Abstract
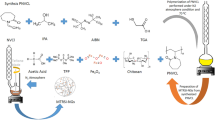
In this study, the process of manufacturing nanohydrogels containing papain and how to release it was investigated. Chitosan nanohydrogels and chitosan–polyethylene glycol hybrid nanohydrogels were used to entrapment of papain as a protein model. In order to evaluate and confirm different properties of nanohydrogels such as size, shape, the rate of swelling and flexibility, different methods was used. The maximum amount of papain entrapment was observed in 0.75% concentration of chitosan and 1% concentration of sodium Tripolyphosphate (TPP) as linker. The results of scanning electron microscope (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns showed that nanohydrogels containing papain on a nano scale are very porous and swollen. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) thermograms analysis showed that nanohydrogels have relatively good water absorption capacity. Also, by adding polyethylene glycol to chitosan, the melting temperature of hybrid nanohydrogels decreased and this can be a reason for the formation of flexible structures in these nanohydrogels. In chitosan nanohydrogels, the highest release rate of papain was observed at pH lower than 7 and high temperatures, but by adding polyethylene glycol to the chitosan, in addition to increasing papain release, a proper and continuous release of papain was observed at temperature and pH close to physiological conditions, especially at low ratios of polyethylene glycol. According to the present results, hybrid nanohydrogels can have a good potential in protein delivery systems in terms of structure and release.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anwar, M., Muhammad, F., & Akhtar, B. (2021). Biodegradable nanoparticles as drug delivery devices. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 64, 102638.
Asghari, F., Samiei, M., Adibkia, K., Akbarzadeh, A., & Davaran, S. (2017). Biodegradable and biocompatible polymers for tissue engineering application: A review. Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology, 45, 185–192.
Azadi, A., Hamidi, M., & Rouini, M.-R. (2013). Methotrexate-loaded chitosan nanogels as ‘Trojan Horses’ for drug delivery to brain: Preparation and in vitro/in vivo characterization. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 62, 523–530.
Yousefpour, P., Atyabi, F., Dinarvand, R., & Vasheghani-Farahani, E. (2011). Preparation and comparison of chitosan nanoparticles with different degrees of glutathione thiolation. Daru, 19, 367.
Zhao, D., Yu, S., Sun, B., Gao, S., Guo, S., & Zhao, K. (2018). Biomedical applications of chitosan and its derivative nanoparticles. Polymers, 10, 462.
Yang, H., Zhang, Y., Zhou, F., Guo, J., Tang, J., Han, Y., Li, Z., & Fu, C. (2020). Preparation, bioactivities and applications in food industry of chitosan-based maillard products: A review. Molecules, 26, 166.
Dalwadi, C., & Patel, G. (2015). Application of nanohydrogels in drug delivery systems: Recent patents review. Recent Patents on Nanotechnology, 9, 17–25.
Khoee, S., & Kardani, M. (2013). Hydrogels as controlled drug delivery carriers. Polymerization Quarterly, 2, 16–27.
Bruno, B. J., Miller, G. D., & Lim, C. S. (2013). Basics and recent advances in peptide and protein drug delivery. Therapeutic Delivery, 4, 1443–1467.
Verma, S., Goand, U. K., Husain, A., Katekar, R. A., Garg, R., & Gayen, J. R. (2021). Challenges of peptide and protein drug delivery by oral route: Current strategies to improve the bioavailability. Drug Development Research, 82, 927–944.
Bickel, U., Yoshikawa, T., & Pardridge, W. M. (2001). Delivery of peptides and proteins through the blood–brain barrier. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 46, 247–279.
Soni, G., & Yadav, K. S. (2016). Nanogels as potential nanomedicine carrier for treatment of cancer: A mini review of the state of the art. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal, 24, 133–139.
Hendrickson, G. R., & Lyon, L. A. (2010). Microgel translocation through pores under confinement. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 49, 2193–2197.
Zhao, L., Zhu, L., Liu, F., Liu, C., Wang, Q., Zhang, C., Li, J., Liu, J., Qu, X., & Yang, Z. (2011). pH triggered injectable amphiphilic hydrogel containing doxorubicin and paclitaxel. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 410, 83–91.
Lee, S., Tong, X., & Yang, F. (2016). Effects of the poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogel crosslinking mechanism on protein release. Biomaterials Science, 4, 405–411.
Kamaci, M., & Kaya, I. (2023). Chitosan based hybrid hydrogels for drug delivery: Preparation, biodegradation, thermal, and mechanical properties. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 34, 779–788.
