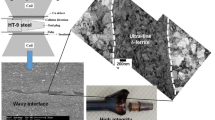
Abstract
Electromagnetic welding uses environment-friendly, unconventional non-contacting magnetic pulse force for joining of two metals. The present paper focuses on the welding of tubular mild steel to two different steel bars, ferrite-pearlite 1018 carbon steel and austenite 304 stainless steel using a 40 kJ electromagnetic instrument. A qualitative metallurgical bonding was obtained for a selected set of optimum process parameters. The bonded region did not show localized melting for a mild steel–carbon steel joint and was found to be homogeneous liquid state bonding for a mild steel–stainless steel joint within a restricted distance of \(3~\upmu \hbox {m}\) from the interface. Both the joints indicated good peel strength and leak tightness. Simulation studies were validated using experimental parameters such as voltage, current, impact velocity, magnetic flux and displacement.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shanthala K and Sreenivasa T N 2016 Front. Mech. Eng. 11 363
Kapil A and Sharma A 2015 J. Cleaner Prod. 100 35
Shanthala K, Sreenivasa T N, Choudhury H, Dond S and Sharma A 2018 J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 32 1725
Shribman V 2008 Magnetic pulse welding for dissimilar and similar materials, 3rd International conference on high speed forming – 2008 (ICHSF 2008) in Dortmund
Marya M and Marya S 2004 Sci. Technol. Weld. Joining 9 541
Aizawa T, Kashani M and Okagawa K 2007 Weld. Joint 86 119
Kore S D, Imbert J, Worswick M J and Zhou Y 2009 Sci. Technol. Weld. Joining 14 549
Marya M, Marya S and Priem D 2005 Weld. World 49 74
Stern A and Aizenshtein M 2002 Sci. Technol. Weld. Joining 7 339
Ghosh P, Patra S, Chattterjee S and Shome M 2018 J. Mater. Process. Technol. 254 25
Kacar R and Acarer M 2003 Mater. Sci. Eng. A 363 290
Kacar R and Acarer M 2004 J. Mater. Process. Technol. 152 91
Ehsan Z and Liaghat G 2012 J. Mater. Sci. 47 685
Kumar S, Kulkarni M R, Saroj P C, Mittal K C and Gantayet L M 2013 Metallurgical and mechanical testing of electromagnetically welded copper and iron sample Asia Pacific conference on non-distructive testing (14th APCNDT) Mumbai, India, November 18–22 (APCNDT 2013)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the authorities of APPD, Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC), for giving permission to conduct the experiment. The authors also acknowledge the support extended while conducting the experiments by the EMM team of PPSS, APPD at BARC, Mumbai.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shanthala, K., Sreenivasa, T.N., Murthy, H.N.N. et al. Joining of tubular steel–steel by unconventional magnetic pulse force: environmentally friendly technology. Bull Mater Sci 42, 260 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-019-1947-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-019-1947-5