Abstract
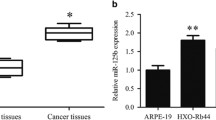
Retinoblastoma (RB) is a malignant ocular cancer that affects children. Several microRNAs (miRNAs) have been implicated in RB regulation. The present study aimed to investigate the role of miR-4529-3p in RB pathogenesis. Scratch, Transwell, and Cell Counting Kit (CCK)-8 assays were conducted to assess the migratory, invasive, and proliferative abilities of RB cells. The expression levels of miR-4529-3p, RB1, and ERK pathway-related proteins were analyzed using western blotting and real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Target relationships were verified using dual-luciferase reporter experiments. A murine RB model was developed to analyze the effects of miR-4529-3p on RB tumor growth in vivo. Our experiments revealed high levels of miR-4529-3p and low levels of RB1 in RB tissues. Functional analyses revealed that the migratory, invasive, and proliferative abilities of RB cells were repressed by miR-4529-3p inhibition. Similarly, p-ERK 1/2 protein levels were suppressed by miR-4529-3p inhibition. Furthermore, downregulation of miR-4529-3p limited tumor growth in vivo. Mechanistically, miR-4259-3p targets RB1. Interestingly, RB1 silencing abrogated the alleviative effects of miR-4529-3p downregulation in RB cells. MiR-4529-3p promotes RB progression by inhibiting RB1 and activating the ERK pathway. This evidence suggests that the miR-4529-3p/RB1 regulatory axis may be a prospective target for RB treatment in clinical settings.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
This article contains all of the data that were created or examined during this investigation.
References
Lohmann, D. (2010). Retinoblastoma. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 685, 220–227.
Rodriguez-Galindo, C., Orbach, D. B., & VanderVeen, D. (2015). Retinoblastoma. Pediatric clinics of North America, 62, 201–223.
Yun, J., Li, Y., Xu, C. T., & Pan, B. R. (2011). Epidemiology and Rb1 gene of retinoblastoma. International Journal of Ophthalmology, 4, 103–109.
Broaddus, E., Topham, A., & Singh, A. D. (2009). Incidence of retinoblastoma in the USA: 1975–2004. The British Journal of Ophthalmology, 93, 21–23.
Bowman, R. J., Mafwiri, M., Luthert, P., Luande, J., & Wood, M. (2008). Outcome of retinoblastoma in east Africa. Pediatric Blood & Cancer, 50, 160–162.
Zhang, J., He, J., & Zhang, L. (2018). The down-regulation of microRNA-137 contributes to the up-regulation of retinoblastoma cell proliferation and invasion by regulating COX-2/PGE2 signaling. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & Pharmacotherapie, 106, 35–42.
Hu, H., Zhang, W., Wang, Y., Huang, D., Shi, J., Li, B., Zhang, Y., & Zhou, Y. (2018). Characterization, treatment and prognosis of retinoblastoma with central nervous system metastasis. BMC Ophthalmology, 18, 107.
Künkele, A., Wilm, J., Holdt, M., Lohmann, D., Bornfeld, N., Eggert, A., Temming, P., & Schulte, J. H. (2015). Neoadjuvant/adjuvant treatment of high-risk retinoblastoma: A report from the German Retinoblastoma Referral Centre. The British Journal of Ophthalmology, 99, 949–953.
Al-Nawaiseh, I., Ghanem, A. Q., & Yousef, Y. A. (2017). Familial retinoblastoma: Raised awareness improves early diagnosis and outcome. Journal of Ophthalmology, 2017, 5053961.
Pan, J. H., Abernathy, B., Kim, Y. J., Lee, J. H., Kim, J. H., Shin, E. C., & Kim, J. K. (2018). Cruciferous vegetables and colorectal cancer prevention through microRNA regulation: A review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 58, 2026–2038.
Guarnieri, D. J., & DiLeone, R. J. (2008). MicroRNAs: A new class of gene regulators. Annals of Medicine, 40, 197–208.
Li, H., Fan, D., Wang, W., Zhang, X., Song, L., & Huang, Y. (2021). MiR-142-5p serves as a tumor suppressor in retinoblastoma cells by regulating MYCN. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 574, 20–26.
