Abstract
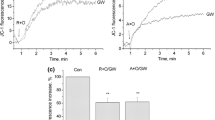
Brain ischemia is accompanied by lowering of intra- and extracellular pH. Stroke often leads to irreversible damage of synaptic transmission by unknown mechanism. We investigated an influence of lowering of pHi and pHo on free radical formation in synaptosomes. Three models of acidosis were used: (1) pHo 6.0 corresponding to pHi decrease down to 6.04; (2) pHo 7.0 corresponding to the lowering of pHi down to 6.92: (3) 1 mM amiloride corresponding to pHi decrease down to 6.65. We have shown that both types of extracellular acidification, but not intracellular acidification, increase 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate fluorescence that reflects free radical formation. These three treatments induce the rise of the dihydroethidium fluorescence that reports synthesis of superoxide anion. However, the impact of amiloride on superoxide anion synthesis was less than that induced by moderate extracellular acidification. Superoxide anion synthesis at pHo 7.0 was almost completely eliminated by mitochondrial uncoupler carbonyl cyanide 4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenylhydrazone. Furthermore, using fluorescent dyes JC-1 and rhodamine-123, we confirmed that pHo lowering, but not intracellular acidification, led to depolarization of intrasynaptosomal mitochondria. We have shown that pHo but not pHi lowering led to oxidative stress in neuronal presynaptic endings that might underlie the long-term irreversible changing in synaptic transmission.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ASIC:
-
Acid-sensitive ion channel
- BCECF-AM:
-
2′7′-bis(2-Carboxyethyl)-5(6)-carboxyfluorescein acetoxymethyl ester
- CCCP:
-
Carbonyl cyanide 4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenylhydrazone
- DCF:
-
2′,7′-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein
- DCFDA:
-
2′,7′-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate
- DPI:
-
Diphenyleniodinium chloride
- HEPES:
-
4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazine-N’-1-ethanesulfonic acid
- Ie-Ic, R.U.:
-
Fluorescence intensity; the control curve was extracted from the experimental curve; relative units
- Ifl:
-
Fluorescence intensity
- Ifl, R.U.:
-
Fluorescence intensity; relative units
- IP3 :
-
1,4,5-Triphosphate
- JC-1:
-
5,5′,6,6′-Tetrachloro-1,1′3,3′-tetraethylbenzimidazolo-carbocyanine iodide
- MES:
-
4-Morpholineethanesulfonic acid
- NMDA:
-
N-Methyl-d-aspartate
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- Tris:
-
Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane
References
Alekseenko AV, Waseem TV, Fedorovich SV (2008) Ferritin, a protein containing iron nanoparticles, induces reactive oxygen species formation and inhibits glutamate uptake in rat brain synaptosomes. Brain Res 1241:193–200
Alekseenko AV, Lemeshchenko VV, Pekun TG, Waseem TV, Fedorovich SV (2012) Glutamate-induced free radical formation in rat brain synaptosomes is not dependent on intrasynaptosomal mitochondria membrane potential. Neurosci Lett 513:238–242
Behrens MM, Ali SS, Dao DN et al (2007) Ketamine-induced loss of phenotype of fast-spiking interneurons is mediated by NADPH-oxidase. Science 318:1645–1647
Bindokas VP, Jordan J, Lee CC, Miller RJ (1996) Superoxide production in rat hippocampal neurons: selective imaging with hydroethidine. J Neurosci 16:1324–1336
Bolay H, Gursoy-Ozdemir Y, Sara Y, Onur R, Can A, Dalkara T (2002) Persistent defect in transmitter release and synapsin phosphorylation in cerebral cortex after transient moderate ischemic injury. Stroke 33:1369–1375
Bralet J, Bouvier C, Schreiber L, Boquilon M (1991) Effect of acidosis on lipid peroxidation in brain slices. Brain Res 539:175–177
Bralet J, Schreiber L, Bouviern C (1992) Effect of acidosis and anoxia on iron delocalization from brain homogenates. Biochem Pharmacol 43:979–983
Chesler M (2003) Regulation and modulation of pH in the brain. Physiol Rev 83:1183–1221
Chinopoulos C, Tretter L, Adam-Vizi V (1999) Depolarization of in situ mitochondria due to hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in nerve terminals: inhibition of ά-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase. J Neurochem 73:220–228
Correia SC, Carvalho C, Cardoso S et al (2010) Mitochondrial preconditioning: a potential neuroprotective strategy. Front Aging Neurosci 2:A138
Crowell JW, Kaufmann BN (1961) Changes in tissue pH after cardiac arrest. Am J Physiol 200:743–745
