Abstract
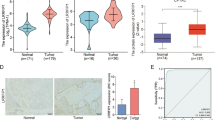
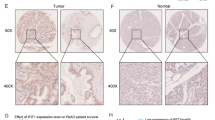
Pancreatic cancer is known for its bad prognosis. Micro-RNAs mis-expressions are associated with various human cancers and offer new candidate targets for diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. Micro-RNA-222 has been shown to play a crucial role in cancer cell proliferation in recent studies. However, its correlations with the clinicopathological characters of pancreatic cancer still remain unclear. Through a prospective study of 60 pairs of pancreatic cancer tissues, adjacent normal tissues were examined by quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction. The correlation between the expression of micro-RNA-222 and clinico-pathological characters was performed using the two-sample Student’s t test. The survival correlations were analyzed by the Kaplan–Meier method and the Cox’s proportional hazards model. Results showed that the expression levels of micro-RNA-222 were significantly elevated in the pancreatic cancer tissue compared with that in adjacent normal tissue. In addition, the overexpression of the tissue micro-RNA-222 strongly related to the expression level of Ki67. Finally, Cox’s proportional hazards model analysis confirmed that micro-RNA-222 high expression level was an independent predictor of poor prognosis. This study provides the first evidence of a potential link between Ki67 and micro-RNA-222, which are both relevant to cell proliferation. Our data suggest the potential of micro-RNA-222 as a prognostic biomarker for the pancreatic cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012. doi:10.3322/caac.20138.
Raimondi S, Maisonneuve P, Lowenfels AB. Epidemiology of pancreatic cancer: an overview. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2009.177.
Hidalgo M. Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0901557.
Vincent A, Herman J, Schulick R, Hruban RH, Goggins M. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 2011. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62307-0.
Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6(11):857–66.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116(2):281–97.
Harfe BD. MicroRNAs in vertebrate development. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2005;15(4):410–5.
Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431(7006):350–5.
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ. Oncomirs—microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6(4):259–69.
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA, Downing JR, Jacks T, Horvitz HR, Golub TR. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 2005;435(7043):834–8.
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, Prueitt RL, Yanaihara N, Lanza G, Scarpa A, Vecchione A,Negrini M, Harris CC, Croce CM. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2006;103(7):2257–61.
le Sage C, Nagel R, Egan DA, Schrier M, Mesman E, Mangiola A, Anile C, Maira G, Mercatelli N, Ciafrè SA, Farace MG, Agami R. Regulation of the p27 (Kip1) tumor suppressor by miR-221 and miR-222 promotes cancer cell proliferation. EMBO J. 2007;26(15):3699–708.
Hwang MS, Yu N, Stinson SY, Yue P, Newman RJ, Allan BB, Dornan D. miR-221/222 Targets Adiponectin Receptor 1 to Promote the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Breast Cancer. PLoS One. 2013. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066502.
Puerta-Gil P, García-Baquero R, Jia AY, Ocaña S, Alvarez-Múgica M, Alvarez-Ossorio JL, Cordon-Cardo C, Cava F, Sánchez-Carbayo M. miR-143, miR-222, and miR-452 are useful as tumor stratification and noninvasive diagnostic biomarkers for bladder cancer. Am J Pathol. 2012. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.01.034.
Xu K, Liang X, Shen K, Sun L, Cui D, Zhao Y, Tian J, Ni L, Liu J. miR-222 modulates multidrug resistance in human colorectal carcinoma by down-regulating ADAM-17. Exp Cell Res. 2012. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2012.04.014.
Quintavalle C, Garofalo M, Zanca C, Romano G, Iaboni M, del Basso De Caro M, Martinez-Montero JC, Incoronato M, Nuovo G, Croce CM, Condorelli G. miR-221/222 overexpression in human glioblastoma increases invasiveness by targeting the protein phosphate PTPμ. Oncogen. 2013. doi:10.1038/onc.2011.280.
Huuhtanen RL, Blomqvist CP, Wiklund TA, Böhling TO, Virolainen MJ, Tukiainen EJ, Tribukait B, Andersson LC. Comparison of the Ki-67 score and S-phase fraction as prognostic variables in soft-tissue sarcoma. Br J Cancer. 1999;79(5–6):945–51.
Lee EJ, Gusev Y, Jiang J, Nuovo GJ, Lerner MR, Frankel WL, Morgan DL, Postier RG, Brackett DJ, Schmittgen TD. Expression profiling identifies microRNA signature in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer. 2007;120(5):1046–54.
Szafranska AE, Davison TS, John J, Cannon T, Sipos B, Maghnouj A, Labourier E, Hahn SA. MicroRNA expression alterations are linked to tumorigenesis and non-neoplastic processes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene. 2007;26(30):4442–52.