Liu, X. M., Li, X. F., & Li, J. C. (2021). MiR-146a functions as a potential tumor suppressor in retinoblastoma by negatively regulate neuro-oncological ventral antigen-1. The Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences, 37, 286–293.
Li, L., Yu, H., & Ren, Q. (2020). MiR-218-5p suppresses the progression of retinoblastoma through targeting NACC1 and inhibiting the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Cancer Management and Research, 12, 6959–6967.
Li, K., Han, F., Wu, Y., & Wang, X. (2021). miR-340 promotes retinoblastoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion through targeting WIF1. OncoTargets and Therapy, 14, 3635–3648.
Xu, F., Liu, G., Wang, L., Wang, X., Jin, X., & Bo, W. (2020). miR-494 promotes progression of retinoblastoma via PTEN through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Oncology Letters, 20, 1952–1960.
Pérez-Sánchez, C., Barbarroja, N., Pantaleão, L. C., López-Sánchez, L. M., Ozanne, S. E., Jurado-Gámez, B., Aranda, E., Lopez-Pedrera, C., & Rodríguez-Ariza, A. (2021). Clinical utility of microRNAs in exhaled breath condensate as biomarkers for lung cancer. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11, 111.
Farina, N. H., Ramsey, J. E., Cuke, M. E., Ahern, T. P., Shirley, D. J., Stein, J. L., Stein, G. S., Lian, J. B., & Wood, M. E. (2017). Development of a predictive miRNA signature for breast cancer risk among high-risk women. Oncotarget, 8, 112170–112183.
Castro-Magdonel, B. E., Orjuela, M., Alvarez-Suarez, D. E., Camacho, J., Cabrera-Muñoz, L., Sadowinski-Pine, S., Medina-Sanson, A., Lara-Molina, C., García-Vega, D., Vázquez, Y., Durán-Figueroa, N., Orozco-Romero, M. J., Hernández-Ángeles, A., & Ponce-Castañeda, M. V. (2020). Circulating miRNome detection analysis reveals 537 miRNAS in plasma, 625 in extracellular vesicles and a discriminant plasma signature of 19 miRNAs in children with retinoblastoma from which 14 are also detected in corresponding primary tumors. PLoS ONE, 15, e0231394.
Claudio, P. P., Tonini, T., & Giordano, A. (2002). The retinoblastoma family: Twins or distant cousins? Genome biology, 3, 3012.
Falls, H. F., & Neel, J. V. (1951). Genetics of retinoblastoma. Archives of Ophthalmology, 46, 367–389.
Pozzoli, G., Marei, H. E., Althani, A., Boninsegna, A., Casalbore, P., Marlier, L., Lanzilli, G., Zonfrillo, M., Petrucci, G., Rocca, B., Navarra, P., Sgambato, A., & Cenciarelli, C. (2019). Aspirin inhibits cancer stem cells properties and growth of glioblastoma multiforme through Rb1 pathway modulation. Journal of Cellular Physiology., 234(9), 15459–15471.
Ostovarpour, M., Khalaj-Kondori, M., & Ghasemi, T. (2021). Correlation between expression levels of lncRNA FER1L4 and RB1 in patients with colorectal cancer. Molecular Biology Reports, 48, 4581–4589.
Gordon, C. A., Gulzar, Z. G., & Brooks, J. D. (2015). NUSAP1 expression is upregulated by loss of RB1 in prostate cancer cells. The Prostate, 75, 517–526.
Liu, F., Cai, Y., Rong, X., Chen, J., Zheng, D., Chen, L., Zhang, J., Luo, R., Zhao, P., & Ruan, J. (2017). MiR-661 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis by directly inhibiting RB1 in non small cell lung cancer. Molecular Cancer, 16, 122.
Liu, C., Wang, C., Wang, J., & Huang, H. (2016). miR-1297 promotes cell proliferation by inhibiting RB1 in liver cancer. Oncology Letters, 12, 5177–5182.
Le, F., Luo, P., Yang, Q. O., & Zhong, X. M. (2017). MiR-181a promotes growth of thyroid cancer cells by targeting tumor suppressor RB1. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 21, 5638–5647.