Deyev IE, Sohet F, Vassilenko KP et al (2011) Insulin receptor-related receptor as an extracellular alkali sensor. Cell Metab 13:679–689
Drapeau P, Nachshen DA (1988) Effects of lowering extracellular and cytosolic pH on calcium fluxes, cytosolic calcium levels and transmitter release in presynaptic nerve terminals isolated from rat brain. J Gen Physiol 91:305–315
Eccles RM, Loyning Y, Oshima T (1966) Effects of hypoxia on the monosynaptic reflex pathway in the cat spinal cord. J Neurophysiol 29:315–331
Fedorovich SV, Aksentsev SL, Konev SV (1996) Acidosis inhibits calcium accumulation in intrasynaptosomal mitochondria. Acta Neurobiol Exp 56:703
Fedorovich SV, Aksentsev SL, Lyskova TI, Kaler GV, Fedulov AS, Konev SV (1997) Effect of acidosis on membrane potential and calcium transport in rat brain synaptosomes. Biofizika 42:412–416 (in Russian)
Fedorovich SV, Kaler GV, Konev SV (2003) Effect of low pH on glutamate uptake and release in isolated presynaptic endings from rat brain. Neurochem Res 28:715–721
Giniatullin AR, Darios F, Shakirzyanova A, Davletov B, Giniatullin R (2006) SNAP25 is a pre-synaptic target for the depressant action of reactive oxygen species on transmitter release. J Neurochem 98:1789–1797
Hajos F (1975) An improved method for the preparation of synaptosomal fractions in high purity. Brain Res 93:485–489
Halliwell B (2006) Oxidative stress and neurodegeneration: where are we now? J Neurochem 97:1634–1658
Herschkowitz N, Katchman AN, Veregge S (1993) Site of synaptic depression during hypoxia: a patch-clamp analysis. J Neurophysiol 69:432–441
Hofmeijer J, van Putten MJAM (2012) Ischemic cerebral damage. An appraisal of synaptic failure. Stroke 43:607–615
Hsu KS, Liang YC, Huang CC (2000) Influence of an extracellular acidosis on excitatory synaptic transmission and long-term potentiation in the CA1 region of rat hippocampal slices. J Neurosci Res 62:403–415
Hutchinson DS, Csikasz RI, Yamamoto DL et al (2007) Diphenylene iodinium stimulates glucose uptake in skeletal muscle cells through mitochondrial complex I inhibition and activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Cell Signal 19:1610–1620
Isaev NK, Stelmashook EV, Plotnikov EY et al (2008) Role of acidosis, NMDA receptors, and acid-sensitive ion channel 1a (ASIC1a) in neuronal death induced by ischemia. Biochem Mosc 73:1171–1175
Kalyanaraman B, Darley-Usmar V, Davies KJA et al (2012) Measuring reactive oxygen species and nitrogen species with fluorescent probes: challenges and limitations. Free Rad Biol Med 52:1–6
Keating DI (2008) Mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, regulation of exocytosis and their relevance to neurodegenerative diseases. J Neurochem 104:298–305
Kellenberger S, Schild L (2002) Epithelial sodium channel/degenerin family of ion channels: a variety of functions for a shared structure. Physiol Rev 82:735–767
Kraig RP, Chesler M (1990) Astrocytic acidosis in hyperglycemic and complete ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 10:104–114
Krishtal OA, Pidoplichko VI (1981) A receptor for protons in the membrane of sensory neurons may participate in nociception. Neuroscience 6:2599–2601
LeBel CP, Bondy SC (1990) Sensitive and rapid quantitation of oxygen reactive species formation in rat synaptosomes. Neurochem Int 17:435–440
Lowry O, Rosenbrough H, Farr H, Randall R (1951) Protein measurements with folin reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–279
Lyskova TI, Aksentsev SL, Fedorovich SV et al (1997) Effect of ischemic damage factors on lipid peroxidation in rat brain synaptosomes. Biofizika 42:408–411 (In Russian)
Misra H, Fridovich I (1972) The role of superoxide anion in the autooxidation of epinephrine and simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem 247:3170–3175
Mittmann T, Qu M, Zilles K, Luhmann HI (1998) Long-term cellular dysfunction after focal cerebral ischemia: in vitro analysis. Neuroscience 85:15–27
Moody W (1984) Effects of intracellular H+ on the electrical properties of excitable cells. Annu Rev Neurosci 7:257–278
Nachshen DA, Drapeau P (1988) The regulation of cytosolic pH in isolated presynaptic nerve terminals from rat brain. J Gen Physiol 91:289–303
Neumann-Haefilin T, Witte OW (2000) Periinfarct and remote excitability changes after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20:45–52
Obara M, Szeliga M, Albrecht J (2008) Regulation of pH in the mammalian central nervous system under normal and pathological conditions: fact and hypotheses. Neurochem Int 52:905–919
