Abstract
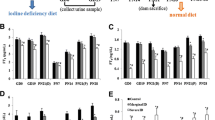
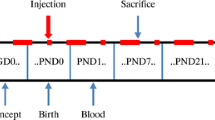
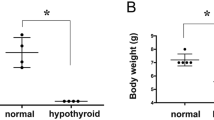
Hypothyroidism induced by severe iodine deficiency (ID) during developmental period seriously damages the central nervous system function. In addition to developmental hypothyroidism induced by severe ID, developmental hypothyroxinemia induced by mild ID is potentially damaging for neurodevelopment and learning and memory in children. Wistar rats were treated with iodine-deficient diet or methimazole (MMZ) during pregnancy and lactation to induce developmental hypothyroxinemia or hypothyroidism in the present study. Pups were weaned on postnatal day (PN) 21 and used for electrophysiological recordings on PN80. It is generally accepted that long-term depression (LTD) is induced at low-frequency stimulation (LFS) in hippocampal CA1 region. Surprisingly, we observed developmental hypothyroxinemia as well as developmental hypothyroidism led to high-frequency stimulation (HFS)-induced LTD in hippocampal CA1 region. The abnormal HFS-induced LTD suggests not only developmental hypothyroidism but also developmental hypothyroxinemia impairs learning and memory. To explore the mechanisms responsible for the HFS-induced LTD, the phosphorylation status of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors (AMPARs) was investigated. The results showed that developmental hypothyroxinemia as well as developmental hypothyroidism decreased the phosphorylation of AMPAR subunit glutamate receptor 1 (GluR1) at serine 831 and serine 845 in hippocampal CA1 region. Neither developmental hypothyroxinemia nor developmental hypothyroidism altered the phosphorylation of AMPAR subunit glutamate receptor 2 (GluR2) at serine 880. Increased levels of protein phosphatase-1 (PP1) were also observed in hippocampal CA1 regions of pups subjected to developmental hypothyroxinemia or hypothyroidism. Taken together, our results suggest that the increased levels of PP1 caused by developmental hypothyroxinemia or hypothyroidism may account for the dephosphorylation of GluR1 at serine 831 and serine 845, which may contribute to HFS-induced LTD in hippocampal CA1 region.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Puig-Domingo M, Vila L (2012) The implications of iodine and its supplementation during pregnancy in fetal brain development. Curr Clin Pharmacol 8(2):97–109
Berbel P, Obregon MJ, Bernal J, Escobar del Rey F, Morreale de Escobar G (2007) Iodine supplementation during pregnancy: a public health challenge. Trends Endocrinol Metab 18(9):338–343
Lavado-Autric R, Calvo RM, de Mena RM, de Escobar GM, Obregon MJ (2013) Deiodinase activities in thyroids and tissues of iodine-deficient female rats. Endocrinology 154(1):529–536
Zimmermann MB (2009) Iodine deficiency. Endocr Rev 30(4):376–408
Bath SC, Steer CD, Golding J, Emmett P, Rayman MP (2013) Effect of inadequate iodine status in UK pregnant women on cognitive outcomes in their children: results from the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC). Lancet 382(9889):331–337
Lavado-Autric R, Auso E, Garcia-Velasco JV, Arufe Mdel C, Escobar del Rey F, Berbel P, Morreale de Escobar G (2003) Early maternal hypothyroxinemia alters histogenesis and cerebral cortex cytoarchitecture of the progeny. J Clin Invest 111(7):1073–1082
Morreale de Escobar G, Obregon MJ, Escobar del Rey F (2000) Is neuropsychological development related to maternal hypothyroidism or to maternal hypothyroxinemia? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85(11):3975–3987
Morreale de Escobar G, Obregon MJ, Escobar del Rey F (2004) Role of thyroid hormone during early brain development. Eur J Endocrinol 151(Suppl 3):U25–U37
Pop VJ, Brouwers EP, Vader HL, Vulsma T, van Baar AL, de Vijlder JJ (2003) Maternal hypothyroxinaemia during early pregnancy and subsequent child development: a 3-year follow-up study. Clin Endocrinol 59(3):282–288
Kibirige MS, Hutchison S, Owen CJ, Delves HT (2004) Prevalence of maternal dietary iodine insufficiency in the north east of England: implications for the fetus. Arch Dis Child 89(5):F436–F439
Collingridge GL, Peineau S, Howland JG, Wang YT (2010) Long-term depression in the CNS. Nat Rev 11(7):459–473
Sui L, Gilbert ME (2003) Pre- and postnatal propylthiouracil-induced hypothyroidism impairs synaptic transmission and plasticity in area CA1 of the neonatal rat hippocampus. Endocrinology 144(9):4195–4203
