Abstract
Background
Worldwide, gastric carcinoma (GC) is the 5th most common malignancies in both sexes representing 6.8% of the total fatalities and is the 3rd leading cause of cancer death representing 8.8% of total fatalities. In Egypt, GC considers the 12th leading cause of cancer death representing 2.2% of the total cancer mortality. A growing body of evidence supports that cancer stem cells (CSCs) are resistant to chemotherapy or radiation, and the cell adhesion molecule CD44 has been identified as a cell surface marker associated with cancer stem cell in several types of tumors including gastric cancer. CD44 regulates gastric stem cell proliferation by increasing cyclin D1 expression which represents an important regulatory protein in the cell cycle transition from G1 phase to S phase. This study aimed to investigate whether cyclin D1 and CD44 can be used as prognostic indicators in gastric cancer.
Material and Methods
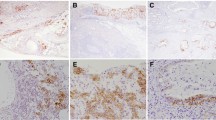
Forty formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded gastric tissues, obtained from patients who underwent endoscopic resection or surgical resection, constituted the group of our study. The immunohistochemical expression of cyclin D1 and CD44 was examined and correlated with clinical-pathological parameters and outcome of the patients.
Results
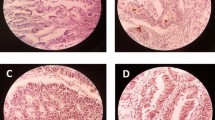
Overexpression of CD44 and cyclin D1 was noted (in of 55 and 50% respectively). Cyclin D1 and CD44 positive expressions in GC were positively correlated with tumor differentiation (p = 0.020, p = 0.004 respectively), TNM stage (p < 0.001 for both), poor survival (p < 0.001 for both), and with increased rate of recurrence (p = 0.020, p = 0.005 respectively).
Conclusion
CD44 and cyclin D1 were associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer, and so, they comprise an attractive target for anticancer drug development.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, et al. GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 11 [Internet].Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2013. Available from: http://globocan.iarc.fr. Accessed on day/month/year.
Zeen eldein AA, Ramadan H, El Gamal MM, Saber MM, Elgamal D, Sherisher MA. Gastric carcinoma at Tanta Cancer Center: a comparative retrospective clinicopathological study of the elderly versus the non-elderly. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2014;26:127–37.
The National Cancer Registry Program of Egypt (NCRPE). Reports and Statistics: Aswan, Damietta & El-Minia [Internet]. [cited 2014 Feb 22]. Available from: http://www.Cancerregistry.gov.eg/oops.aspx?aspxerrorpath=/publications.aspx.
Zhang X, Zhou C, Gu H, Yan L, Zhang G. Original article correlation of RKIP, STAT3 and cyclin D1 expression in the pathogenesis of gastric cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(9):5902–8.
Boman BM, Wicha MS. Cancer stem cells: a step toward the cure. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2008;26(17):2795–9.
Nishii T, Yashiro M, Shinto O, Sawada T, Ohira M, Hirakawa K. Cancer stem cell-like SP cells have a high adhesion ability to the peritoneum in gastric carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2009;100(8):1397–402.
Naor D, Sionov R, Ish-Shalom D. CD44: structure, function, and association with the malignant process. Adv Cancer Res. 1997;71:241–319.
Negi LM, Talegaonkar S, Manu Jaggi FJA, Iqbal Z, Khar RK. Role of CD44 in tumor progression and strategies for targeting. J Drug Target. 2012;20(7):561–73.
Takaishi S, Okumura T, Tu S, Wang SS, Shibata W, Vigneshwaran R, et al. Identification of gastric cancer stem cells using the cell surface marker CD44. Stem Cells. 2009;27(5):1006–20.
Liu D, Sun J, Zhu J, Zhou H, Zhang X, Zhang Y. Expression and clinical significance of colorectal cancer stem cell marker EpCAMhigh/CD44+ in colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett. 2014;7:1544–8.
Diehl JA, Cheng M, Roussel MF, Sherr CJ. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta regulates cyclin D1 proteolysis and subcellular localization. Genes Dev. 1998;12(22):3499–511.
Hall M, Peters G. Genetic alterations of cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, and Cdk inhibitors in human cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1996;68:67–108.
Alao JP. The regulation of cyclin D1 degradation: roles in cancer development and the potential for therapeutic invention. Mol Cancer. 2007;6:24.
Edge SB, Compton CC. The American Joint Committee on Cancer: the 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17(6):1471–4. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-010-0985-4.
Khoo ML, Beasley NJ, Ezzat SJ, Freeman LASL. Overexpression of cyclin D1 and underexpression of p27 predicts lymph node metastases in papillary thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:1814–8.
Ghaffarzadehgan K, Jaffarzadhen M, Raziel H, Sima H, Esmaili E, Hosseinnezhad H, et al. Expression of cell adhesion molecule Cd44 in gastric adenocarcinoma and its prognostic importance. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14(41):6376–81.
Wang Y, Liu Y, Xiao B. Rapid and reliable detection of CD44 variants in gastric carcinoma using a nested reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Oncol Lett. 2015;10(5):2962–6.
Minarikova P, Benesova L, Halkova T, Belsanova B, Tuckova I, Belina F, et al. Prognostic importance of cell cycle regulators cyclin D1 (CCND1) and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B (CDKN1B/p27) in sporadic gastric cancers. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2016;2016:9408190.
Yan Y, Zuo OX, We D. Concise review: emerging role of CD44 in cancer stem cells: a promising biomarker and therapeutic target. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4(9):1033–43.
