Abstract
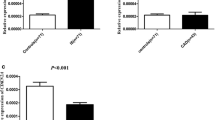
A quantitative transcriptomics analysis has reported that Calmodulin 1 (CALM1) is highly expressed in human brain tissues. This study aims to evaluate the relationship between CALM1 rs3179089 polymorphism and ischemic stroke (IS) in Chinese Han population. A total of 550 patients with IS and 550 control subjects were recruited and genotyped using Sequenom MassArray technology. The mRNA expression of CALM1 was measured using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. CALM1 mRNA expression was significantly higher in patients with IS than that in control subjects (P = 0.006). The genomic frequency distribution was significantly different between female patients with IS and female controls (χ2 = 6.043, P = 0.047). In recessive model, CALM1 rs3179089 polymorphism was associated with the risk of IS in female patients. GG genotype significantly increased the risk of IS compared with the CC+GC genotype in females (OR 8.68, P = 0.042; adjusted OR 8.72, Padj = 0.042). Rs3179089 polymorphism was associated positively with plasmas D-Dimer of patients with IS in recessive model (βa = 3.24, P = 0.018; βb = 3.20, Padj = 0.019). Moreover, rs3179089 polymorphism was related positively to thrombin time of patients with IS in addictive (βa = 2.32, P = 0.005, βb = 2.26, Padj=0.006) and recessive model (βa = 11.19, P = 0.001, βb = 11.13, Padj = 0.001). CALM1 expression was involved in the development of IS. CALM1 rs3179089 polymorphism was associated with IS risk in Chinese females, and related to blood coagulation of IS patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azghandi, S., Prell, C., van der Laan, S. W., Schneider, M., Malik, R., Berer, K., et al. (2015). Deficiency of the stroke relevant HDAC9 gene attenuates atherosclerosis in accord with allele-specific effects at 7p21.1. Stroke, 46(1), 197–202.
Boczek, N. J., Gomez-Hurtado, N., Ye, D., Calvert, M. L., Tester, D. J., Kryshtal, D., et al. (2016). Spectrum and prevalence of CALM1-, CALM2-, and CALM3-encoded calmodulin variants in long QT syndrome and functional characterization of a novel long QT syndrome-associated calmodulin missense variant, E141G. Circulation: Cardiovascular Genetics, 9(2), 136–146.
Boehme, A. K., Esenwa, C., & Elkind, M. S. (2017). Stroke risk factors, genetics, and prevention. Circulation Research, 120(3), 472–495.
Celi, A., Lorenzet, R., Furie, B. C., & Furie, B. (2004). Microparticles and a P-selectin-mediated pathway of blood coagulation. Disease Markers, 20(6), 347–352.
Chen, C., Li, Q., Nie, X., Han, B., Chen, Y., Xia, F., et al. (2017). Association of lead exposure with cardiovascular risk factors and diseases in Chinese adults. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24, 22275–22283.
Chin, D., & Means, A. R. (2000). Calmodulin: A prototypical calcium sensor. Trends in Cell Biology, 10(8), 322–328.
Cordazzo, C., Neri, T., Petrini, S., Lombardi, S., Balia, C., Cianchetti, S., et al. (2013). Angiotensin II induces the generation of procoagulant microparticles by human mononuclear cells via an angiotensin type 2 receptor-mediated pathway. Thrombosis Research, 131(4), e168–e174.
Cordazzo, C., Petrini, S., Neri, T., Lombardi, S., Carmazzi, Y., Pedrinelli, R., et al. (2014). Rapid shedding of proinflammatory microparticles by human mononuclear cells exposed to cigarette smoke is dependent on Ca2+ mobilization. Inflammation Research, 63(7), 539–547.
Distler, J. H., & Distler, O. (2010). Inflammation: Microparticles and their roles in inflammatory arthritides. Nature Reviews Rheumatology, 6(7), 385–386.
Distler, J. H., Huber, L. C., Gay, S., Distler, O., & Pisetsky, D. S. (2006). Microparticles as mediators of cellular cross-talk in inflammatory disease. Autoimmunity, 39(8), 683–690.
Fagerberg, L., Hallstrom, B. M., Oksvold, P., Kampf, C., Djureinovic, D., Odeberg, J., et al. (2014). Analysis of the human tissue-specific expression by genome-wide integration of transcriptomics and antibody-based proteomics. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 13(2), 397–406.