Pekun TG, Waseem TV, Fedorovich SV (2012) Extracellular acidification leads to reactive oxygen species formation in rat brain synaptosomes. Biofizika 57:253–257 (in Russian)
Ravati A, Ahlemeyer B, Becker A, Klumpp S, Krieglstein J (2001) Preconditioning-induced neuroprotection is mediated by reactive oxygen species and activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor kappaB. J Neurochem 78:909–919
Reynolds IJ, Hastings TG (1995) Glutamate induces the production of reactive oxygen species in cultured forebrain neurons following NMDA receptor activation. J Neurosci 15:3318–3327
Rizzuto R, Pozzan T (2006) Microdomains of intracellular Ca2+: molecular determinants and functional consequences. Physiol Rev 86:369–408
Saadoun S, Lluch M, Rodriguez-Alvarez J, Blanco I, Rodriguez R (1998) Extracellular acidification modifies Ca2+ fluxes in rat brain synaptosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Com 242:123–128
Schrimpf SP, Meskenaite V, Brunner E et al (2005) Proteomic analysis of synaptosomes using isotope-coded affinity tags and mass spectrometry. Proteomics 5:2631–2641
Selivanov VA, Zeak JA, Roca J, Cascante M, Trucco M, Votyakova TV (2008) The role of external and matrix pH in mitochondrial reactive oxygen species generation. J Biol Chem 288:29292–29300
Setsukinai T-I, Urano Y, Kakinuma K, Majima HJ, Nagano T (2003) Development of novel fluorescence probes that can reliably detect reactive oxygen species and distinguish specific species. J Biol Chem 278:3170–3175
Siesjo BK, Bendek G, Koide T, Westerberg E, Wieloch T (1985) Influence of acidosis on lipid peroxidation in brain tissues in vitro. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 5:253–258
Sudhof TC (2004) The synaptic vesicle cycle. Annu Rev Neurosci 27:509–547
Thorn WG, Heitman R (1954) pH der Gehirunde vom Kaninchen in situ wahrend perakuter, totaler Ischaemie, reiner Anoxie und in der Erholung. Pflug Arch 218:501–510
Tombaugh GC, Sapolsky RM (1993) Evolving concepts about the role of acidosis in ischemic neuropathology. J Neurochem 61:793–803
Tretter L, Chinopoulos C, Adam-Vizi V (1997) Enhances depolarization-evoked calcium signal and reduced [ATP]/[ADP] ratio are unrelated events induced by oxidative stress in synaptosomes. J Neurochem 69:2529–2537
Voglis G, Tavernarakis N (2008) A synaptic DEG/ENaC ion channel mediates learning in C. elegans by facilitating dopamine signaling. EMBO J 27:3288–3299
Waseem TV, Konev SV, Fedorovich SV (2004) Influence of hypotonic shock on glutamate and GABA uptake in rat brain synaptosomes. Neurochem Res 29:1653–1658
Waseem TV, Rakovich AA, Lavrukevich TV, Konev SV, Fedorovich SV (2005) Calcium regulates the mode of exocytosis induced by hypotonic shock in isolated neuronal presynaptic endings. Neurochem Int 46:235–242
Waseem TV, Kolos VA, Lapatsina LP, Fedorovich SV (2007) Hypertonic shrinking but not hypotonic swelling increases sodium concentration in rat brain synaptosomes. Brain Res Bull 73:135–142
Wind S, Beuerlin K, Eucker T et al (2010) Comparative pharmacology of chemically distinct NADPH oxidase inhibitors. Br J Pharmacol 161:885–898
Xiong Z-G, Zhu X-M, Chu X-P et al (2004) Neuroprotection in ischemia: blocking calcium-permeable acid-sensing ion channels. Cell 118:687–698
Yates CM, Butterworth J, Tennant MC, Gordon A (1990) Enzyme activities in relation to pH and lactate in postmortem brain in Alzheimer-type and other dementia. J Neurochem 55:1624–1630
Ying W, Han S-K, Miller JW, Swanson RA (1999) Acidosis potentiates oxidative neuronal death by multiple mechanisms. J Neurochem 73:1549–1556
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Committee for Aid and Education in Neurochemistry-International Society for Neurochemistry (CAEN-ISN). Foundation body had no involvement in study design, in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data, in the writing of the report, and in the decision to submit the article for publication.
We thank Mrs. Claire Roulston for improvement of English.
Declaration of competing interests
Authors declare no competing financial, personal, or other interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pekun, T.G., Lemeshchenko, V.V., Lyskova, T.I. et al. Influence of Intra- and Extracellular Acidification on Free Radical Formation and Mitochondria Membrane Potential in Rat Brain Synaptosomes. J Mol Neurosci 49, 211–222 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9913-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9913-3