Abstract
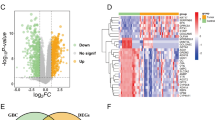
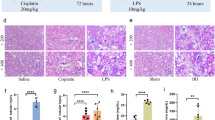
Chronic pancreatitis (CP) as a progressive inflammatory disorder, remains untreatable. The novel treatment strategy for CP is imperative. We attempted to explore the therapeutic biomarkers for CP. The single-cell sequencing data were retrieved from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in idiopathic CP were identified, followed by function and pathway annotation, and PPI network established. DEGs of interest were verified in human tissue samples. The function of candidate biomarker was determined in the murine model with CP. A total of 208 genes were specially differentially expressed in idiopathic patients. Functional enrichment analysis showed DEGs were mainly enriched in glycogen catabolic process, RNA splicing, and glucagon signaling pathway. A PPI network centered on HDAC1 was constructed. HDAC1 was overexpressed in CP patients. The murine model with CP was induced by repetitive cerulein treatment. Silencing sh-HDAC1 treatment reversed cerulein-induced inflammatory cells accumulation, high expression of TGF-β1, and collagen 1 in pancreas in vivo. HDAC1 might be served as potential biomarker for CP. The present study provided insights into the molecular mechanism of CP that may be useful in further investigations.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Weiss, F. U., Laemmerhirt, F., & Lerch, M. M. (2019). Etiology and risk factors of acute and chronic pancreatitis. Visceral Medicine, 35, 73–81.
Tirkes, T., Shah, Z. K., Takahashi, N., Grajo, J. R., Chang, S. T., Venkatesh, S. K., et al. (2019). Reporting standards for chronic pancreatitis by using CT, MRI, and MR cholangiopancreatography: The Consortium for the Study of Chronic Pancreatitis, Diabetes, and Pancreatic Cancer. Radiology, 290, 207–215.
Whitcomb, D. C. (2010). Genetic aspects of pancreatitis. Annual Review of Medicine, 61, 413–424.
Kumar, S., Ooi, C. Y., Werlin, S., Abu-El-Haija, M., Barth, B., Bellin, M. D., et al. (2016). Risk factors associated with pediatric acute recurrent and chronic pancreatitis: Lessons from INSPPIRE. JAMA Pediatrics, 170, 562–569.
Hu, C., Wen, L., Deng, L., Zhang, C., Lugea, A., Su, H.-Y., et al. (2017). The differential role of human cationic trypsinogen (PRSS1) p. R122H mutation in hereditary and nonhereditary chronic pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology Research and Practice, 2017, 9505460.
Kleeff, J., Whitcomb, D., Shimosegawa, T., Esposito, I., Lerch, M., Gress, T., et al. (2017). Chronic pancreatitis. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 3, 17060.
Habtezion, A. (2015). Inflammation in acute and chronic pancreatitis. Current Opinion in Gastroenterology, 31, 395–399.
Deng, X., Wang, L., Elm, M. S., Gabazadeh, D., Diorio, G. J., Eagon, P. K., et al. (2005). Chronic alcohol consumption accelerates fibrosis in response to cerulein-induced pancreatitis in rats. American Journal of Pathology, 166, 93–106.
Lin, Y., Chen, Y., Feng, W., Hua, R., Zhang, J., Huo, Y., et al. (2021). Neddylation pathway alleviates chronic pancreatitis by reducing HIF1α-CCL5-dependent macrophage infiltration. Cell Death and Disease, 12, 1–11.
Schmitz-Winnenthal, H., Pietsch, D. H., Schimmack, S., Bonertz, A., Udonta, F., Ge, Y., et al. (2010). Chronic pancreatitis is associated with disease-specific regulatory T-cell responses. Gastroenterology, 138, 1178–1188.
Xue, J., Sharma, V., Hsieh, M. H., Chawla, A., Murali, R., Pandol, S. J., et al. (2015). Alternatively activated macrophages promote pancreatic fibrosis in chronic pancreatitis. Nature Communications, 6, 7158.
Xue, J., Zhao, Q., Sharma, V., Nguyen, L. P., Lee, Y. N., Pham, K. L., et al. (2016). Aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands in cigarette smoke induce production of interleukin-22 to promote pancreatic fibrosis in models of chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology, 151, 1206–1217.
Bansod, S., Doijad, N., & Godugu, C. (2020). Berberine attenuates severity of chronic pancreatitis and fibrosis via AMPK-mediated inhibition of TGF-β1/Smad signaling and M2 polarization. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 403, 115162.
Glaubitz, J., Wilden, A., Golchert, J., Homuth, G., Völker, U., Bröker, B. M., et al. (2022). In mouse chronic pancreatitis CD25+FOXP3+ regulatory T cells control pancreatic fibrosis by suppression of the type 2 immune response. Nature Communications, 13, 4502.
Saad, M. I., Weng, T., Lundy, J., Gearing, L. J., West, A. C., Harpur, C. M., et al. (2022). Blockade of the protease ADAM17 ameliorates experimental pancreatitis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 119, e2213744119.
Butler, A., Hoffman, P., Smibert, P., Papalexi, E., & Satija, R. (2018). Integrating single-cell transcriptomic data across different conditions, technologies, and species. Nature Biotechnology, 36, 411–420.
Lun, A. T., McCarthy, D. J., & Marioni, J. C. (2016). A step-by-step workflow for low-level analysis of single-cell RNA-Seq data with Bioconductor. F1000Res, 5, 2122.
Tirosh, I., Izar, B., Prakadan, S. M., Wadsworth, M. H., II., Treacy, D., Trombetta, J. J., et al. (2016). Dissecting the multicellular ecosystem of metastatic melanoma by single-cell RNA-Seq. Science, 352, 189–196.
