Abstract
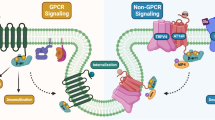
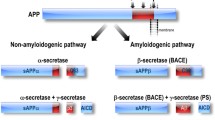
β-arrestins represent a small family of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) regulators, which provide modulating effects by facilitating desensitization and internalization of GPCRs as well as initiating their own signalings. Recent reports have demonstrated that β-arrestins levels were correlated with amyloid-β peptide (Aβ) pathology in brains of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patients and animal models. β-arrestins could enhance the activity of γ-secretase via interacting with anterior pharynx defective 1 subunit, which increased Aβ production and contributed to the pathogenesis of AD. In addition, Aβ-induced internalization of β2-adrenergic receptor internalization and loss of dendritic spine in neurons were proven to be mediated by β-arrestins, further establishing their pathogenic role in AD. More importantly, deletion of β-arrestins markedly attenuated AD pathology, without causing any gross abnormality. Here, we review the evidence about the roles of β-arrestins in the progression of AD. In addition, the established and postulated mechanisms by which β-arrestins mediated in AD pathogenesis are also discussed. Based on the role of β-arrestins in AD pathogenesis, genetically or pharmacologically targeting β-arrestins might provide new opportunities for AD treatment.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hardy J, Selkoe DJ (2002) The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 297(5580):353–356. doi:10.1126/science.1072994
Thathiah A, De Strooper B (2011) The role of G protein-coupled receptors in the pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 12(2):73–87. doi:10.1038/nrn2977
Yu NN, Wang XX, Yu JT, Wang ND, Lu RC, Miao D, Tian Y, Tan L (2010) Blocking beta2-adrenergic receptor attenuates acute stress-induced amyloid beta peptides production. Brain Res 1317:305–310. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2009.12.087
Yu JT, Tan L, Ou JR, Zhu JX, Liu K, Song JH, Sun YP (2008) Polymorphisms at the beta2-adrenergic receptor gene influence Alzheimer’s disease susceptibility. Brain Res 1210:216–222. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2008.03.019
Yu JT, Wang ND, Ma T, Jiang H, Guan J, Tan L (2011) Roles of beta-adrenergic receptors in Alzheimer’s disease: implications for novel therapeutics. Brain Res Bull 84(2):111–117. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2010.11.004
Liu X, Zhao X, Zeng X, Bossers K, Swaab DF, Zhao J, Pei G (2013) beta-Arrestin1 regulates gamma-secretase complex assembly and modulates amyloid-beta pathology. Cell Res 23(3):351–365. doi:10.1038/cr.2012.167
Thathiah A, Horre K, Snellinx A, Vandewyer E, Huang Y, Ciesielska M, De Kloe G, Munck S, De Strooper B (2013) beta-arrestin 2 regulates Abeta generation and gamma-secretase activity in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Med 19(1):43–49. doi:10.1038/nm.3023
Wolfe MS (2013) Alzheimer’s gamma-secretase under arrestin. Nat Med 19(1):22–24. doi:10.1038/nm.3053
Wood H (2013) Alzheimer disease: Arrestin’ Alzheimer disease progression? beta-arrestin 2 is a potential therapeutic target. Nat Rev Neuro 9(2):60. doi:10.1038/nrneurol.2012.278
Lagerstrom MC, Schioth HB (2008) Structural diversity of G protein-coupled receptors and significance for drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7(4):339–357. doi:10.1038/nrd2518
DeWire SM, Ahn S, Lefkowitz RJ, Shenoy SK (2007) Beta-arrestins and cell signaling. Annu Rev Physiol 69:483–510. doi:10.1146/annurev.ph.69.013107.100021
Shenoy SK, Lefkowitz RJ (2011) beta-Arrestin-mediated receptor trafficking and signal transduction. Trends Pharmacol Sci 32(9):521–533. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2011.05.002
Shukla AK, Xiao K, Lefkowitz RJ (2011) Emerging paradigms of beta-arrestin-dependent seven transmembrane receptor signaling. Trends Biochem Sci 36(9):457–469. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2011.06.003
Reiter E, Ahn S, Shukla AK, Lefkowitz RJ (2012) Molecular mechanism of beta-arrestin-biased agonism at seven-transmembrane receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 52:179–197. doi:10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.010909.105800
Gurevich EV, Benovic JL, Gurevich VV (2002) Arrestin2 and arrestin3 are differentially expressed in the rat brain during postnatal development. Neuroscience 109(3):421–436