Shao, L., Sheng, Z., Zhu, Y., Li, J., & Meng, R. (2020). Effect of miR-215 on the expression of tumor suppressor gene Rb1 in retinoblastoma cell lines. Iranian Journal of Public Health, 49, 1298–1306.
Yi, Q. Y., Bai, Z. S., Cai, B., Chen, N., Chen, L. S., Yuan, T., & Mao, J. H. (2018). HSV-TK/GCV can induce cytotoxicity of retinoblastoma cells through autophagy inhibition by activating MAPK/ERK. Oncology Reports, 40, 682–692.
Rodríguez, J., Calvo, F., González, J. M., Casar, B., Andrés, V., & Crespo, P. (2010). ERK1/2 MAP kinases promote cell cycle entry by rapid, kinase-independent disruption of retinoblastoma-lamin A complexes. The Journal of Cell Biology, 191, 967–979.
McEvoy, J. D., & Dyer, M. A. (2015). Genetic and epigenetic discoveries in human retinoblastoma. Critical Reviews in Oncogenesis, 20, 217–225.
Mendoza, P. R., & Grossniklaus, H. E. (2015). The biology of retinoblastoma. Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science, 134, 503–516.
Ramírez-Ortiz, M. A., Lansingh, V. C., Eckert, K. A., Haik, B. G., Phillips, B. X., Bosch-Canto, V., González-Pérez, G., Villavicencio-Torres, A., & Etulain-González, A. (2017). Systematic review of the current status of programs and general knowledge of diagnosis and management of retinoblastoma. Boletin medico del Hospital Infantil de Mexico, 74, 41–54.
Dimaras, H., Dimba, E. A., & Gallie, B. L. (2010). Challenging the global retinoblastoma survival disparity through a collaborative research effort. The British Journal of Ophthalmology, 94, 1415–1416.
Yang, L., Zhang, L., Lu, L., & Wang, Y. (2019). Long noncoding RNA SNHG16 sponges miR-182-5p and miR-128-3p to promote retinoblastoma cell migration and invasion by targeting LASP1. OncoTargets and Therapy, 12, 8653–8662.
Philiponnet, A., Grange, J. D., & Baggetto, L. G. (2014). Application of gene therapy to oncologic ophthalmology. Journal francais d’ophtalmologie, 37, 155–165.
Li, Y., Liang, L., & Zhang, C. Y. (2013). Isothermally sensitive detection of serum circulating miRNAs for lung cancer diagnosis. Analytical Chemistry, 85, 11174–11179.
Kawakubo-Yasukochi, T., Morioka, M., Hazekawa, M., Yasukochi, A., Nishinakagawa, T., Ono, K., Kawano, S., Nakamura, S., & Nakashima, M. (2018). miR-200c-3p spreads invasive capacity in human oral squamous cell carcinoma microenvironment. Molecular Carcinogenesis, 57, 295–302.
Liu, L., He, L., Li, W., Zhao, T., Li, G., Xiu, X., Xu, Y., Bourbonne, V., Käsmann, L., Kowalchuk, R. O., & Zhong, Q. (2021). The miR-4306/IGF2R axis modulates the lung adenocarcinoma response to irradiation in vitro and in vivo. Translational Lung Cancer Research, 10, 4494–4510.
Zhou, Q., Zeng, H., Ye, P., Shi, Y., Guo, J., & Long, X. (2018). Differential microRNA profiles between fulvestrant-resistant and tamoxifen-resistant human breast cancer cells. Anti-cancer Drugs, 29, 539–548.
Modi, S., Kubo, A., Oie, H., Coxon, A. B., Rehmatulla, A., & Kaye, F. J. (2000). Protein expression of the RB-related gene family and SV40 large T antigen in mesothelioma and lung cancer. Oncogene, 19, 4632–4639.
Lim, Z., & Quah, B. L. (2010). Unilateral retinoblastoma in an eye with Peters anomaly. Journal of AAPOS: The Official Publication of the American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus, 14, 184–186.
Kanber, D., Berulava, T., Ammerpohl, O., Mitter, D., Richter, J., Siebert, R., Horsthemke, B., Lohmann, D., & Buiting, K. (2009). The human retinoblastoma gene is imprinted. PLoS Genetics, 5, e1000790.