Chu, Y., Song, R., Zhang, L., Dai, H., & Wu, W. (2020). Water-dispersible, biocompatible and fluorescent poly(ethylene glycol)-grafted cellulose nanocrystals. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 153, 46–54.
Pereira, M. P., de Gomes, M. G., Izoton, J. C., Nakama, K. A., Dos Santos, R. B., Savall, A. S. P., Ramalho, J. B., Roman, S. S., Luchese, C., & Cibin, F. W. (2019). Cationic and anionic unloaded polymeric nanocapsules: Toxicological evaluation in rats shows low toxicity. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy, 116, 109014.
Wang, X., Song, R., Johnson, M., Shen, P., Zhang, N., Lara-Sáez, I., Xu, Q., & Wang, W. (2023). Chitosan-based hydrogels for infected wound treatment. Macromolecular Bioscience, 23(9), e2300094.
Channamade, C., Raju, J. M., Vijayaprakash, S. B., Bora, R., & Shekhar, N. R. (2021). Promise approach on chemical stability enhancement of papain by encapsulation system: A review. Journal of Young Pharmacists, 13, 87.
Mamboya, E. A. F., & Amri, E. (2012). Papain, a plant enzyme of biological importance: A review. American Journal of Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 8, 99–104.
Moreira Filho, R. N. F., Vasconcelos, N. F., Andrade, F. K., de Freitas Rosa, M., & Vieira, R. S. (2020). Papain immobilized on alginate membrane for wound dressing application. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 194, 111222.
Trickett, P. (1964). Proteolytic enzymes in treatment of athletic injuries. Applied Therapeutics, 6, 647–652.
Abd Elgadir, M., Uddin, M. S., Ferdosh, S., Adam, A., Chowdhury, A. J. K., & Sarker, M. Z. I. (2015). Impact of chitosan composites and chitosan nanoparticle composites on various drug delivery systems: A review. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis, 23, 619–629.
Ningrum, D. R., Kosasih, W., & Priatni, S. (2018). The comparative study of papain enzyme from papaya fruits California variant and Indonesian local variant. Jurnal Kimia Terapan Indonesia, 19, 42–48.
Mitchel, R. E., Chaiken, I. M., & Smith, E. L. (1970). The complete amino acid sequence of papain: Additions and corrections. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 245, 3485–3492.
Shukla, S. K., Mishra, A. K., Arotiba, O. A., & Mamba, B. B. (2013). Chitosan-based nanomaterials: A state-of-the-art review. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 59, 46–58.
Ailincai, D., Morariu, S., Rosca, I., Sandu, A. I., & Marin, L. (2023). Drug delivery based on a supramolecular chemistry approach by using chitosan hydrogels. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 248, 125800.
Taokaew, S., Kaewkong, W., & Kriangkrai, W. (2023). Recent development of functional chitosan-based hydrogels for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Gels, 9, 277.
Gan, Q., & Wang, T. (2007). Chitosan nanoparticle as protein delivery carrier—Systematic examination of fabrication conditions for efficient loading and release. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 59, 24–34.
Gonçalves, A. C. R., Duarte, L. G., Fiocco, A. C. T., Alencar, W. M., Iacuzio, R., Silva, N. C., & Picone, C. S. (2023). Improving chitosan properties through ionic and chemical cross-linking and their impact on emulsified systems. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 58, 4324–4331.
Lusiana, R. A., Protoningtyas, W. P., Wijaya, A. R., Siswanta, D., & Santosa, S. J. (2017). Chitosan-tripoly phosphate (CS-TPP) synthesis through cross-linking process: The effect of concentration towards membrane mechanical characteristic and urea permeation. Oriental Journal of Chemistry, 33, 2913–2919.
Bozoğlan, B. K., Duman, O., & Tunç, S. (2020). Preparation and characterization of thermosensitive chitosan/carboxymethylcellulose/scleroglucan nanocomposite hydrogels. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 162, 781–797.
Mi, F. L., Shyu, S. S., Lee, S. T., & Wong, T. B. (1999). Kinetic study of chitosan-tripolyphosphate complex reaction and acid-resistive properties of the chitosan-tripolyphosphate gel beads prepared by in-liquid curing method. Journal of Polymer Science Part B: Polymer Physics, 37, 1551–1564.
