Abstract
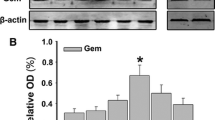
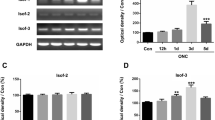
Raf-1 kinase inhibitory protein (RKIP), a member of the phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein (PEBP) family, plays an important role in neuronal apoptosis and cognitive deficits associated with neurodegenerative diseases. However, the biological function of RKIP in the retina is still unclear. Therefore, in the present study, we investigated the expression of RKIP in mouse retina following optic nerve crush (ONC) and evaluated the effects of RKIP on retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) apoptosis and axonal regeneration after ONC. Our results showed that the expression of RKIP was markedly decreased in the injured retina. Overexpression of RKIP inhibits RGC apoptosis and promotes axonal regeneration after ONC. Furthermore, overexpression of RKIP significantly increased the phosphorylation in extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK)1/2 and AKT in the injured retina. Taken together, these results suggest that RKIP promotes RGCs survival and axonal regeneration following ONC through promoting the ERK signaling pathway, implying that RKIP may serve as a potential molecular target for the treatment of glaucoma.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blaugrund E, Lavie V, Cohen I, Solomon A, Schreyer D, Schwartz M (1993) Axonal regeneration is associated with glial migration: comparison between the injured optic nerves of fish and rats. J Comp Neurol 330:105–112
Doster SK, Lozano AM, Aguayo AJ, Willard MB (1991) Expression of the growth-associated protein GAP-43 in adult rat retinal ganglion cells following axon injury. Neuron 6:635–647
Fan T-J, Han L-H, Cong R-S, Liang J (2005) Caspase family proteases and apoptosis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 37:719–727
Hellmann J, Rommelspacher H, Mühlbauer E, Wernicke C (2010) Raf kinase inhibitor protein enhances neuronal differentiation in human SH-SY5Y cells. Dev Neurosci 32:33–46
Kanamori A, Nakamura M, Nakanishi Y, Nagai A, Mukuno H, Yamada Y, Negi A (2004) Akt is activated via insulin/IGF-1 receptor in rat retina with episcleral vein cauterization. Brain Res 1022:195–204
Keller ET, Fu Z, Brennan M (2004) The role of Raf kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) in health and disease. Biochem Pharmacol 68:1049–1053
Kelliher C, Kenny D, O’Brien C (2006) Trends in blind registration in the adult population of the Republic of Ireland 1996–2003. Br J Ophthalmol 90:367–371
Kilic Ü, Kilic E, Järve A, Guo Z, Spudich A, Bieber K, Barzena U, Bassetti CL, Marti HH, Hermann DM (2006) Human vascular endothelial growth factor protects axotomized retinal ganglion cells in vivo by activating ERK-1/2 and Akt pathways. J Neurosci 26:12439–12446
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Maki M, Matsukawa N, Yuasa H, Otsuka Y, Yamamoto T, Akatsu H, Okamoto T, Ueda R, Ojika K (2002) Decreased expression of hippocampal cholinergic neurostimulating peptide precursor protein mRNA in the hippocampus in Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61:176–185
Pearson G, Robinson F, Beers Gibson T, Xu B-e, Karandikar M, Berman K, Cobb MH (2001) Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: regulation and physiological functions 1. Endocr Rev 22:153–183
Pernet V, Schwab ME (2014) Lost in the jungle: new hurdles for optic nerve axon regeneration. Trends Neurosci 37:381–387
Quigley HA, Broman AT (2006) The number of people with glaucoma worldwide in 2010 and 2020. Br J Ophthalmol 90:262–267
Quigley HA, Nickells RW, Kerrigan LA, Pease ME, Thibault DJ, Zack DJ (1995) Retinal ganglion cell death in experimental glaucoma and after axotomy occurs by apoptosis. Investig Ophth Vis Sci 36:774–786
Riedl SJ, Shi Y (2004) Molecular mechanisms of caspase regulation during apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:897–907
Sang A, Xu Y, Zhou T, Wang J, Zhu J, Chen C, Shi J, Shuai J, Xu G, Gu Z (2013) Involvement of transcription initiation factor IIB in the light-induced death of rat retinal ganglion cells in vivo. J Mol Histol 44:11–18
Shioda N, Han F, Fukunaga K (2009) Role of Akt and ERK signaling in the neurogenesis following brain ischemia. Int Rev Neurobiol 85:375–387
Sun J-C, Xu T, Zuo Q, Wang R-B, Qi A-Q, Cao W-L, Sun A-J, Sun X-J, Xu J (2014) Hydrogen-rich saline promotes survival of retinal ganglion cells in a rat model of optic nerve crush. PLoS One 9, e99299
Toborek M, Son KW, Pudelko A, King‐Pospisil K, Wylegala E, Malecki A (2007) ERK 1/2 signaling pathway is involved in nicotine-mediated neuroprotection in spinal cord neurons. J Cell Biochem 100:279–292
Wu Y, Shang Y, Sun S, Liang H, Liu R (2007) Erythropoietin prevents PC12 cells from 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion-induced apoptosis via the Akt/GSK-3β/caspase-3 mediated signaling pathway. Apoptosis 12:1365–1375
Wu Y, Xu F, Huang H, Chen L, Wen M, Jiang L, Lu L, Li L, Song D, Zeng S (2014) Up-regulation of SKIP relates to retinal ganglion cells apoptosis after optic nerve crush in vivo. J Mol Histol 45:715–721
Yeung KC, Rose DW, Dhillon AS, Yaros D, Gustafsson M, Chatterjee D, McFerran B, Wyche J, Kolch W, Sedivy JM (2001) Raf kinase inhibitor protein interacts with NF-κB-inducing kinase and TAK1 and inhibits NF-κB activation. Mol Cell Biol 21:7207–7217
Zhang G, Han M, Wang X, Xiao A (2015) GRP75 involves in retinal ganglion cell apoptosis after rat optic nerve crush. J Mol Neurosci: 1–9
Zuo H, Lin T, Wang D, Peng R, Wang S, Gao Y, Xu X, Zhao L, Wang S, Su Z (2014) RKIP regulates neural cell apoptosis induced by exposure to microwave radiation partly through the MEK/ERK/CREB pathway. Mol Neurobiol 1–10
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, J., Jiang, H., Gao, H. et al. Raf-1 Kinase Inhibitory Protein (RKIP) Promotes Retinal Ganglion Cell Survival and Axonal Regeneration Following Optic Nerve Crush. J Mol Neurosci 57, 243–248 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0612-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0612-8