Wilson, P. F., Nagasawa, H., Fitzek, M. M., Little, J. B., & Bedford, J. S. (2010). G2-phase chromosomal radiosensitivity of primary fibroblasts from hereditary retinoblastoma family members and some apparently normal controls. Radiation Research, 173, 62–70.
Degirmenci, U., Wang, M., & Hu, J. (2020). Targeting aberrant RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling for cancer therapy. Cells, 9, 198.
Ma, L., Chen, Z., Erdjument-Bromage, H., Tempst, P., & Pandolfi, P. P. (2005). Phosphorylation and functional inactivation of TSC2 by Erk implications for tuberous sclerosis and cancer pathogenesis. Cell, 121, 179–193.
Pullikuth, A. K., & Catling, A. D. (2007). Scaffold mediated regulation of MAPK signaling and cytoskeletal dynamics: A perspective. Cellular Signalling, 19, 1621–1632.
Wolf, I., Rubinfeld, H., Yoon, S., Marmor, G., Hanoch, T., & Seger, R. (2017). Involvement of the activation loop of ERK in the detachment from cytosolic anchoring. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 292, 8853.
Zassadowski, F., Rochette-Egly, C., Chomienne, C., & Cassinat, B. (2012). Regulation of the transcriptional activity of nuclear receptors by the MEK/ERK1/2 pathway. Cellular Signalling, 24, 2369–2377.
Kohno, M., & Pouyssegur, J. (2006). Targeting the ERK signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Annals of Medicine, 38, 200–211.
Liu, T., Liu, Y., Bao, X., Tian, J., Liu, Y., & Yang, X. (2013). Overexpression of TROP2 predicts poor prognosis of patients with cervical cancer and promotes the proliferation and invasion of cervical cancer cells by regulating ERK signaling pathway. PLoS ONE, 8, e75864.
Ono, H., Basson, M. D., & Ito, H. (2014). PTK6 promotes cancer migration and invasion in pancreatic cancer cells dependent on ERK signaling. PLoS ONE, 9, e96060.
Randhawa, H., Kibble, K., Zeng, H., Moyer, M. P., & Reindl, K. M. (2013). Activation of ERK signaling and induction of colon cancer cell death by piperlongumine. Toxicology In Vitro : An International Journal Published in Association with BIBRA, 27, 1626–1633.
Zeng, Z., Gao, Z. L., Zhang, Z. P., Jiang, H. B., Yang, C. Q., Yang, J., & Xia, X. B. (2019). Downregulation of CKS1B restrains the proliferation, migration, invasion and angiogenesis of retinoblastoma cells through the MEK/ERK signaling pathway. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 44, 103–114.
Asl, E. R., Amini, M., Najafi, S., Mansoori, B., Mokhtarzadeh, A., Mohammadi, A., Lotfinejad, P., Bagheri, M., Shirjang, S., Lotfi, Z., Rasmi, Y., & Baradaran, B. (2021). Interplay between MAPK/ERK signaling pathway and MicroRNAs: A crucial mechanism regulating cancer cell metabolism and tumor progression. Life Sciences, 278, 119499.
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
No funding was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YG and PD executed the experiments and analyzed the results. PD developed and created this study. YG did the investigation. The data processing and interpretation were conducted by YG and PD. YG authored the paper. PD critically revised the manuscript. This article has been reviewed and approved by all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there were no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
This study was accepted by the medical ethics committee of Wuhan No.1 Hospital (Wuhan, China). The handling of the clinical tissue samples complied with the ethical precepts of the Declaration of Helsinki. An informed consent form was completed by each patient. The Institution Animal Ethics Committee at Wuhan No.1 Hospital allowed the animal experiment, which also adhered to the ARRIVE principles (Wuhan, China).
Consent to Participate
All patients signed a written informed consent.
Consent for Publication
The participants gave their consent for the study to be published.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Y., Du, P. miR-4529-3p Promotes the Progression of Retinoblastoma by Inhibiting RB1 Expression and Activating the ERK Signaling Pathway. Mol Biotechnol 66, 102–111 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-00738-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-00738-7