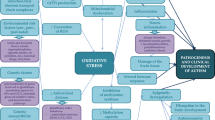
Abstract
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disability that causes social impairment, debilitated verbal or nonverbal conversation, and restricted/repeated behavior. Recent research reveals that mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress might play a pivotal role in ASD condition. The goal of this case–control study was to investigate oxidative stress and related alterations in ASD patients. In addition, the impact of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) mutations, particularly MT-ATP6, and its link with oxidative stress in ASD was studied. We found that ASD patient’s plasma had lower superoxide dismutase (SOD) and higher catalase (CAT) activity, resulting in lower SOD/CAT ratio. MT-ATP6 mutation analysis revealed that four variations, 8865 G>A, 8684 C>T, 8697 G>A, and 8836 A>G, have a frequency of more than 10% with missense and synonymous (silent) mutations. It was observed that abnormalities in mitochondrial complexes (I, III, V) are more common in ASD, and it may have resulted in MT-ATP6 changes or vice versa. In conclusion, our findings authenticate that oxidative stress and genetics both have an equal and potential role behind ASD and we recommend to conduct more such concurrent research to understand their unique mechanism for better diagnosis and therapeutic for ASD.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
Available.
Change history
04 July 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-023-02137-8
References
Adams JB, Audhya T, McDonough-Means S et al (2011) Nutritional and metabolic status of children with autism vs. neurotypical children, and the association with autism severity. Nutr Metab (Lond) 8(1):34. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-7075-8-34
Arora NK, Nair MKC, Gulati S et al (2018) Neurodevelopmental disorders in children aged 2–9 years: population-based burden estimates across five regions in India. PLoS Med 15(7):e1002615. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002615
Bakouie F (2015) The increase of AMP-activated protein kinase during physical activities can reduce symptoms of autistic children. Neonat Pediatr Med 1:S1002. https://doi.org/10.4172/2572-5203.1000102
Balachandar V, Bharathi G, Jayaramayya K et al (2021) Autism spectrum disorder (ASD)-a case-control study to investigate the prenatal, perinatal and neonatal factors in Indian Population. Brain Disorders 4:100024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dscb.2021.100024
Balachandar V, Dhivya V, Gomathi M, Mohanadevi S, Venkatesh B, Geetha B (2016) A review of Rett syndrome (RTT) with induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Investig 3:52. https://doi.org/10.21037/sci.2016.09.05
Balachandar V, Rajagopalan K, Jayaramayya K, Jeevanandam M, Iyer M (2020) Mitochondrial dysfunction: a hidden trigger of autism? Genes Dis 8(5):629–639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2020.07.002
Bambini-Junior V, Rodrigues L, Behr GA, Moreira JC, Riesgo R, Gottfried C (2011) Animal model of autism induced by prenatal exposure to valproate: behavioral changes and liver parameters. Brain Res 1408:8–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2011.06.015
Bjørklund G, Meguid NA, El-Bana MA et al (2020) Oxidative stress in autism spectrum disorder. Mol Neurobiol 57(5):2314–2332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-01742-2
Chauhan A, Chauhan V (2006) Oxidative stress in autism. Pathophysiology 13(3):171–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pathophys.2006.05.007
Chauhan A, Gu F, Chauhan V (2012) Mitochondrial respiratory chain defects in autism and other neurodevelopmental disorders. J Pediatr Biochem 2:213–223. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPB-120063
Detanico BC, Rozisky JR, Battastini AM, Torres IL (2011) Physiological level of norepinephrine increases adenine nucleotides hydrolysis in rat blood serum. Purinergic Signal 7(4):373–379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-011-9253-8
Feng C, Chen Y, Pan J et al (2017) Redox proteomic identification of carbonylated proteins in autism plasma: insight into oxidative stress and its related biomarkers in autism. Clin Proteomics 14:2–2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12014-017-9138-0
Frustaci A, Neri M, Cesario A et al (2012) Oxidative stress-related biomarkers in autism: systematic review and meta-analyses. Free Radic Biol Med 52(10):2128–2141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.03.011
Frye RE, Delatorre R, Taylor H et al (2013) Redox metabolism abnormalities in autistic children associated with mitochondrial disease. Transl Psychiatry 3(6):e273. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2013.51