Bossers K, Wirz KT, Meerhoff GF, Essing AH, van Dongen JW, Houba P, Kruse CG, Verhaagen J, Swaab DF (2010) Concerted changes in transcripts in the prefrontal cortex precede neuropathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain : J Neurol 133(Pt 12):3699–3723. doi:10.1093/brain/awq258
Liu Y, Liu F, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Gong CX (2011) Deficient brain insulin signalling pathway in Alzheimer’s disease and diabetes. J Pathol 225(1):54–62. doi:10.1002/path.2912
De Strooper B (2003) Aph-1, Pen-2, and Nicastrin with Presenilin generate an active gamma-Secretase complex. Neuron 38(1):9–12
Flight MH (2009) Orphan receptor coupled to Abeta production. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8(4):276. doi:10.1038/nrd2858
Ni Y, Zhao X, Bao G, Zou L, Teng L, Wang Z, Song M, Xiong J, Bai Y, Pei G (2006) Activation of beta2-adrenergic receptor stimulates gamma-secretase activity and accelerates amyloid plaque formation. Nat Med 12(12):1390–1396. doi:10.1038/nm1485
Teng L, Zhao J, Wang F, Ma L, Pei G (2010) A GPCR/secretase complex regulates beta- and gamma-secretase specificity for Abeta production and contributes to AD pathogenesis. Cell Res 20(2):138–153. doi:10.1038/cr.2010.3
Wang D, Yuen EY, Zhou Y, Yan Z, Xiang YK (2011) Amyloid beta peptide-(1–42) induces internalization and degradation of beta2 adrenergic receptors in prefrontal cortical neurons. J Biol Chem 286(36):31852–31863. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.244335
Pontrello CG, Sun MY, Lin A, Fiacco TA, DeFea KA, Ethell IM (2012) Cofilin under control of beta-arrestin-2 in NMDA-dependent dendritic spine plasticity, long-term depression (LTD), and learning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(7):E442–451. doi:10.1073/pnas.1118803109
Oakley RH, Laporte SA, Holt JA, Caron MG, Barak LS (2000) Differential affinities of visual arrestin, beta arrestin1, and beta arrestin2 for G protein-coupled receptors delineate two major classes of receptors. J Biol Chem 275(22):17201–17210. doi:10.1074/jbc.M910348199
Jiang T, Yu JT, Tan L (2012) Novel disease-modifying therapies for Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheim Dis : JAD 31(3):475–492. doi:10.3233/JAD-2012-120640
Wang D, Fu Q, Zhou Y, Xu B, Shi Q, Igwe B, Matt L, Hell JW, Wisely EV, Oddo S, Xiang YK (2013) beta2 Adrenergic Receptor, Protein Kinase A (PKA) and c-Jun N-terminal Kinase (JNK) Signaling Pathways Mediate Tau Pathology in Alzheimer Disease Models. J Biol Chem 288(15):10298–10307. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.415141
Cameron B, Landreth GE (2010) Inflammation, microglia, and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 37(3):503–509. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2009.10.006
Walker JK, Fong AM, Lawson BL, Savov JD, Patel DD, Schwartz DA, Lefkowitz RJ (2003) Beta-arrestin-2 regulates the development of allergic asthma. J Clin Invest 112(4):566–574. doi:10.1172/JCI17265
Hollingsworth JW, Theriot BS, Li Z, Lawson BL, Sunday M, Schwartz DA, Walker JK (2010) Both hematopoietic-derived and non-hematopoietic-derived {beta}-arrestin-2 regulates murine allergic airway disease. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 43(3):269–275. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2009-0198OC
Rafei M, Berchiche YA, Birman E, Boivin MN, Young YK, Wu JH, Heveker N, Galipeau J (2009) An engineered GM-CSF-CCL2 fusokine is a potent inhibitor of CCR2-driven inflammation as demonstrated in a murine model of inflammatory arthritis. J Immunol 183(3):1759–1766. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0900523
Zhuang LN, Hu WX, Xin SM, Zhao J, Pei G (2011) Beta-arrestin-1 protein represses adipogenesis and inflammatory responses through its interaction with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARgamma). J Biol Chem 286(32):28403–28413. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.256099
Vroon A, Lombardi MS, Kavelaars A, Heijnen CJ (2003) Changes in the G-protein-coupled receptor desensitization machinery during relapsing-progressive experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol 137(1–2):79–86
Tsutsui S, Vergote D, Shariat N, Warren K, Ferguson SS, Power C (2008) Glucocorticoids regulate innate immunity in a model of multiple sclerosis: reciprocal interactions between the A1 adenosine receptor and beta-arrestin-1 in monocytoid cells. FASEB J : Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 22(3):786–796. doi:10.1096/fj.07-9002com
Kohno H, Sakai T, Saito S, Okano K, Kitahara K (2007) Treatment of experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis with atorvastatin and lovastatin. Exp Eye Res 84(3):569–576. doi:10.1016/j.exer.2006.11.011
