Abstract
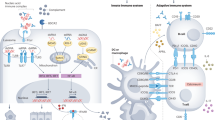
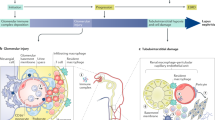
Lupus nephritis is an important cause of kidney failure in patients of Asian, African, or Hispanic descent. Its etiology and pathogenesis are multifactorial and remain to be elucidated. Accumulating evidence suggests that anti-double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) antibodies play a critical role in the pathogenesis, through its direct binding to cross-reactive antigens on resident renal cells or indirect binding through chromatin material to extracellular matrix components, resulting in complement activation, cell activation and proliferation, and induction of inflammatory and fibrotic processes. While tubulo-interstitial damage portends poor long-term renal prognosis, the mechanisms leading to tubulo-interstitial injury in lupus nephritis has received relatively less attention to date. Immune deposition along the tubular basement membrane is often observed in lupus nephritis and correlates with tubulo-interstitial infiltration of immune cells and interstitial fibrosis. Anti-dsDNA antibodies bind to resident renal cells, including proximal renal tubular epithelial cells, and contribute to renal inflammation and fibrosis. There is emerging evidence that epigenetic influence such as DNA methylation, histone modification, and microRNAs (miRs) also contribute to kidney fibrosis. Overexpression of miR-150 is observed in renal biopsies from patients with lupus nephritis and correlates with kidney fibrosis and chronicity score. Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) is an established and effective standard-of-care therapy for patients with lupus nephritis. Accumulating data suggest that in addition to its immunosuppressive actions on lymphocyte proliferation, mycophenolic acid (MPA), the active metabolite of MMF, can exert a direct effect on nonimmune cells. Mediators of inflammation and fibrosis induced by anti-dsDNA antibodies in cultured proximal renal tubular epithelial cells are ameliorated by the addition of MPA, suggesting that in addition to its immunosuppressive actions, MPA may also have a beneficial effect in improving tubulo-interstitial inflammation and fibrosis through its direct action on proximal renal tubular epithelial cells.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APOL1:
-
Apolipoprotein 1
- CDR:
-
Complementarity-determining region
- CpG:
-
Cytosine-phosphate-guanine
- DNMT1:
-
DNA methyltransferase 1
- dsDNA:
-
Double-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- GBM:
-
Glomerular basement membrane
- HAS2:
-
Hyaluronan synthase 2
- HDAC:
-
Histone deacetylase
- HLA:
-
Human leukocyte antigen
- IgG:
-
Immunoglobulin G
- IgM:
-
Immunoglobulin M
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- IL-8:
-
Interleukin-8
- IMPDH:
-
Inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase
- ITGAM:
-
Integrin alpha M
- JNK:
-
C-Jun N-terminal kinase
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MCP-1:
-
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
- MHC:
-
Major histocompatibility complex
- miR:
-
MicroRNA
- MMF:
-
Mycophenolate mofetil
- MPA:
-
Mycophenolic acid
- NFκB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa B
- NZB/W:
-
New Zealand black and white
- PDGFRA:
-
Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha
- PKC:
-
Protein kinase C
- PTEC:
-
Proximal renal tubular epithelial cells
- RASAL1:
-
Ras-GTPase-activating-like protein 1
- RNA:
-
Ribonucleic acid
- SCID:
-
Severe combined immunodeficiency
- SLE:
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus
- snRNP protein:
-
Small nuclear ribonuclear protein
- SOCS1:
-
Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1
- ss:
-
Single-stranded
- STAT4:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 4
- TGF-β1:
-
Transforming growth factor beta1
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
- TNFSF4:
-
Tumor necrosis factor superfamily member 4
- TRL:
-
Toll-like receptor
- UUO:
-
Unilateral urethral obstruction
References
Magil AB, Tyler M (1984) Tubulo-interstitial disease in lupus nephritis. A morphometric study. Histopathology 8:81–87
Yung S, Tsang RC, Sun Y, Leung JK, Chan TM (2005) Effect of human anti-DNA antibodies on proximal renal tubular epithelial cell cytokine expression: implications on tubulointerstitial inflammation in lupus nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:3281–3294
Schwartz MM, Fennell JS, Lewis EJ (1982) Pathologic changes in the renal tubule in systemic lupus erythematosus. Hum Pathol 13:534–547
Foster MH (2007) T cells and B cells in lupus nephritis. Semin Nephrol 27:47–58
Okamoto A, Fujio K, Tsuno NH, Takahashi K, Yamamoto K (2012) Kidney-infiltrating CD4+ T-cell clones promote nephritis in lupus-prone mice. Kidney Int 82:969–979
Kelley VR (2007) Leukocyte-renal epithelial cell interactions regulate lupus nephritis. Semin Nephrol 27:59–68
