Abstract
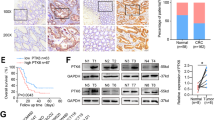
Colorectal cancer is the third most common malignancy worldwide. 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) is the commonly used chemotherapeutic agent, however, more patients develop resistance. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases (PI3Ks) play a crucial role in a wide range of cellular processes associated with malignant behavior including cell growth, migration, and survival. In this study, we show increased expression of PI3K p85α during the progression of colorectal cancer. Silencing of PI3K p85α in colorectal cancer cells increased disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential and enhanced 5-FU-induced apoptosis. Furthermore, PI3K p85α-depletion results in activated expression of apoptosis-associated genes Bcl-6, Bim, and Bax. Our results suggest that knockdown of PI3K p85α is a potential therapeutic strategy in the treatment of colorectal cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57(1):43–66.
Kabbinavar FF, Schulz J, McCleod M, Patel T, Hamm JT, Hecht JR, et al. Addition of bevacizumab to bolus fluorouracil and leucovorin in first-line metastatic colorectal cancer: results of a randomized phase II trial. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2005;23(16):3697–705. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.05.112.
Goldberg RM, Sargent DJ, Morton RF, Fuchs CS, Ramanathan RK, Williamson SK, et al. A randomized controlled trial of fluorouracil plus leucovorin, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin combinations in patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2004;22(1):23–30. doi:10.1200/JCO.2004.09.046.
Hoff PM, Ansari R, Batist G, Cox J, Kocha W, Kuperminc M, et al. Comparison of oral capecitabine versus intravenous fluorouracil plus leucovorin as first-line treatment in 605 patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: results of a randomized phase III study. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2001;19(8):2282–92.
Philp AJ, Campbell IG, Leet C, Vincan E, Rockman SP, Whitehead RH, et al. The phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase p85alpha gene is an oncogene in human ovarian and colon tumors. Cancer Res. 2001;61(20):7426–9.
Yu J, Zhang Y, McIlroy J, Rordorf-Nikolic T, Orr GA, Backer JM. Regulation of the p85/p110 phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase: stabilization and inhibition of the p110 alpha catalytic subunit by the p85 regulatory subunit. Mol Cell Biol. 1998;18(3):1379–87.
Osaki M, Oshimura M, Ito H. PI3K–Akt pathway: its functions and alterations in human cancer. Apoptosis Int J Programmed Cell Death. 2004;9(6):667–76. doi:10.1023/B:APPT.0000045801.15585.dd.
Vivanco I, Sawyers CL. The phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2(7):489–501. doi:10.1038/nrc839.
Sun Y, Tian H, Xiao FM, Xie XY, Song YG. PI3K p85alpha expression and its role in the progression of colorectal cancer. Nan Fang yi ke da Xue Xue Bao J South Med Univ. 2009;29(3):416–8.
Sun Y, Zhao S, Tian H, Xie X, Xiao F, Li K, et al. Depletion of PI3K p85alpha induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2009;22(6):1435–41.
Li J, Shao ZH, Xie JT, Wang CZ, Ramachandran S, Yin JJ, et al. The effects of ginsenoside Rb1 on JNK in oxidative injury in cardiomyocytes. Arch Pharmacal Res. 2012;35(7):1259–67. doi:10.1007/s12272-012-0717-3.
Lai HC, Liu TJ, Ting CT, Sharma PM, Wang PH. Insulin-like growth factor-1 prevents loss of electrochemical gradient in cardiac muscle mitochondria via activation of PI 3 kinase/Akt pathway. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2003;205(1–2):99–106.
Rampino N, Yamamoto H, Ionov Y, Li Y, Sawai H, Reed JC, et al. Somatic frameshift mutations in the BAX gene in colon cancers of the microsatellite mutator phenotype. Science. 1997;275(5302):967–9.
Morson BC. The evolution of colorectal carcinoma. Clin Radiol. 1984;35(6):425–31.
Zhang SQ. Screening and prevention of colorectal cancer in Haining County. Dis Colon Rectum. 1985;28(5):300–4.
Sherman DW, Ye XY, McSherry C, Parkas V, Calabrese M, Gatto M. Quality of life of patients with advanced cancer and acquired immune deficiency syndrome and their family caregivers. J Palliat Med. 2006;9(4):948–63. doi:10.1089/jpm.2006.9.948.
Rychahou PG, Jackson LN, Silva SR, Rajaraman S, Evers BM. Targeted molecular therapy of the PI3 K pathway: therapeutic significance of PI3 K subunit targeting in colorectal carcinoma. Ann Surg. 2006;243(6):833–42; discussion 43–4. doi:10.1097/01.sla.0000220040.66012.a9.
Ohta T, Ohmichi M, Hayasaka T, Mabuchi S, Saitoh M, Kawagoe J, et al. Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase increases efficacy of cisplatin in in vivo ovarian cancer models. Endocrinology. 2006;147(4):1761–9. doi:10.1210/en.2005-1450.
Nita ME, Nagawa H, Tominaga O, Tsuno N, Fujii S, Sasaki S, et al. 5-Fluorouracil induces apoptosis in human colon cancer cell lines with modulation of Bcl-2 family proteins. Br J Cancer. 1998;78(8):986–92.
Nakamura T, Sakamoto K. Forkhead transcription factor FOXO subfamily is essential for reactive oxygen species-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2008;281(1–2):47–55. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2007.10.007.
Kojima T, Norose T, Tsuchiya K, Sakamoto K. Mouse 3T3-L1 cells acquire resistance against oxidative stress as the adipocytes differentiate via the transcription factor FoxO. Apoptosis Int J Programmed Cell Death. 2010;15(1):83–93. doi:10.1007/s10495-009-0415-x.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Science and Information Technology Foundation of Guangzhou (2011J4100051) and Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (S2012040006707).
Conflict of interest
We confirm that this manuscript has not been published elsewhere and is not under consideration by another journal. All authors have approved the manuscript and agree with submission to Medical Oncology. The authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y., Tian, H., Wang, L. et al. The effects of silencing of PI3K p85α on 5-FU-induced colorectal cancer cells apoptosis. Med Oncol 30, 704 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-013-0704-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-013-0704-7