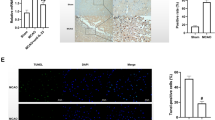
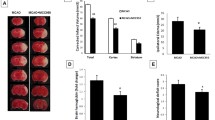
Abstract
Cerebral ischemia represents a major cause of disability, yet its precise mechanism remains unknown. In addition, ischemia-reperfusion injury which occurs during the blood recovery process increases the risk of mortality, and is not adequately addressed with current treatment. To improve therapeutic options, it is important to explore the vital substances that play a pivotal role in ischemia-reperfusion injury. This study is the first to investigate the role of IL-32, a vital pro-inflammatory factor, in models of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. The results showed that IL-32 was highly expressed in both in vivo and in vitro models. The proteins of the NOD/MAPK/NF-κB pathway were also up-regulated, indicating a potential signaling pathway mechanism. Inhibition of IL-32 and blocking of the NOD/MAPK/NF-κB pathway increased cell survival, decreased the level of inflammatory factors and inflammasomes, and attenuated nitrosative stress. Taken together, the results show that inhibition of IL-32 expression ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via the NOD/MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway. The findings in this study reveal that IL-32 is a vital target of ischemia-reperfusion injury, providing a new avenue for treatment development.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam MB, Ju MK, Kwon YG, Lee SH (2019) Protopine attenuates inflammation stimulated by carrageenan and LPS via the MAPK/NF-kappaB pathway. Food Chem Toxicol : Int J Publ Brit Industrial Biol Res Assoc 131:110583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2019.110583
Chen L et al (2019) Beta-arrestin 2 negatively regulates NOD2 signalling pathway through association with TRAF6 in microglia after cerebral ischaemia/reperfusion injury. J Cell Mol Med 23:3325–3335. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14223
Chen X et al (2012) Ischemia-reperfusion impairs blood-brain barrier function and alters tight junction protein expression in the ovine fetus. Neuroscience 226:89–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.08.043
Damen M, Schraa K, Tweehuysen L, den Broeder AA, Netea MG, Popa CD, Joosten LAB (2018) Genetic variant in IL-32 is associated with the ex vivo cytokine production of anti-TNF treated PBMCs from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Sci Rep 8:14050. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-32485-0
Granger DN, Kvietys PR (2015) Reperfusion injury and reactive oxygen species: the evolution of a concept. Redox Biol 6:524–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2015.08.020
He J, Li H, Li G, Yang L (2019a) Hyperoside protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by alleviating oxidative stress. Inflam Apoptosis Rats 33:798–806
He S et al (2019b) Propagermanium, a CCR2 inhibitor, attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through inhibiting inflammatory response induced by microglia. Neurochem Int 125:99–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2019.02.010
Hong JT, Son DJ, Lee CK, Yoon D-Y, Lee DH, Park MH (2017) Interleukin 32, inflammation and cancer. Pharmacol Ther 174:127–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.02.025
Huang XP, Ding H, Lu JD, Tang YH, Deng BX, Deng CQ (2015) Effects of the combination of the Main active components of Astragalus and Panax notoginseng on inflammation and apoptosis of nerve cell after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Am JChinese Med 43:1419–1438. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0192415x15500809
Jiang RH et al (2018) The CD40/CD40L system regulates rat cerebral microvasculature after focal ischemia/reperfusion via the mTOR/S6K signaling pathway. Neurol Res 40:717–723. https://doi.org/10.1080/01616412.2018.1473075
Jianrong S, Yanjun Z, Chen Y, Jianwen X (2019) DUSP14 rescues cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (IR) injury by reducing inflammation and apoptosis via the activation of Nrf-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 509:713–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.12.170
Khawar B, Abbasi MH, Sheikh N (2015) A panoramic spectrum of complex interplay between the immune system and IL-32 during pathogenesis of various systemic infections and inflammation. Eur J Med Res 20:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-015-0083-y
Khawar MB, Abbasi MH, Sheikh N (2016) IL-32: a novel pluripotent inflammatory interleukin, towards gastric inflammation. Gastric Cancer,Chronic Rhino Sinusitis Mediators Inflam 2016:8413768. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8413768
Kim HN et al (2019) Sageretia thea inhibits inflammation through suppression of NF- kappa B and MAPK and activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling pathways in RAW264.7 cells. The Am J Chinese Med 47:385–403. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0192415x19500198
Kim S, Han ST, Yoon D, Dinarello C (2005) Interleukin-32: a cytokine and inducer of TNF alpha. Immunity 22:131–142
Kwon OC, Kim S, Hong S, Lee CK, Yoo B, Chang EJ, Kim YG (2018) Role of IL-32 gamma on bone metabolism in autoimmune. Arthritis Immune Network 18:e20. https://doi.org/10.4110/in.2018.18.e20
Lee YS et al (2019) IL-32gamma suppresses lung cancer stem cell growth via inhibition of ITGAV-mediated STAT5 pathway. Cell Death Dis 10:506. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1737-4
Lin J et al (2018) Interleukin-32 induced thymic stromal lymphopoietin plays a critical role in the inflammatory response in human corneal epithelium. Cell Signal 49:39–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2018.05.007
Lin Y, Liu Q, Chen C, Chen W, Xiao H, Yang Q, Tian H (2017) Effect of acupuncture combined with hypothermia on MAPK/ERK pathway and apoptosis related factors in rats with cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury. Zhong nan da xue xue bao Yi xue ban = J Central South Univ Med Sci 42:380–388. https://doi.org/10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2017.04.003
Liu H et al (2015) NOD2 is involved in the inflammatory response after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury and triggers NADPH oxidase 2-derived reactive oxygen species. Int J Biol Sci 11:525–535. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.10927
Lu S, Li H, Li K, Fan XD (2018) HDAC9 promotes brain ischemic injury by provoking IkappaBalpha/NF-kappaB and MAPKs signaling pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503:1322–1329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.07.043