Rahman A, Isenberg DA (2008) Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 358:929–939
Yung S, Chan TM (2012) Autoantibodies and resident renal cells in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis: getting to know the unknown. Clin Dev Immunol 2012:139365
Hahn BH (1998) Antibodies to DNA. N Engl J Med 338:1359–1368
Rahman A, M. MJ, Isenberg D (2011) Autoantibodies and lupus nephritis. In: Lewis EJ, Schwartz MM, Korbet SM, Chan TM (eds) Lupus nephritis. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 35–58
Arbuckle MR, McClain MT, Rubertone MV, Scofield RH, Dennis GJ, James JA, Harley JB (2003) Development of autoantibodies before the clinical onset of systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 349:1526–1533
Chan TM, Leung JK, Ho SK, Yung S (2002) Mesangial cell-binding anti-DNA antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:1219–1229
Isenberg DA, Manson JJ, Ehrenstein MR, Rahman A (2007) Fifty years of anti-ds DNA antibodies: are we approaching journey’s end? Rheumatology (Oxford) 46:1052–1056
Yung S, Cheung KF, Zhang Q, Chan TM (2010) Anti-dsDNA antibodies bind to mesangial annexin II in lupus nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:1912–1927
D'Andrea DM, Coupaye-Gerard B, Kleyman TR, Foster MH, Madaio MP (1996) Lupus autoantibodies interact directly with distinct glomerular and vascular cell surface antigens. Kidney Int 49:1214–1221
Suzuki M, Hatakeyama A, Kameoka J, Tamate E, Yusa A, Kurosawa K, Saito T, Sasaki T, Yoshinaga K (1991) Anti-DNA idiotypes deposited in renal glomeruli of patients with lupus nephritis. Am J Kidney Dis 18:232–239
Vlahakos DV, Foster MH, Adams S, Katz M, Ucci AA, Barrett KJ, Datta SK, Madaio MP (1992) Anti-DNA antibodies form immune deposits at distinct glomerular and vascular sites. Kidney Int 41:1690–1700
Raz E, Brezis M, Rosenmann E, Eilat D (1989) Anti-DNA antibodies bind directly to renal antigens and induce kidney dysfunction in the isolated perfused rat kidney. J Immunol 142:3076–3082
Kieber-Emmons T, Foster MH, Williams WV, Madaio MP (1994) Structural properties of a subset of nephritogenic anti-DNA antibodies. Immunol Res 13:172–185
Foster MH, Cizman B, Madaio MP (1993) Nephritogenic autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus: immunochemical properties, mechanisms of immune deposition, and genetic origins. Lab Investig 69:494–507
Isenberg DA, Ehrenstein MR, Longhurst C, Kalsi JK (1994) The origin, sequence, structure, and consequences of developing anti-DNA antibodies. A human perspective. Arthritis Rheum 37:169–180
Krishnan MR, Wang C, Marion TN (2012) Anti-DNA autoantibodies initiate experimental lupus nephritis by binding directly to the glomerular basement membrane in mice. Kidney Int 82:184–192
Berden JH, Licht R, van Bruggen MC, Tax WJ (1999) Role of nucleosomes for induction and glomerular binding of autoantibodies in lupus nephritis. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 8:299–306
Rekvig OP, Nossent JC (2003) Anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies, nucleosomes, and systemic lupus erythematosus: a time for new paradigms? Arthritis Rheum 48:300–312
Kalaaji M, Mortensen E, Jorgensen L, Olsen R, Rekvig OP (2006) Nephritogenic lupus antibodies recognize glomerular basement membrane-associated chromatin fragments released from apoptotic intraglomerular cells. Am J Pathol 168:1779–1792
Kalaaji M, Fenton KA, Mortensen ES, Olsen R, Sturfelt G, Alm P, Rekvig OP (2007) Glomerular apoptotic nucleosomes are central target structures for nephritogenic antibodies in human SLE nephritis. Kidney Int 71:664–672
Kramers C, Hylkema MN, van Bruggen MC, van de Lagemaat R, Dijkman HB, Assmann KJ, Smeenk RJ, Berden JH (1994) Anti-nucleosome antibodies complexed to nucleosomal antigens show anti-DNA reactivity and bind to rat glomerular basement membrane in vivo. J Clin Invest 94:568–577
Mortensen ES, Fenton KA, Rekvig OP (2008) Lupus nephritis: the central role of nucleosomes revealed. Am J Pathol 172:275–283
Ng KP, Manson JJ, Rahman A, Isenberg DA (2006) Association of antinucleosome antibodies with disease flare in serologically active clinically quiescent patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 55:900–904
Simon JA, Cabiedes J, Ortiz E, Alcocer-Varela J, Sanchez-Guerrero J (2004) Anti-nucleosome antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus of recent onset. Potential utility as a diagnostic tool and disease activity marker. Rheumatology 43:220–224
Mortensen ES, Rekvig OP (2009) Nephritogenic potential of anti-DNA antibodies against necrotic nucleosomes. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:696–704
Waldman M, Madaio MP (2005) Pathogenic autoantibodies in lupus nephritis. Lupus 14:19–24
Mostoslavsky G, Fischel R, Yachimovich N, Yarkoni Y, Rosenmann E, Monestier M, Baniyash M, Eilat D (2001) Lupus anti-DNA autoantibodies cross-react with a glomerular structural protein: a case for tissue injury by molecular mimicry. Eur J Immunol 31:1221–1227
