016) MicroRNA-29a is a candidate biomarker for Alzheimer's disease in cell-free cerebrospinal fluid. Mol Neurobiol 53:2894–2899. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9156-8
van Harten AC, Mulders J, Scheltens P, van der Flier WM, Oudejans CB (2015) Differential expression of microRNA in cerebrospinal fluid as a potential novel biomarker for Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis 47:243–252. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-140075
Teplyuk NM, Mollenhauer B, Gabriely G, Giese A, Kim E, Smolsky M, Kim RY, Saria MG et al (2012) MicroRNAs in cerebrospinal fluid identify glioblastoma and metastatic brain cancers and reflect disease activity. Neuro-Oncology 14:689–700. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nos074
Baraniskin A, Kuhnhenn J, Schlegel U, Maghnouj A, Zollner H, Schmiegel W, Hahn S, Schroers R (2012) Identification of microRNAs in the cerebrospinal fluid as biomarker for the diagnosis of glioma. Neuro-Oncology 14:29–33. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nor169
Wan Y, Liu Y, Wang X, Wu J, Liu K, Zhou J, Liu L, Zhang C (2015) Identification of differential microRNAs in cerebrospinal fluid and serum of patients with major depressive disorder. PLoS One 10:e0121975. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0121975
Lusardi TA, Phillips JI, Wiedrick JT, Harrington CA, Lind B, Lapidus JA, Quinn JF, Saugstad JA (2017) MicroRNAs in human cerebrospinal fluid as biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis 55:1223–1233. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-160835
Shi M, Bradner J, Hancock AM, Chung KA, Quinn JF, Peskind ER, Galasko D, Jankovic J et al (2011) Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for Parkinson disease diagnosis and progression. Ann Neurol 69:570–580. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.22311
Burgos K, Malenica I, Metpally R, Courtright A, Rakela B, Beach T, Shill H, Adler C et al (2014) Profiles of extracellular miRNA in cerebrospinal fluid and serum from patients with Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases correlate with disease status and features of pathology. PLoS One 9:e94839. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0094839
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans J, Huggett J, Kubista M, Mueller R, Nolan T et al (2009) The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem 55:611–622. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2008.112797
Git A, Dvinge H, Salmon-Divon M, Osborne M, Kutter C, Hadfield J, Bertone P, Caldas C (2010) Systematic comparison of microarray profiling, real-time PCR, and next-generation sequencing technologies for measuring differential microRNA expression. RNA 16:991–1006. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.1947110
Benes V, Castoldi M (2010) Expression profiling of microRNA using real-time quantitative PCR, how to use it and what is available. Methods 50:244–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2010.01.026
Podlesniy P, Figueiro-Silva J, Llado A, Antonell A, Sanchez-Valle R, Alcolea D, Lleo A, Molinuevo JL et al (2013) Low cerebrospinal fluid concentration of mitochondrial DNA in preclinical Alzheimer disease. Ann Neurol 74:655–668. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.23955
Pyle A, Brennan R, Kurzawa-Akanbi M, Yarnall A, Thouin A, Mollenhauer B, Burn D, Chinnery PF et al (2015) Reduced cerebrospinal fluid mitochondrial DNA is a biomarker for early-stage Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol 78:1000–1004. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24515
Varhaug KN, Vedeler CA, Myhr KM, Aarseth JH, Tzoulis C, Bindoff LA (2017) Increased levels of cell-free mitochondrial DNA in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis. Mitochondrion 34:32–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2016.12.003
Saugstad JA, Lusardi TA, Van Keuren-Jensen KR, Phillips JI, Lind B, Harrington CA, McFarland TJ, Courtright AL et al (2017) Analysis of extracellular RNA in cerebrospinal fluid. J Extracell Vesicles 6:1317577. https://doi.org/10.1080/20013078.2017.1317577
Wang WX, Fardo DW, Jicha GA, Nelson PT (2017) A customized quantitative PCR MicroRNA panel provides a technically robust context for studying neurodegenerative disease biomarkers and indicates a high correlation between cerebrospinal fluid and choroid plexus MicroRNA expression. Mol Neurobiol 54:8191–8202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0316-2
Wolfinger RD, Beedanagari S, Boitier E, Chen T, Couttet P, Ellinger-Ziegelbauer H, Guillemain G, Mariet C et al (2018) Two approaches for estimating the lower limit of quantitation (LLOQ) of microRNA levels assayed as exploratory biomarkers by RT-qPCR. BMC Biotechnol 18:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12896-018-0415-4
Mestdagh P, Van Vlierberghe P, De Weer A, Muth D, Westermann F, Speleman F, Vandesompele J (2009) A novel and universal method for microRNA RT-qPCR data normalization. Genome Biol 10:R64. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2009-10-6-r64
Wylie D, Shelton J, Choudhary A, Adai AT (2011) A novel mean-centering method for normalizing microRNA expression from high-throughput RT-qPCR data. BMC Res Notes 4:555. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-0500-4-555
Brunet-Vega A, Quilez ME, Ramirez-Lazaro MJ, Lario S (2018) Application of individual qPCR performance parameters for quality control of circulating MicroRNA data. Methods Mol Biol 1699:187–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7435-1_14
Gevaert AB, Witvrouwen I, Vrints CJ, Heidbuchel H, Van Craenenbroeck EM, Van Laere SJ, Van Craenenbroeck AH (2018) MicroRNA profiling in plasma samples using qPCR arrays: Recommendations for correct analysis and interpretation. PLoS One 13:e0193173. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0193173
Acknowledgements
We thank the OHSU Gene Profiling Shared Resource for professional advice and access to core instrumentation. The research reported in this publication was supported by funds awarded to JAS by the Oregon Clinical & Translational Research Institute, which is supported by the NIH National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences grant UL1TR000128, by NIH NCATS UH2/UH3TR000903 (JAS, JFQ), and by the NIH National Institutes of Aging P30AG008017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(XLSX 135 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lusardi, T.A., Wiedrick, J.T., Malone, M. et al. Analytics of Cerebrospinal Fluid MicroRNA Quantitative PCR Studies. Mol Neurobiol 56, 4988–4999 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1422-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1422-0