Bloomston M, Frankel WL, Petrocca F, Volinia S, Alder H, Hagan JP, Liu CG, Bhatt D, Taccioli C. Croce CM. MicroRNA expression patterns to differentiate pancreatic adenocarcinoma from normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis. JAMA. 2007;297(17):1901–8.
Papaconstantinou IG, Manta A, Gazouli M, Lyberopoulou A, Lykoudis PM, Polymeneas G, Voros D. Expression of microRNAs in patients with pancreatic cancer and its prognostic significance. Pancreas. 2013. doi:10.1097/MPA.0b013e3182592ba7.
Yu J, Li A, Hong SM, Hruban RH, Goggins M. MicroRNA alterations of pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasias. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2347.
Zhang Y, Li M, Wang H, Fisher WE, Lin PH, Yao Q, Chen C. Profiling of 95 microRNAs in pancreatic cancer cell lines and surgical specimens by real-time PCR analysis. World J Surg. 2009. doi:10.1007/s00268-008-9833-0.
Greither T, Grochola LF, Udelnow A, Lautenschläger C, Würl P, Taubert H. Elevated expression of microRNAs 155, 203, 210 and 222 in pancreatic tumors is associated with poorer survival. Int J Cancer. 2010. doi:10.1002/ijc.24687.
Gerdes J, Schwab U, Lemke H, Stein H. Production of a mouse monoclonal antibody reactive with a human nuclear antigen associated with cell proliferation. Int J Cancer. 1983;31(1):13–20.
Scholzen T, Gerdes J. The Ki-67 protein: from the known and the unknown. J Cell Physiol. 2000;182(3):311–22.
Bullwinkel J, Baron-Lühr B, Lüdemann A, Wohlenberg C, Gerdes J, Scholzen T. Ki-67 protein is associated with ribosomal RNA transcription in quiescent and proliferating cells. J Cell Physiol. 2006;206(3):624–35.
Rahmanzadeh R, Hüttmann G, Gerdes J, Scholzen T. Chromophore-assisted light inactivation of pKi-67 leads to inhibition of ribosomal RNA synthesis. Cell Prolif. 2007;40(3):422–30.
Yerushalmi R, Woods R, Ravdin PM, Hayes MM, Gelmon KA. Ki67 in breast cancer: prognostic and predictive potential. Lancet Oncol. 2010. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70262-1.
Cheang MC, Chia SK, Voduc D, Gao D, Leung S, Snider J, Watson M, Davies S, Bernard PS, Parker JS, Perou CM, Ellis MJ, Nielsen TO. Ki57 index, HER2 status, and prognosis of patients with luminal B breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2009. doi:10.1093/jnci/djp082.
Stanton KJ, Sidner RA, Miller GA, Cummings OW, Schmidt CM, Howard TJ, Wiebke EA. Analysis of Ki-67 antigen expression, DNA proliferative fraction, and survival in resected cancer of the pancreas. Am J Surg. 2003;186(5):486–92.
Medina R, Zaidi SK, Liu CG, Stein JL, van Wijnen AJ, Croce CM, Stein GS. MicroRNAs 221 and 222 bypass quiescence and compromise cell survival. Cancer Res. 2008. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6754.
Galardi S, Mercatelli N, Giorda E, Massalini S, Frajese GV, Ciafrè SA, Farace MG. miR-221 and miR-222 expression affects the proliferation potential of human prostate carcinoma cell lines by targeting p27Kip1. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(32):23716–24.
Mercatelli N, Coppola V, Bonci D, Miele F, Costantini A, Guadagnoli M, Bonanno E, Muto G, Frajese GV, De Maria R, Spagnoli LG, Farace MG, Ciafrè SA. The inhibition of the highly expressed miR-221 and miR-222 impairs the growth of prostate carcinoma xenografts in mice. PLoS One. 2008. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0004029.
Visone R, Russo L, Pallante P, De Martino I, Ferraro A, Leone V, Borbone E, Petrocca F, Alder H, Croce CM, Fusco A. MicroRNAs (miR)-221 and miR-222, both overexpressed in human thyroid papillary carcinomas, regulate p27Kip1 protein levels and cell cycle. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2007;14(3):791–8.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the key project of Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Commission (11JC1401600), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81172274), and scientific research of Shanghai Municipal Public Health Bureau (20114v141).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, C., He, H., Jiang, Y. et al. Elevated expression of tumor miR-222 in pancreatic cancer is associated with Ki67 and poor prognosis. Med Oncol 30, 700 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-013-0700-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-013-0700-y