Falati, S., Liu, Q., Gross, P., Merrill-Skoloff, G., Chou, J., Vandendries, E., et al. (2003). Accumulation of tissue factor into developing thrombi in vivo is dependent upon microparticle P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 and platelet P-selectin. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 197(11), 1585–1598.
Gu, L., Huang, J., Liang, B., Chen, Q., Xie, J., Yang, J., et al. (2018). TLR4 polymorphisms affect stroke risk and inflammatory response in Chinese ischemic stroke patients. Neurological Sciences, 39(1), 127–133.
Haast, R. A., Gustafson, D. R., & Kiliaan, A. J. (2012). Sex differences in stroke. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism, 32(12), 2100–2107.
Han, T. S., Wang, H. H., Wei, L., Pan, Y., Ma, Y., Wang, Y., et al. (2017). Impacts of undetected and inadequately treated hypertension on incident stroke in China. British Medical Journal Open, 7(10), e016581.
Hanley, R. M., Shenolikar, S., Pollack, J., Steplock, D., & Weinman, E. J. (1990). Identification of calcium-calmodulin multifunctional protein kinase II in rabbit kidney. Kidney International, 38(1), 63–66.
Kraft, P., Schuhmann, M. K., Garz, C., Jandke, S., Urlaub, D., Mencl, S., et al. (2017). Hypercholesterolemia induced cerebral small vessel disease. PLoS ONE, 12(8), e0182822.
Leroyer, A. S., Anfosso, F., Lacroix, R., Sabatier, F., Simoncini, S., Njock, S. M., et al. (2010). Endothelial-derived microparticles: Biological conveyors at the crossroad of inflammation, thrombosis and angiogenesis. Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 104(3), 456–463.
Lewsey, J. D., Gillies, M., Jhund, P. S., Chalmers, J. W., Redpath, A., Briggs, A., et al. (2009). Sex differences in incidence, mortality, and survival in individuals with stroke in Scotland, 1986 to 2005. Stroke, 40(4), 1038–1043.
Li, S. H., Shi, C. H., Li, Y. S., Li, F., Tang, M. B., Liu, X. J., et al. (2017). Association of GWAS-reported variant rs11196288 near HABP2 with ischemic stroke in Chinese Han Population. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 62(2), 209–214.
Loo, K. W., & Gan, S. H. (2012). Burden of stroke in Malaysia. International Journal of Stroke, 7(2), 165–167.
Luke, M. M., O’Meara, E. S., Rowland, C. M., Shiffman, D., Bare, L. A., Arellano, A. R., et al. (2009). Gene variants associated with ischemic stroke: the cardiovascular health study. Stroke, 40(2), 363–368.
Moha Ou Maati, H. C, Widmann, D., Sedjelmaci, B., Gallois, C., Heurteaux, M., et al. (2013). Mapacalcine protects mouse neurons against hypoxia by blocking cell calcium overload. PLoS ONE, 8(7), e66194.
Moisoi, N., Erent, M., Whyte, S., Martin, S., & Bayley, P. M. (2002). Calmodulin-containing substructures of the centrosomal matrix released by microtubule perturbation. Journal of Cell Science, 115(Pt 11), 2367–2379.
Neri, T., Armani, C., Pegoli, A., Cordazzo, C., Carmazzi, Y., Brunelleschi, S., et al. (2011). Role of NF-kappaB and PPAR-gamma in lung inflammation induced by monocyte-derived microparticles. European Respiratory Journal, 37(6), 1494–1502.
Neri, T., Cordazzo, C., Carmazzi, Y., Petrini, S., Balia, C., Stefanelli, F., et al. (2012). Effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonists on the generation of microparticles by monocytes/macrophages. Cardiovascular Research, 94(3), 537–544.
Otite, F. O., Liaw, N., Khandelwal, P., Malik, A. M., Romano, J. G., Rundek, T., et al. (2017). Increasing prevalence of vascular risk factors in patients with stroke: A call to action. Neurology, 89, 1985–1994.
Oury, C., Sticker, E., Cornelissen, H., De Vos, R., Vermylen, J., & Hoylaerts, M. F. (2004). ATP augments von Willebrand factor-dependent shear-induced platelet aggregation through Ca2+-calmodulin and myosin light chain kinase activation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279(25), 26266–26273.
Petrea, R. E., Beiser, A. S., Seshadri, S., Kelly-Hayes, M., Kase, C. S., & Wolf, P. A. (2009). Gender differences in stroke incidence and poststroke disability in the Framingham heart study. Stroke, 40(4), 1032–1037.