Nosrati A, Naghshvar F, Khanari S. Cancer stem cell markers CD44, CD133 in primary gastric adenocarcinoma. Int J Mol Cell Med. 2014;3(4):279–86.
Feakins RM, Nickols CD, Bidd H, Walton SJ. Abnormal expression of pRb, p16, and cyclin D1 in gastric adenocarcinoma and its lymph node metastases: relationship with pathological features and survival. Hum Pathol. 2003;34(12):1276–82.
Begnami MD, Fregnani JTG, Nonogaki S, Soares F. Evaluation of cell cycle protein expression in gastric cancer: cyclin B1 expression and its prognostic implication. Hum Pathol. 2010;41:1120–7.
Casasola SV, Menéndez MJ, Martínez OA, Rodríguez JM. Prognostic value of clinicopathologic factors Ki67, cyclin D1, cyclin D3 and CDK4 in gastric carcinoma. Oncologia. 2004;27(9):537–43.
Arici DS, Tuncer E, Ozer H, Sime KG, Koyuncu A. Expression of retinoblastoma and cyclin D1 in gastric carcinoma. Neoplasma. 2009;56:1.
Takano Y, Kato Y, Masuda M, Ohshima Y, Okayasu I. Cyclin D2, but not cyclin D1, overexpression closely correlates with gastric cancer progression and prognosis. J Pathol. 1999;189:194–200.
Jares P, Colomer D, Campo E. Genetic and molecular pathogenesis of mantle cell lymphoma: perspectives for new targeted therapeutics. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7(10):750–62.
Ahn MJ, Kim B, Jang SJ, Ki LM. Expression of cyclin D1 and cyclin E in human gastric carcinoma and its clinicopathologic significance. J Korean Med Sci. 1998;13(5):513–8.
Harlozinska A. Progress in molecular mechanisms of tumor metastasis and angiogenesis. Anticancer Res. 2005;25(5):3327–33.
Yasui M, Yamamoto H, Ngan C, Damdinsuren B, Sugita Y, Fukunaga H. Antisense to cyclin D1 inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor-stimulated growth of vascular endothelial cells: implication of tumor vascularization. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(15):4720–9.
Shintani M, Okazaki A, Masuda T, Kawada M, Ishizuka M, Doki Y, et al. Overexpression of cyclin DI contributes to malignant properties of esophageal tumor cells by increasing VEGF production and decreasing Fas expression. Anticancer Res. 2002;22(2A):639–47.
Yoon C, Park DJ, Schmidt B, Thomas NJ, Lee HJ, Kim TS, et al. CD44 expression denotes a subpopulation of gastric cancer cells in which hedgehog signaling promotes chemotherapy resistance. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20(15):3974–88. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0011.
Dhingra S, Feng W, Brown RE, Zhou Z, Khoury T, Zhang R, et al. Clinicopathological significance of putative stem cell markers, CD44 and nestin, in gastric adenocarcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2011;4(8):733–41.
Yamaguchi A, Goi T, Yu J, Hirono Y, Ishida M, Iida A, et al. Expression of CD44v6 in advanced gastric cancer and its relationship to hematogenous metastasis and long-term prognosis. J Surg Oncol. 2002;79(4):230–5.
Kim JY, Bae BN, Kim KS, Shin E, Kl P. Osteopontin, CD44, and NF-kappa B expression in gastric adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res Treat. 2009;41(1):29–35.
Wang T, Ong C, Shi J, Srivastava S, Yan B, Cheng C, et al. Sequential expression of putative stem cell markers in gastric carcinogenesis. Br J Cancer. 2011;105:658–65.
Zavrides HN, Zizi-Sermpetzoglou A, Panousopoulos D, Athanasios G, Elemenoglou I, Peros G. Prognostic evaluation of the CD44 expression in correlation with BCL-2 and p53 in colorectal cancer. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2005;43(1):31–6.
Chen Y, Fu Z, Xu S, Xu Y, Xu P. The prognostic value of the CD44 expression in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2014;68:693–7.
Cao X, Cao D, Jin M, Jia Z, Kong F, Ma H, et al. CD44 but not CD24 expression is related to poor prognosis in non-cardia adenocarcinoma of the stomach. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014;14:157.
Yong C, Yang C, Chou Y, Liao C, Lee CW, Lee CC. Cd44\Cd24 expression in recurrent gastric cancer: a retrospective analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012;12:95.
Chen W, Zhang X, Chu C, Cheung W, Ng L, Lam S, et al. Identification of Cd44 positive cancer stem cell in human gastric cancer. Hepato-Gastroenterology. 2013;60(124):949–54.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
(I) Conception and design: Hanaa M. Ibrahim and Amr Ibrahim. (II) Administrative support: Abeer M. Abdelbary and Salem Y Mohamed. (III). Provision of study materials or patients: Hanaa M. Ibrahim, Abeer M Abdelbary, and Mohamed I Abdelhamid (IV). Collection and assembly of data: Hanaa M. Ibrahim and Salem Y Mohamed. (V) Data analysis and interpretation: All authors. (VI) Manuscript writing: All authors. (VII) Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ibrahim, H.M., AbdElbary, A.M., Mohamed, S.Y. et al. Prognostic Value of Cyclin D1 and CD44 Expression in Gastric Adenocarcinoma. J Gastrointest Canc 50, 370–379 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-018-0079-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-018-0079-2