Selkoe DJ (2011) Resolving controversies on the path to Alzheimer’s therapeutics. Nat Med 17(9):1060–1065. doi:10.1038/nm.2460
Pamren A, Wanngren J, Tjernberg LO, Winblad B, Bhat R, Naslund J, Karlstrom H (2011) Mutations in nicastrin protein differentially affect amyloid beta-peptide production and Notch protein processing. J Biol Chem 286(36):31153–31158. doi:10.1074/jbc.C111.235267
De Strooper B, Annaert W, Cupers P, Saftig P, Craessaerts K, Mumm JS, Schroeter EH, Schrijvers V, Wolfe MS, Ray WJ, Goate A, Kopan R (1999) A presenilin-1-dependent gamma-secretase-like protease mediates release of Notch intracellular domain. Nature 398(6727):518–522. doi:10.1038/19083
Milano J, McKay J, Dagenais C, Foster-Brown L, Pognan F, Gadient R, Jacobs RT, Zacco A, Greenberg B, Ciaccio PJ (2004) Modulation of notch processing by gamma-secretase inhibitors causes intestinal goblet cell metaplasia and induction of genes known to specify gut secretory lineage differentiation. Toxicol Sci : Off J Soc Toxicol 82(1):341–358. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfh254
Wong GT, Manfra D, Poulet FM, Zhang Q, Josien H, Bara T, Engstrom L, Pinzon-Ortiz M, Fine JS, Lee HJ, Zhang L, Higgins GA, Parker EM (2004) Chronic treatment with the gamma-secretase inhibitor LY-411,575 inhibits beta-amyloid peptide production and alters lymphopoiesis and intestinal cell differentiation. J Biol Chem 279(13):12876–12882. doi:10.1074/jbc.M311652200
Wolfe MS (2012) gamma-Secretase as a target for Alzheimer’s disease. Adv Pharmacol 64:127–153. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-394816-8.00004-0
Bittner T, Fuhrmann M, Burgold S, Jung CK, Volbracht C, Steiner H, Mitteregger G, Kretzschmar HA, Haass C, Herms J (2009) Gamma-secretase inhibition reduces spine density in vivo via an amyloid precursor protein-dependent pathway. J Neurosci : Off J Soc Neurosci 29(33):10405–10409. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2288-09.2009
Dewachter I, Reverse D, Caluwaerts N, Ris L, Kuiperi C, Van den Haute C, Spittaels K, Umans L, Serneels L, Thiry E, Moechars D, Mercken M, Godaux E, Van Leuven F (2002) Neuronal deficiency of presenilin 1 inhibits amyloid plaque formation and corrects hippocampal long-term potentiation but not a cognitive defect of amyloid precursor protein [V717I] transgenic mice. J Neurosci : Off J Soc Neurosci 22(9):3445–3453
Saura CA, Chen G, Malkani S, Choi SY, Takahashi RH, Zhang D, Gouras GK, Kirkwood A, Morris RG, Shen J (2005) Conditional inactivation of presenilin 1 prevents amyloid accumulation and temporarily rescues contextual and spatial working memory impairments in amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice. J Neurosci : Off JX Soc Neurosci 25(29):6755–6764. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1247-05.2005
Mitani Y, Yarimizu J, Saita K, Uchino H, Akashiba H, Shitaka Y, Ni K, Matsuoka N (2012) Differential effects between gamma-secretase inhibitors and modulators on cognitive function in amyloid precursor protein-transgenic and nontransgenic mice. J Neurosci : Off J Soc Neurosci 32(6):2037–2050. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4264-11.2012
Whalen EJ, Rajagopal S, Lefkowitz RJ (2011) Therapeutic potential of beta-arrestin- and G protein-biased agonists. Trends Mol Med 17(3):126–139. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2010.11.004
Gurevich EV, Benovic JL, Gurevich VV (2004) Arrestin2 expression selectively increases during neural differentiation. J Neurochem 91(6):1404–1416. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02830.x
Li Y, Li H, Liu X, Bao G, Tao Y, Wu Z, Xia P, Wu C, Li B, Ma L (2009) Regulation of amygdalar PKA by beta-arrestin-2/phosphodiesterase-4 complex is critical for fear conditioning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(51):21918–21923. doi:10.1073/pnas.0906941106
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81000544, 81171209), the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China (ZR2010HQ004, ZR2011HZ001), and the Shandong Provincial Outstanding Medical Academic Professional Program.
Conflicts of interest
We declare that we have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, T., Yu, JT., Tan, MS. et al. β-Arrestins as Potential Therapeutic Targets for Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol Neurobiol 48, 812–818 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8469-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8469-8