Poorthuis, M. H., Algra, A. M., Algra, A., Kappelle, L. J., & Klijn, C. J. (2017). Female- and male-specific risk factors for stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Neurology, 74(1), 75–81.
Rothwell, P. M., Coull, A. J., Silver, L. E., Fairhead, J. F., Giles, M. F., Lovelock, C. E., et al. (2005). Population-based study of event-rate, incidence, case fatality, and mortality for all acute vascular events in all arterial territories (Oxford Vascular Study). Lancet, 366(9499), 1773–1783.
Saiz, L. C., Gorricho, J., Garjon, J., Celaya, M. C., Muruzabal, L., Malon, M. D. M., et al. (2017). Blood pressure targets for the treatment of people with hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 10, CD010315.
Samai, A. A., & Martin-Schild, S. (2015). Sex differences in predictors of ischemic stroke: Current perspectives. Vascular Health and Risk Management, 11, 427–436.
Tang, L. H., Xia, Z. Y., Zhao, B., Wei, X. D., Luo, T., & Meng, Q. T. (2011). Phosphocreatine preconditioning attenuates apoptosis in ischemia-reperfusion injury of rat brain. Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology, 2011, 107091.
Teng, M. S., Hsu, L. A., Juan, S. H., Lin, W. C., Lee, M. C., Su, C. W., et al. (2017). A GDF15 3′ UTR variant, rs1054564, results in allele-specific translational repression of GDF15 by hsa-miR-1233-3p. PLoS ONE, 12(8), e0183187.
Titov, B. V., Matveeva, N. A., Martynov, M. Y., & Favorova, O. O. (2016). Multilocus analysis of the association of polymorphic variants of inflammation genes with ischemic stroke in Russians. Molecular Biology (Mosk), 50(4), 674–684.
Turtzo, L. C., & McCullough, L. D. (2008). Sex differences in stroke. Cerebrovascular Diseases, 26(5), 462–474.
Tyteca, D., van Ijzendoorn, S. C., & Hoekstra, D. (2005). Calmodulin modulates hepatic membrane polarity by protein kinase C-sensitive steps in the basolateral endocytic pathway. Experimental Cell Research, 310(2), 293–302.
VanWijk, M. J., VanBavel, E., Sturk, A., & Nieuwland, R. (2003). Microparticles in cardiovascular diseases. Cerebrovascular Diseases, 59(2), 277–287.
Wang, J., Ning, X., Yang, L., Tu, J., Gu, H., Zhan, C., et al. (2014). Sex differences in trends of incidence and mortality of first-ever stroke in rural Tianjin, China, from 1992 to 2012. Stroke, 45(6), 1626–1631.
Wang, Y., Yin, X., Li, L., Deng, S., & He, Z. (2016). Association of apolipoprotein C3 genetic polymorphisms with the risk of ischemic stroke in the Northern Chinese Han Population. PLoS ONE, 11(9), e0163910.
Xu, Z., Li, Y., Huang, X., Shen, W., Bai, J., Shen, C., et al. (2017). ESR2 genetic variants and combined oral contraceptive use associated with the risk of stroke. Archives of Medical Research, 48(2), 203–211.
Xue, W. Y., Xu, Y. C., Wu, Y. W., & Yang, M. (2017). Observation of elevated fasting blood glucose and functional outcome after ischemic stroke in patients with and without diabetes. Oncotarget, 8(40), 67980–67989.
Yin, Z., Guo, Y., Zhang, J., Zhang, Q., Li, L., Wang, S., et al. (2017). Association between an indel polymorphism in the 3′UTR of COL1A2 and the risk of sudden cardiac death in Chinese populations. Legal Medicine (Tokyo), 28, 22–26.
Yuan, M., Tang, Y., Zhou, C., Liu, F., Chen, L., & Yuan, H. (2016). Elevated plasma CaM expression in patients with acute cerebral infarction predicts poor outcomes and is inversely associated with miR-26b expression. International Journal of Neuroscience, 126(5), 408–414.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81660741; 81473670; 81573756).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The research was approved by the ethics committee of First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine.
Informed Consent
All subjects agreed with the ethics examination and signed informed consent.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, L., Huang, J., Li, J. et al. Association of CALM1 rs3179089 Polymorphism with Ischemic Stroke in Chinese Han Population. Neuromol Med 20, 271–279 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-018-8492-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-018-8492-z