Vara H, Munoz-Cuevas J, Colino A (2003) Age-dependent alterations of long-term synaptic plasticity in thyroid-deficient rats. Hippocampus 13(7):816–825
Nicholls RE, Alarcon JM, Malleret G, Carroll RC, Grody M, Vronskaya S, Kandel ER (2008) Transgenic mice lacking NMDAR-dependent LTD exhibit deficits in behavioral flexibility. Neuron 58(1):104–117
Kazuhisa I, Akemi H, Kunio K (2007) Induction of synaptic depression by high-frequency stimulation in area CA1 of the rat hippocampus: modeling and experimental studies. Neurocomputing 70(10–12):2055–2059
Santos SD, Carvalho AL, Caldeira MV, Duarte CB (2009) Regulation of AMPA receptors and synaptic plasticity. Neuroscience 158(1):105–125
Lee HK, Takamiya K, Han JS, Man H, Kim CH, Rumbaugh G, Yu S, Ding L, He C, Petralia RS, Wenthold RJ, Gallagher M, Huganir RL (2003) Phosphorylation of the AMPA receptor GluR1 subunit is required for synaptic plasticity and retention of spatial memory. Cell 112(5):631–643
Nicoll RA, Tomita S, Bredt DS (2006) Auxiliary subunits assist AMPA-type glutamate receptors. Science 311(5765):1253–1256
Ogasawara H, Doi T, Kawato M (2008) Systems biology perspectives on cerebellar long-term depression. Neuro-Signals 16(4):300–317
Greger IH, Ziff EB, Penn AC (2007) Molecular determinants of AMPA receptor subunit assembly. Trends Neurosci 30(8):407–416
Wenthold RJ, Petralia RS, Blahos J II, Niedzielski AS (1996) Evidence for multiple AMPA receptor complexes in hippocampal CA1/CA2 neurons. J Neurosci 16(6):1982–1989
Lee HK, Takamiya K, He K, Song L, Huganir RL (2010) Specific roles of AMPA receptor subunit GluR1 (GluA1) phosphorylation sites in regulating synaptic plasticity in the CA1 region of hippocampus. J Neurophysiol 103(1):479–489
Lee HK, Barbarosie M, Kameyama K, Bear MF, Huganir RL (2000) Regulation of distinct AMPA receptor phosphorylation sites during bidirectional synaptic plasticity. Nature 405(6789):955–959
Meng Y, Zhang Y, Jia Z (2003) Synaptic transmission and plasticity in the absence of AMPA glutamate receptor GluR2 and GluR3. Neuron 39(1):163–176
Hu XD, Huang Q, Yang X, Xia H (2007) Differential regulation of AMPA receptor trafficking by neurabin-targeted synaptic protein phosphatase-1 in synaptic transmission and long-term depression in hippocampus. J Neurosci 27(17):4674–4686
Jouvenceau A, Hedou G, Potier B, Kollen M, Dutar P, Mansuy IM (2006) Partial inhibition of PP1 alters bidirectional synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci 24(2):564–572
Kemp N, Bashir ZI (2001) Long-term depression: a cascade of induction and expression mechanisms. Prog Neurobiol 65(4):339–365
Kikuchi S, Fujimoto K, Kitagawa N, Fuchikawa T, Abe M, Oka K, Takei K, Tomita M (2003) Kinetic simulation of signal transduction system in hippocampal long-term potentiation with dynamic modeling of protein phosphatase 2A. Neural Netw 16(9):1389–1398
Bear MF, Abraham WC (1996) Long-term depression in hippocampus. Annu Rev Neurosci 19:437–462
Morishita W, Connor JH, Xia H, Quinlan EM, Shenolikar S, Malenka RC (2001) Regulation of synaptic strength by protein phosphatase 1. Neuron 32(6):1133–1148
Liu Y, Zhang L, Li J, Shan Z, Teng W (2013) Maternal marginal iodine deficiency affects the expression of relative proteins during brain development in rat offspring. J Endocrinol 217(1):21–29
Gong J, Dong J, Wang Y, Xu H, Wei W, Zhong J, Liu W, Xi Q, Chen J (2010) Developmental iodine deficiency and hypothyroidism impair neural development, up-regulate caveolin-1 and down-regulate synaptophysin in rat hippocampus. J Neuroendocrinol 22(2):129–139
Reeves PG, Nielsen FH, Fahey GC Jr (1993) AIN-93 purified diets for laboratory rodents: final report of the American Institute of Nutrition ad hoc writing committee on the reformulation of the AIN-76A rodent diet. J Nutr 123(11):1939–1951
Newton IG, Forbes ME, Legault C, Johnson JE, Brunso-Bechtold JK, Riddle DR (2005) Caloric restriction does not reverse aging-related changes in hippocampal BDNF. Neurobiol Aging 26(5):683–688
Wang Y, Wang Y, Dong J, Wei W, Song B, Min H, Teng W, Chen J (2013) Developmental Hypothyroxinemia and hypothyroidism limit dendritic growth of cerebellar Purkinje cells in rat offspring: involvement of MAP2 and stathmin. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. doi:10.1111/nan.12074
Mayer ML (2005) Glutamate receptor ion channels. Curr Opin Neurobiol 15(3):282–288
Hu XD, Huang Q, Roadcap DW, Shenolikar SS, Xia H (2006) Actin-associated neurabin-protein phosphatase-1 complex regulates hippocampal plasticity. J Neurochem 98(6):1841–1851