Tang, Y.-F., Du, Y.-M., Hu, X.-W., Shi, X.-W., & Kennedy, J. F. (2007). Rheological characterisation of a novel thermosensitive chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) blend hydrogel. Carbohydrate Polymers, 67, 491–499.
Hirakura, T., Yasugi, K., Nemoto, T., Sato, M., Shimoboji, T., Aso, Y., Morimoto, N., & Akiyoshi, K. (2010). Hybrid hyaluronan hydrogel encapsulating nanogel as a protein nanocarrier: New system for sustained delivery of protein with a chaperone-like function. Journal of Controlled Release, 142, 483–489.
Bhumkar, D. R., & Pokharkar, V. B. (2006). Studies on effect of pH on cross-linking of chitosan with sodium tripolyphosphate: A technical note. AAPS PharmSciTech, 7, E138–E143.
Vaezifar, S., Razavi, S., Golozar, M. A., Karbasi, S., Morshed, M., & Kamali, M. (2013). Effects of some parameters on particle size distribution of chitosan nanoparticles prepared by ionic gelation method. Journal of Cluster Science, 24, 891–903.
Yuan, Q., Shah, J., Hein, S., & Misra, R. (2010). Controlled and extended drug release behavior of chitosan-based nanoparticle carrier. Acta Biomaterialia, 6, 1140–1148.
Osada, Y., & Khokhlov, A. (2001). Polymer gels and networks. CRC Press.
Tarhan, T., Dik, G., Ulu, A., Tural, B., Tural, S., & Ateş, B. (2023). Newly synthesized multifunctional biopolymer coated magnetic core/shell Fe3O4@Au nanoparticles for evaluation of L-asparaginase immobilization. Topics in Catalysis, 66, 577–591.
Cho, J., Heuzey, M.-C., Bégin, A., & Carreau, P. J. (2005). Physical gelation of chitosan in the presence of β-glycerophosphate: The effect of temperature. Biomacromolecules, 6, 3267–3275.
Pourjavadi, A., Hosseinzadeh, H., & Sadeghi, M. (2007). Synthesis, characterization and swelling behavior of gelatin-g-poly(sodium acrylate)/kaolin superabsorbent hydrogel composites. Journal of Composite Materials, 41, 2057–2069.
Maleki Dizaj, S., Barzegar-Jalali, M., Zarrintan, M. H., Adibkia, K., & Lotfipour, F. (2015). Calcium carbonate nanoparticles as cancer drug delivery system. Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery, 12, 1649–1660.
Khurma, J. R., & Nand, A. V. (2008). Temperature and pH sensitive hydrogels composed of chitosan and poly(ethylene glycol). Polymer Bulletin, 59, 805–812.
Kaneko, Y., Nakamura, S., Sakai, K., Aoyagi, T., Kikuchi, A., Sakurai, Y., & Okano, T. (1998). Rapid deswelling response of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels by the formation of water release channels using poly(ethylene oxide) graft chains. Macromolecules, 31, 6099–6105.
Ghaeini-Hesaroeiye, S., Razmi Bagtash, H., Boddohi, S., Vasheghani-Farahani, E., & Jabbari, E. (2020). Thermoresponsive nanogels based on different polymeric moieties for biomedical applications. Gels, 6, 20.
Yang, Y., Feng, G., Wang, J., Zhang, R., Zhong, S., Wang, J., & Cui, X. (2023). Injectable chitosan-based self-healing supramolecular hydrogels with temperature and pH dual-responsivenesses. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 227, 1038–1047.
Ahmadian, E., Eftekhari, A., Dizaj, S. M., Sharifi, S., Mokhtarpour, M., Nasibova, A. N., Khalilov, R., & Samiei, M. (2019). The effect of hyaluronic acid hydrogels on dental pulp stem cells behavior. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 140, 245–254.
Rezaie, J., Akbari, A., Rahimkhoei, V., Lighvani, Z. M., & Jafari, H. (2021). Halloysite nanotubes/carbohydrate-based hydrogels for biomedical applications: From drug delivery to tissue engineering. Polymer Bulletin, 79, 4497–4513.
Acknowledgements
The authors express their gratitude to the research council of Azarbaijan Shahid Madani University for their supportive role during this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jafari, N., Najavand, S., Pazhang, M. et al. Entrapment of Papain in Chitosan–Polyethylene Glycol Hybrid Nanohydrogels: Presenting a Model for Protein Delivery Systems. Mol Biotechnol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-024-01129-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-024-01129-2