Meng XL, Zhang DL, Sui SH (2019) Acute remote ischemic preconditioning alleviates free radical injury and inflammatory response in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion rats. Exp Therapeutic Med 18:1953–1960. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2019.7797
Mohagheghi F, Ahmadiani A, Rahmani B, Moradi F, Romond N, Khalaj L (2013) Gemfibrozil pretreatment resulted in a sexually dimorphic outcome in the rat models of global cerebral ischemia-reperfusion via modulation of mitochondrial pro-survival and apoptotic cell death factors as well as MAPKs. J Mole Neurosci : MN 50:379–393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9932-0
Naderi Y, Sabetkasaei M, Parvardeh S, Zanjani TM (2017) Neuroprotective effect of minocycline on cognitive impairments induced by transient cerebral ischemia/reperfusion through its anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant properties in male rat. Brain Res Bull 131:207–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2017.04.010
Neupane S et al (2018) Enhanced neuroinflammatory responses after systemic LPS injection in IL-32beta transgenic mice. J Chem Neuroanat 94:173–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchemneu.2018.07.002
Nito C, Kamada H, Endo H, Narasimhan P, Lee YS, Chan PH (2012) Involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in expression of the water channel protein aquaporin-4 after ischemia in rat cortical astrocytes. J Neurotrauma 29:2404–2412. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2012.2430
Song XD, Feng JP, Yang RX (2019) Alamandine protects rat from myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by activating JNK and inhibiting NF-kappaB. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23:6718–6726. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201908_18563
Szydlowska K, Tymianski M (2010) Calcium, ischemia and excitotoxicity. Cell Calcium 47:122–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceca.2010.01.003
Ting JP, Duncan JA, Lei Y (2010) How the noninflammasome NLRs function in the innate immune system. Science (New York, NY) 327:286–290. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1184004
Tsoi B, Chen X, Gao C, Wang S, Yuen SC, Yang D, Shen J (2019) Neuroprotective effects and Hepatorenal toxicity of Angong Niuhuang wan against ischemia-reperfusion brain injury in rats. Front Pharmacol 10:593. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.00593
Wang H, Zhong D, Chen H, Jin J, Liu Q, Li G (2019) NLRP3 inflammasome activates interleukin-23/interleukin-17 axis during ischaemia-reperfusion injury in cerebral ischaemia in mice. Life Sci 227:101–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.04.031
Wu F, Qiu J, Fan Y, Zhang Q, Cheng B, Wu Y, Bai B (2018) Apelin-13 attenuates ER stress-mediated neuronal apoptosis by activating Gαi/Gαq-CK2 signaling in ischemic stroke. Exp Neurol 302:136–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2018.01.006
Xin T, Chen M, Duan L, Xu Y, Gao P (2018) Interleukin-32: its role in asthma and potential as a therapeutic agent. Respir Res 19:124. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-018-0832-x
Xiong H et al (2019) Tibetan medicine Kuan-Jin-Teng exerts anti-arthritic effects on collagen-induced arthritis rats via inhibition the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and down-regulation of MAPK signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 57:271–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2018.12.023
Xuan W, Huang W, Wang R, Chen C, Chen Y, Wang Y, Tan X (2017) Elevated circulating IL-32 presents a poor prognostic outcome in patients with heart failure after myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol 243:367–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.03.065
Xue BB, Chen BH, Tang YN, Weng CW, Lin LN (2019) Dexmedetomidine protects against lung injury induced by limb ischemia-reperfusion via the TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB pathway. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/kjm2.12115
Yan H et al (2018) Role of interleukin-32 in cancer biology. Oncol Lett 16:41–47. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.8649
Yang L, Yuan Y, Wu Y (2019) Polyphyllin I alleviates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via nuclear factor-KappaB signal pathway. Zhonghua wei zhong bing ji jiu yi xue 31:746–749. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.06.017
Yang Z, Shi L, Xue Y, Zeng T, Shi Y, Lin Y, Liu L (2019b) Interleukin-32 increases in coronary arteries and plasma from patients with coronary artery disease. Clin Chim Acta 497:104–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2019.07.019
Yao X, Wang Y, Zhang D (2018) microRNA-21 confers Neuroprotection against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury and alleviates blood-brain barrier disruption in rats via the MAPK Signaling pathway. J Mole Neurosci : MN 65:43–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-018-1067-5
Zhang TS, Yang L, Hu R, Qiao XL, Yang X, Liu XG (2007) Effect of electroacupuncture on the contents of excitatory amino acids in cerebral tissue at different time courses in rats with cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury. Zhen ci yan jiu = Acupunct Res 32:234–236
Availability of Data and Material
The data sets generated and analyzed in the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. The design and writing of the manuscript were performed by Chao Liu. Data collection and analysis were performed by Chao Liu, Xiaohui Xu and Chao Huang. All functional experiments were conducted by Dandan Shang and Li Zhang.
The second draft of the manuscript was written by Yupeng Wang. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics Approval
All procedures involving animal experiments were approved by the Animal Research Ethics Committee of Luoyang Central Hospital Affiliated to Zhengzhou University, Henan, China, and conducted according to the Animal Protection Law of the People’s Republic of China-2009.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Xu, X., Huang, C. et al. Inhibition of IL-32 Expression Ameliorates Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via the NOD/MAPK/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. J Mol Neurosci 70, 1713–1727 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01557-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01557-0