Abstract
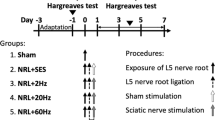
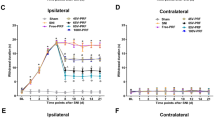
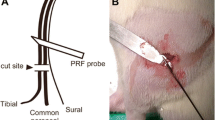
Pulsed radiofrequency (PRF) treatment is a minimally invasive technique with multiple therapeutic applications. Hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channel mediating Ih may regulate neuropathic pain signaling. This study aimed to determine whether PRF suppresses neuropathic pain by altering HCN channel expression in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons. Male Sprague Dawley rats with sciatic nerve chronic constriction injury (CCI) were randomly assigned to PRF (n = 60) and sham control (n = 60) groups, respectively. On postoperative day 7 (D07), PRF or sham treatment was delivered to the proximal sciatic nerve for 8 min. Behavioral tests were performed before surgery (D0), on D07, and on D1, D7, and D14 after PRF or sham treatment. HCN1 and HCN2 expression levels in the DRG were examined by immunohistochemistry and Western blot. The results showed that thermal hyperalgesia, mechano-allodynia, and mechano-hyperalgesia were lower, and DRG expression levels of HCN1 and HCN2 higher, in the PRF group compared with sham control animals (all P < 0.05 at D14). In conclusion, PRF can upregulate HCN channel expression in the DRG of rats with sciatic nerve CCI. How this regulation of Ih in nociceptive afferents contributes to the suppression of neuropathic pain by PRF remains to be determined.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksu R, Ugur F, Bicer C et al (2010) The efficiency of pulsed radiofrequency application on L5 and l6 dorsal roots in rabbits developing neuropathic pain. Reg Anesth Pain Med 35(1):11–15
Bennett GJ, Xie YK (1988) A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain 33(1):87–107
Biel M, Wahl-Schott C, Michalakis S, Zong X (2009) Hyperpolarization-activated cation channels: from genes to function. Physiol Rev 89(3):847–885
Chaplan SR, Guo HQ, Lee DH et al (2003) Neuronal hyperpolarization-activated pacemaker channels drive neuropathic pain. J Neurosci 23(4):1169–1178
Chung JM, Chung K (2002) Importance of hyperexcitability of DRG neurons in neuropathic pain. Pain Pract 2(2):87–97
Cohen SP, Sireci A, Wu CL, Larkin TM, Williams KA, Hurley RW (2006) Pulsed radiofrequency of the dorsal root ganglia is superior to pharmacotherapy or pulsed radiofrequency of the intercostal nerves in the treatment of chronic postsurgical thoracic pain. Pain Physician 9(3):227–235
Dalle C, Eisenach JC (2005) Peripheral block of the hyperpolarization-activated cation current (Ih) reduces mechanical allodynia in animal models of postoperative and neuropathic pain. Reg Anesth Pain Med 30(3):243–248
Du L, Wang SJ, Cui J, He WJ, Ruan HZ (2013a) Inhibition of HCN channels within the periaqueductal gray attenuates neuropathic pain in rats. Behav Neurosci 127(2):325–329
Du L, Wang SJ, Cui J, He WJ, Ruan HZ (2013b) The role of HCN channels within the periaqueductal gray in neuropathic pain. Brain Res 150036-44
Emery EC, Young GT, Berrocoso EM, Chen L, McNaughton PA (2011) HCN2 ion channels play a central role in inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Science 333(6048):1462–1466
Emery EC, Young GT, McNaughton PA (2012) HCN2 ion channels: an emerging role as the pacemakers of pain. Trends Pharmacol Sci 33(8):456–463
Flatters SJ, Bennett GJ (2004) Ethosuximide reverses paclitaxel- and vincristine-induced painful peripheral neuropathy. Pain 109(1-2):150–161
Hagiwara S, Iwasaka H, Takeshima N, Noguchi T (2009) Mechanisms of analgesic action of pulsed radiofrequency on adjuvant-induced pain in the rat: Roles of descending adrenergic and serotonergic systems. Eur J Pain 13(3):249–252
Hains BC, Saab CY, Klein JP, Craner MJ, Waxman SG (2004) Altered sodium channel expression in second-order spinal sensory neurons contributes to pain after peripheral nerve injury. J Neurosci 24(20):4832–4839
Hamann W, Abou-Sherif S, Thompson S, Hall S (2006) Pulsed radiofrequency applied to dorsal root ganglia causes a selective increase in ATF3 in small neurons. Eur J Pain 10(2):171–176
Hargreaves K, Dubner R, Brown F, Flores C, Joris J (1988) A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain 32(1):77–88
Hatch RJ, Jennings EA, Ivanusic JJ (2013) Peripheral hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channels contribute to inflammation-induced hypersensitivity of the rat temporomandibular joint. Eur J Pain 17(7):972–982
He C, Chen F, Li B, Hu Z (2014) Neurophysiology of HCN channels: from cellular functions to multiple regulations. Prog Neurobiol 1121-23