Ganesan H, Balasubramanian V, Iyer M, Venugopal A, Subramaniam MD, Cho SG, Vellingiri B (2019) mTOR signalling pathway-A root cause for idiopathic autism? BMB Rep 52:424. https://doi.org/10.5483/BMBRep.2019.52.7.137
Garcia-Gil M, Camici M, Allegrini S, Pesi R, Tozzi MG (2021) Metabolic aspects of adenosine functions in the brain. Front Pharmacol 12:672182. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.672182
Geetha B, Sukumar C, Dhivyadeepa E, Reddy JK, Balachandar V (2019) Autism in India: a case-control study to understand the association between socio-economic and environmental risk factors. Acta Neurol Belg 119(3):393–401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-018-01057-4
Gomathi M, Balachandar V (2017) Novel therapeutic approaches: Rett syndrome and human induced pluripotent stem cell technology. Stem Cell Investig 4:20. https://doi.org/10.21037/sci.2017.02.11
Gonzalez- Fraguela M, Díaz ML, Vera H, Maragoto C, Noris E, Blanco L (2013) Oxidative stress markers in children with autism spectrum disorders. Br J Med Med Res 3:307–317
Gu F, Chauhan V, Kaur K et al (2013) Alterations in mitochondrial DNA copy number and the activities of electron transport chain complexes and pyruvate dehydrogenase in the frontal cortex from subjects with autism. Transl Psychiatry 3(9):e299 https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2013.68
Haas RH (2010) Autism and mitochondrial disease. Dev Disabil Res Rev 16(2):144–153. https://doi.org/10.1002/ddrr.112
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JM (1986) Oxygen free radicals and iron in relation to biology and medicine: some problems and concepts. Arch Biochem Biophys 246(2):501–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(86)90305-x
Janssen RJ, van den Heuvel LP, Smeitink JA (2004) Genetic defects in the oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) system. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 4(2):143–156. https://doi.org/10.1586/14737159.4.2.143
Jesina P, Tesarová M, Fornůsková D et al (2004) Diminished synthesis of subunit a (ATP6) and altered function of ATP synthase and cytochrome c oxidase due to the mtDNA 2 bp microdeletion of TA at positions 9205 and 9206. Biochem J 383(Pt. 3):561–571. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20040407
Mahalaxmi I, Subramaniam MD, Gopalakrishnan AV, Vellingiri B (2021) Dysfunction in mitochondrial electron transport chain complex I, pyruvate dehydrogenase activity, and mutations in ND1 and ND4 gene in autism spectrum disorder subjects from Tamil Nadu Population. India Mol Neurobiol 58(10):5303–5311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-021-02492-w
Masino SA, Kawamura M Jr, Cote JL, Williams RB, Ruskin DN (2013) Adenosine and autism: a spectrum of opportunities. Neuropharmacology 68:116–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.08.013
Miwa S, Brand MD (2003) Mitochondrial matrix reactive oxygen species production is very sensitive to mild uncoupling. Biochem Soc Trans 31(Pt 6):1300–1301. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst0311300
Mohan G, Bharathi G, Vellingiri B (2021) A middle-aged woman with severe scoliosis and encephalopathy. JAMA Neurol 78(2):251–252. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.4270
Mohan G, Sarma RJ, Iyer M, Kumar NS, Vellingiri B (2022) Highlighting novel genes associated with the classical Rett syndrome patient from India. Genes Dis. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2021.12.002
Murphy MP (2009) How mitochondria produce reactive oxygen species. Biochem J 417(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20081386
Palmieri L, Persico AM (2010) Mitochondrial dysfunction in autism spectrum disorders: cause or effect? Biochim Biophys Acta 1797(6–7):1130–1137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2010.04.018
Piryaei F, Houshmand M, Aryani O, Dadgar S, Soheili ZS (2012) Investigation of the Mitochondrial ATPase 6/8 and tRNA(Lys) Genes Mutations in Autism. Cell J 14(2):98–101
Rose S, Melnyk S, Pavliv O et al (2012) Evidence of oxidative damage and inflammation associated with low glutathione redox status in the autism brain. Transl Psychiatry 2(7):e134. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2012.61
Roselló-Díez E, Hove-Madsen L, Pérez-Grijalba V et al (2021) Mitochondrial genetic effect on atrial fibrillation: a case-control study. Mitochondrion 56:15–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2020.11.007
Rossignol DA, Frye RE (2012) Mitochondrial dysfunction in autism spectrum disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry 17(3):290–314. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2010.136