Wu, T., Hu, E., Xu, S., Chen, M., Guo, P., Dai, Z., et al. (2021). clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. The Innovation, 2, 100141.
Szklarczyk, D., Franceschini, A., Wyder, S., Forslund, K., Heller, D., Huerta-Cepas, J., et al. (2014). STRING v10: Protein–protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Research. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1003
Bhasin, D. K., Singh, G., Rana, S. S., Chowdry, S. M., Shafiq, N., Malhotra, S., et al. (2009). Clinical profile of idiopathic chronic pancreatitis in North India. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology: The Official Clinical Practice Journal of the American Gastroenterological Association, 7, 594–599.
Kim, H. (2008). Cerulein pancreatitis: Oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. Gut and Liver, 2, 74–80.
Neuschwander-Tetri, B. A., Burton, F. R., Presti, M. E., Britton, R. S., Janney, C. G., Garvin, P. R., et al. (2000). Repetitive self-limited acute pancreatitis induces pancreatic fibrogenesis in the mouse. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 45, 665–674.
McGuigan, A., Kelly, P., Turkington, R. C., Jones, C., Coleman, H. G., & McCain, R. S. (2018). Pancreatic cancer: A review of clinical diagnosis, epidemiology, treatment and outcomes. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 24, 4846–4861.
Wu, J., Mulatibieke, T., Ni, J., Han, X., Li, B., Zeng, Y., et al. (2017). Dichotomy between receptor-interacting protein 1- and receptor-interacting protein 3-mediated necroptosis in experimental pancreatitis. The American Journal of Pathology, 187, 1035–1048.
Manohar, M., Verma, A. K., Venkateshaiah, S. U., & Mishra, A. (2018). Role of eosinophils in the initiation and progression of pancreatitis pathogenesis. American Journal of Physiology Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology, 314, G211–G222.
Zheng, L., Xue, J., Jaffee, E. M., & Habtezion, A. (2013). Role of immune cells and immune-based therapies in pancreatitis and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology, 144, 1230–1240.
Lee, B., Adamska, J. Z., Namkoong, H., Bellin, M. D., Wilhelm, J., Szot, G. L., et al. (2020). Distinct immune characteristics distinguish hereditary and idiopathic chronic pancreatitis. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 130, 2705–2711.
Ye, L., Robertson, M. A., Hesselson, D., Stainier, D. Y., & Anderson, R. M. (2015). Glucagon is essential for alpha cell transdifferentiation and beta cell neogenesis. Development, 142, 1407–1417.
Yadav, S. S., & Chouhan, U. (2018). Analysis of protein–protein interaction network of laminopathy based on topological properties. Biomedical and Pharmacology Journal, 11, 1091–1103.
Shakespear, M. R., Halili, M. A., Irvine, K. M., Fairlie, D. P., & Sweet, M. J. (2011). Histone deacetylases as regulators of inflammation and immunity. Trends in Immunology, 32, 335–343.
Gonneaud, A., Gagné, J. M., Turgeon, N., & Asselin, C. (2014). The histone deacetylase Hdac1 regulates inflammatory signalling in intestinal epithelial cells. Journal of Inflammation, 11, 1–10.
Guo, C.-J., Xie, J.-J., Hong, R.-H., Pan, H.-S., Zhang, F.-G., & Liang, Y.-M. (2019). Puerarin alleviates streptozotocin (STZ)-induced osteoporosis in rats through suppressing inflammation and apoptosis via HDAC1/HDAC3 signaling. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy, 115, 108570.
Deng, X., He, Y., Miao, X., & Yu, B. (2021). ATF4-mediated histone deacetylase HDAC1 promotes the progression of acute pancreatitis. Cell Death and Disease, 12, 5.
Ouyang, C., Huang, L., Ye, X., Ren, M., & Han, Z. (2022). HDAC1 promotes myocardial fibrosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy by inhibiting BMP-7 transcription through histone deacetylation. Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology and Diabetes, 130(10), 660–670.
Lai, L., Cheng, P., Yan, M., Gu, Y., & Xue, J. (2019). Aldosterone induces renal fibrosis by promoting HDAC1 expression, deacetylating H3K9 and inhibiting klotho transcription. Molecular Medicine Reports, 19, 1803–1808.
Nural-Guvener, H. F., Zakharova, L., Nimlos, J., Popovic, S., Mastroeni, D., & Gaballa, M. A. (2014). HDAC class I inhibitor, Mocetinostat, reverses cardiac fibrosis in heart failure and diminishes CD90+ cardiac myofibroblast activation. Fibrogenesis and Tissue Repair, 7, 10.
Bombardo, M., Saponara, E., Malagola, E., Chen, R., Seleznik, G. M., Haumaitre, C., et al. (2017). Class I histone deacetylase inhibition improves pancreatitis outcome by limiting leukocyte recruitment and acinar-to-ductal metaplasia. British Journal of Pharmacology, 174, 3865–3880.
Bombardo, M., Chen, R., Malagola, E., Saponara, E., Hills, A. P., Graf, R., et al. (2018). Inhibition of Class I histone deacetylases abrogates tumor growth factor β expression and development of fibrosis during chronic pancreatitis. Molecular Pharmacology, 94, 793–801.
Zhang, S.-K., Cui, N.-Q., Zhuo, Y.-Z., Hu, J.-G., Liu, J.-H., Li, D.-H., et al. (2020). Modified Xiaochaihu Decoction () promotes collagen degradation and inhibits pancreatic fibrosis in chronic pancreatitis rats. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine, 26, 599–603.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Li, R. Single-Cell Sequencing Data Analysis Unveiled HDAC1 as the Therapeutic Target for Chronic Pancreatitis. Mol Biotechnol 66, 68–78 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-00718-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-00718-x