Skeaff SA (2011) Iodine deficiency in pregnancy: the effect on neurodevelopment in the child. Nutrients 3(2):265–273
Pedraza PE, Obregon MJ, Escobar-Morreale HF, del Rey FE, de Escobar GM (2006) Mechanisms of adaptation to iodine deficiency in rats: thyroid status is tissue specific. Its relevance for man. Endocrinology 147(5):2098–2108
Vermiglio F, Lo Presti VP, Moleti M, Sidoti M, Tortorella G, Scaffidi G, Castagna MG, Mattina F, Violi MA, Crisa A, Artemisia A, Trimarchi F (2004) Attention deficit and hyperactivity disorders in the offspring of mothers exposed to mild-moderate iodine deficiency: a possible novel iodine deficiency disorder in developed countries. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(12):6054–6060
Zimmermann MB, Jooste PL, Pandav CS (2008) Iodine-deficiency disorders. Lancet 372(9645):1251–1262
Hasegawa M, Kida I, Wada H (2010) A volumetric analysis of the brain and hippocampus of rats rendered perinatal hypothyroid. Neurosci Lett 479(3):240–244
Wada H, Yumoto S, Iso H (2013) Irreversible damage to auditory system functions caused by perinatal hypothyroidism in rats. Neurotoxicol Teratol 37:18–22
Shin MS, Ko IG, Kim SE, Kim BK, Kim TS, Lee SH, Hwang DS, Kim CJ, Park JK, Lim BV (2013) Treadmill exercise ameliorates symptoms of methimazole-induced hypothyroidism through enhancing neurogenesis and suppressing apoptosis in the hippocampus of rat pups. Int J Dev Neurosci 31(3):214–223
Martin SJ, Grimwood PD, Morris RG (2000) Synaptic plasticity and memory: an evaluation of the hypothesis. Annu Rev Neurosci 23:649–711
Zimmermann MB (2009) Iodine deficiency in pregnancy and the effects of maternal iodine supplementation on the offspring: a review. Am J Clin Nutr 89(2):668S–672S
Cooper LN, Bear MF (2012) The BCM theory of synapse modification at 30: interaction of theory with experiment. Nat Rev 13(11):798–810
Alzoubi KH, Aleisa AM, Alkadhi KA (2008) The sliding threshold of modification hypothesis: application to the effect of hypothyroidism or chronic psychosocial stress and nicotine on synaptic plasticity. Neurosci Lett 430(3):203–206
Song I, Huganir RL (2002) Regulation of AMPA receptors during synaptic plasticity. Trends Neurosci 25(11):578–588
Alzoubi KH, Aleisa AM, Alkadhi KA (2007) Adult-onset hypothyroidism facilitates and enhances LTD: reversal by chronic nicotine treatment. Neurobiol Dis 26(1):264–272
Barria A, Muller D, Derkach V, Griffith LC, Soderling TR (1997) Regulatory phosphorylation of AMPA-type glutamate receptors by CaM-KII during long-term potentiation. Science 276(5321):2042–2045
Kameyama K, Lee HK, Bear MF, Huganir RL (1998) Involvement of a postsynaptic protein kinase A substrate in the expression of homosynaptic long-term depression. Neuron 21(5):1163–1175
Luthi A, Chittajallu R, Duprat F, Palmer MJ, Benke TA, Kidd FL, Henley JM, Isaac JT, Collingridge GL (1999) Hippocampal LTD expression involves a pool of AMPARs regulated by the NSF-GluR2 interaction. Neuron 24(2):389–399
Daw MI, Chittajallu R, Bortolotto ZA, Dev KK, Duprat F, Henley JM, Collingridge GL, Isaac JT (2000) PDZ proteins interacting with C-terminal GluR2/3 are involved in a PKC-dependent regulation of AMPA receptors at hippocampal synapses. Neuron 28(3):873–886
Biou V, Bhattacharyya S, Malenka RC (2008) Endocytosis and recycling of AMPA receptors lacking GluR2/3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(3):1038–1043
VanLeeuwen JE, Petzinger GM, Walsh JP, Akopian GK, Vuckovic M, Jakowec MW (2010) Altered AMPA receptor expression with treadmill exercise in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-lesioned mouse model of basal ganglia injury. J Neurosci Res 88(3):650–668
Mulkey RM, Herron CE, Malenka RC (1993) An essential role for protein phosphatases in hippocampal long-term depression. Science 261(5124):1051–1055
Ehlers MD (2000) Reinsertion or degradation of AMPA receptors determined by activity-dependent endocytic sorting. Neuron 28(2):511–525
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation Committee of China (grant numbers: 30800896, 81102126) and the Program for Liaoning Excellent Talents in University (grant number: LJQ2012070)
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Wei, W., Song, B. et al. Developmental Hypothyroxinemia Caused by Mild Iodine Deficiency Leads to HFS-Induced LTD in Rat Hippocampal CA1 Region: Involvement of AMPA Receptor. Mol Neurobiol 50, 348–357 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8656-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8656-2