Sajdel-Sulkowska EM, Xu M, McGinnis W, Koibuchi N (2011) Brain region-specific changes in oxidative stress and neurotrophin levels in autism spectrum disorders (ASD). Cerebellum 10(1):43–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12311-010-0223-4
Söğüt S, Zoroğlu SS, Ozyurt H et al (2003) Changes in nitric oxide levels and antioxidant enzyme activities may have a role in the pathophysiological mechanisms involved in autism. Clin Chim Acta 331(1–2):111–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0009-8981(03)00119-0
Tórsdóttir G, Hreidarsson S, Kristinsson J, Snaedal J, Jóhannesson T (2005) Ceruloplasmin, superoxide dismutase and copper in autistic patients. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 96(2):146–148. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-7843.2005.pto960210.x
Varga NÁ, Pentelényi K, Balicza P, et al (2018) Mitochondrial dysfunction and autism: comprehensive genetic analyses of children with autism and mtDNA deletion. Behav Brain Funct 14(1):4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12993-018-0135-x
Venugopal A, Chandran M, Eruppakotte N, Kizhakkillach S, Breezevilla SC, Vellingiri B (2018) Monogenic diseases in India. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res 776:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrrev.2018.03.003
Wang L, Jia J, Zhang J, Li K (2016) Serum levels of SOD and risk of autism spectrum disorder: a case-control study. Int J Dev Neurosci 51:12–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2016.04.004
Wang Q, Kong Y, Wu DY et al (2021) Impaired calcium signaling in astrocytes modulates autism spectrum disorder-like behaviors in mice. Nat Commun 12(1):3321. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23843-0
Wang Y, Zhao S, Liu X, Zheng Y, Li L, Meng S (2018) Oxytocin improves animal behaviors and ameliorates oxidative stress and inflammation in autistic mice. Biomed Pharmacother 107:262–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.148
Yenkoyan K, Harutyunyan H, Harutyunyan A (2018) A certain role of SOD/CAT imbalance in pathogenesis of autism spectrum disorders. Free Radic Biol Med 123:85–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.05.070
Yorbik O, Sayal A, Akay C, Akbiyik DI, Sohmen T (2002) Investigation of antioxidant enzymes in children with autistic disorder. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 67(5):341–343. https://doi.org/10.1054/plef.2002.0439
Zimmermann FF, Gaspary KV, Siebel AM et al (2017) Analysis of extracellular nucleotide metabolism in adult zebrafish after embryological exposure to valproic acid. Mol Neurobiol 54(5):3542–3553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9917-z
Zorov DB, Juhaszova M, Sollott SJ (2014) Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ROS-induced ROS release. Physiol Rev 94(3):909–950. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00026.2013
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Bharathiar University, Coimbatore, for providing the necessary infrastructure facility and the Science and Engineering Research Board [grant number: ECR/2016/001688], Government of India, New Delhi, for providing necessary help in carrying out this research study. The authors would like to thank the ASD children and their parents for their full support, and we wish future therapeutic measures would aid children from ASD betterment. The authors would like to thank Dr. Senthil Kumar Nachimuthu, Professor, Department of Biotechnology, Mizoram University, to conduct a part of study in his laboratory.
Funding
This study was funded by the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) Early Career Research (ECR) Award funded by the Government of India, New Delhi (Grant No. ECR/2016/ 001688).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Concept and design: VB. Literature search: IM, DV. Experimental studies: VB, IM, MDS. Data analysis, statistical analysis: VB, IM, DV, GM, PK, MDS, NSK. Manuscript preparation: DV, IM, MDS. Manuscript editing and manuscript review: SR, AN, MDS, AVG, NSK, DV, MI, PK, GM, BV.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Institutional Human Ethics had been obtained from Bharathiar University.
Consent to Participate
Informed consent was obtained from all study participants.
Consent for Publication
All authors have approved for publication.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The affiliation for Gomathi Mohan should be affiliation 1 and affiliation 3 only.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Vellingiri, B., Venkatesan, D., Iyer, M. et al. Concurrent Assessment of Oxidative Stress and MT-ATP6 Gene Profiling to Facilitate Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in Tamil Nadu Population. J Mol Neurosci 73, 214–224 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-023-02111-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-023-02111-4