Jiang YQ, Xing GG, Wang SL et al (2008) Axonal accumulation of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channels contributes to mechanical allodynia after peripheral nerve injury in rat. Pain 137(3):495–506
Ke M, Yinghui F, Yi J et al (2013) Efficacy of pulsed radiofrequency in the treatment of thoracic postherpetic neuralgia from the angulus costae: a randomized, double-blinded, controlled trial. Pain Physician 16(1):15–25
Kerstman E, Ahn S, Battu S, Tariq S, Grabois M (2013) Neuropathic pain. Handb Clin Neurol 110175-187
Li CY, Song YH, Higuera ES, Luo ZD (2004) Spinal dorsal horn calcium channel alpha2delta-1 subunit upregulation contributes to peripheral nerve injury-induced tactile allodynia. J Neurosci 24(39):8494–8499
Ludwig A, Zong X, Jeglitsch M, Hofmann F, Biel M (1998) A family of hyperpolarization-activated mammalian cation channels. Nature 393(6685):587–591
Mazo I, Rivera-Arconada I, Roza C (2013) Axotomy-induced changes in activity-dependent slowing in peripheral nerve fibres: Role of hyperpolarization-activated/HCN channel current. Eur J Pain 17(9):1281–1290
Moosmang S, Stieber J, Zong X, Biel M, Hofmann F, Ludwig A (2001) Cellular expression and functional characterization of four hyperpolarization-activated pacemaker channels in cardiac and neuronal tissues. Eur J Biochem 268(6):1646–1652
Park HW, Ahn SH, Son JY et al (2012) Pulsed radiofrequency application reduced mechanical hypersensitivity and microglial expression in neuropathic pain model. Pain Med 13(9):1227–1234
Perret DM, Kim DS, Li KW et al (2011) Application of pulsed radiofrequency currents to rat dorsal root ganglia modulates nerve injury-induced tactile allodynia. Anesth Analg 113(3):610–616
Podhajsky RJ, Sekiguchi Y, Kikuchi S, Myers RR (2005) The histologic effects of pulsed and continuous radiofrequency lesions at 42 degrees C to rat dorsal root ganglion and sciatic nerve. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 30(9):1008–1013
Postea O, Biel M (2011) Exploring HCN channels as novel drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10(12):903–914
Sluijter ME (2005) Pulsed radiofrequency. Anesthesiology 103(6):1313, author reply 1313-1314
Tanaka N, Yamaga M, Tateyama S, Uno T, Tsuneyoshi I, Takasaki M (2010) The effect of pulsed radiofrequency current on mechanical allodynia induced with resiniferatoxin in rats. Anesth Analg 111(3):784–790
Tibbs GR, Rowley TJ, Sanford RL et al (2013) HCN1 channels as targets for anesthetic and nonanesthetic propofol analogs in the amelioration of mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia in a mouse model of neuropathic pain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 345(3):363–373
Van Zundert J, Brabant S, Van de Kelft E, Vercruyssen A, Van Buyten JP (2003) Pulsed radiofrequency treatment of the Gasserian ganglion in patients with idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. Pain 104(3):449–452
Vranken JH (2012) Elucidation of pathophysiology and treatment of neuropathic pain. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem 12(4):304–314
Wan Y (2008) Involvement of hyperpolarization-activated, cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channels in dorsal root ganglion in neuropathic pain. Sheng Li Xue Bao 60(5):579–580
Wickenden AD, Maher MP, Chaplan SR (2009) HCN pacemaker channels and pain: a drug discovery perspective. Curr Pharm Des 15(18):2149–2168
Xiao J, Nguyen TV, Ngui K et al (2004) Molecular and functional analysis of hyperpolarisation-activated nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels in the enteric nervous system. Neuroscience 129(3):603–614
Xie W, Strong JA, Meij JT, Zhang JM, Yu L (2005) Neuropathic pain: Early spontaneous afferent activity is the trigger. Pain 116(3):243–256
Young GT, Emery EC, Mooney ER, Tsantoulas C, McNaughton PA (2014) Inflammatory and neuropathic pain are rapidly suppressed by peripheral block of hyperpolarisation-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channels. Pain 155(9):1708–1719
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Peking University People’s Hospital Research and Development Funds.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Feng, Y. & Zhang, T. Pulsed Radiofrequency Treatment Enhances Dorsal Root Ganglion Expression of Hyperpolarization-Activated Cyclic Nucleotide-Gated Channels in a Rat Model of Neuropathic Pain. J Mol Neurosci 57, 97–105 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0582-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0582-x