Deocharan B, Qing X, Lichauco J, Putterman C (2002) Alpha-actinin is a cross-reactive renal target for pathogenic anti-DNA antibodies. J Immunol 168:3072–3078
Termaat RM, Assmann KJ, van Son JP, Dijkman HB, Koene RA, Berden JH (1993) Antigen-specificity of antibodies bound to glomeruli of mice with systemic lupus erythematosus-like syndromes. Lab Investig 68:164–173
Haramoto T, Makino H, Ikeda S, Wieslander J, Ota Z (1994) Ultrastructural localization of the three major basement membrane components - type IV collagen, heparan sulfate proteoglycan and laminin - in human membranous glomerulonephritis. Am J Nephrol 14:30–36
Faaber P, Rijke TP, van de Putte LB, Capel PJ, Berden JH (1986) Cross-reactivity of human and murine anti-DNA antibodies with heparan sulfate. The major glycosaminoglycan in glomerular basement membranes. J Clin Investig 77:1824–1830
Koren E, Koscec M, Wolfson-Reichlin M, Ebling FM, Tsao B, Hahn BH, Reichlin M (1995) Murine and human antibodies to native DNA that cross-react with the A and D SnRNP polypeptides cause direct injury of cultured kidney cells. J Immunol 154:4857–4864
Giannakakis K, Faraggiana T (2011) Histopathology of lupus nephritis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 40:170–180
Yung S, Zhang Q, Chau MK, Chan TM (2015) Distinct effects of mycophenolate mofetil and cyclophosphamide on renal fibrosis in NZBWF1/J mice. Autoimmunity 48:471–487
Yung S, Ng CY, Ho SK, Cheung KF, Chan KW, Zhang Q, Chau MK, Chan TM (2015) Anti-dsDNA antibody induces soluble fibronectin secretion by proximal renal tubular epithelial cells and downstream increase of TGF-beta1 and collagen synthesis. J Autoimmun 58:111–122
Copeland JW, Beaumont BW, Merrilees MJ, Pilmore HL (2007) Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of human proximal tubular epithelial cells: effects of rapamycin, mycophenolate, cyclosporin, azathioprine, and methylprednisolone. Transplantation 83:809–814
Liu Y (2004) Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in renal fibrogenesis: pathologic significance, molecular mechanism, and therapeutic intervention. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:1–12
Wynn T (2008) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of fibrosis. J Pathol 214:199–210
Zeisberg M, Duffield JS (2010) Resolved: EMT produces fibroblasts in the kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:1247–1253
Iwano M, Plieth D, Danoff TM, Xue C, Okada H, Neilson EG (2002) Evidence that fibroblasts derive from epithelium during tissue fibrosis. J Clin Invest 110:341–350
Yang J, Liu Y (2001) Dissection of key events in tubular epithelial to myofibroblast transition and its implications in renal interstitial fibrosis. Am J Pathol 159:1465–1475
Eddy AA (2000) Molecular basis of renal fibrosis. Pediatr Nephrol 15:290–301
Liu Y (2010) New insights into epithelial-mesenchymal transition in kidney fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:212–222
Powell DW, Bertram CC, Cummins TD, Barati MT, Zheng S, Epstein PN, Klein JB (2009) Renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis in OVE26 type 1 diabetic mice. Nephron Exp Nephrol 111:e11–19
Yamamoto T, Noble NA, Miller DE, Border WA (1994) Sustained expression of TGF-beta 1 underlies development of progressive kidney fibrosis. Kidney Int 45:916–927
Eddy AA (1996) Molecular insights into renal interstitial fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 7:2495–2508
Rastaldi MP, Ferrario F, Giardino L, Dell'Antonio G, Grillo C, Grillo P, Strutz F, Muller GA, Colasanti G, D'Amico G (2002) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition of tubular epithelial cells in human renal biopsies. Kidney Int 62:137–146
Rastaldi MP (2006) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its implications for the development of renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis. J Nephrol 19:407–412
Gharaee-Kermani M, Wiggins R, Wolber F, Goyal M, Phan SH (1996) Fibronectin is the major fibroblast chemoattractant in rabbit anti-glomerular basement membrane disease. Am J Pathol 148:961–967
Hynes RO, Yamada KM (1982) Fibronectins: multifunctional modular glycoproteins. J Cell Biol 95:369–377
Singh P, Carraher C, Schwarzbauer JE (2010) Assembly of fibronectin extracellular matrix. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 26:397–419
Sechler JL, Corbett SA, Schwarzbauer JE (1997) Modulatory roles for integrin activation and the synergy site of fibronectin during matrix assembly. Mol Biol Cell 8:2563–2573
Burger A, Wagner C, Viedt C, Reis B, Hug F, Hansch GM (1998) Fibronectin synthesis by human tubular epithelial cells in culture: effects of PDGF and TGF-beta on synthesis and splicing. Kidney Int 54:407–415
Vesey DA, Cheung CW, Cuttle L, Endre ZA, Gobe G, Johnson DW (2002) Interleukin-1beta induces human proximal tubule cell injury, alpha-smooth muscle actin expression and fibronectin production. Kidney Int 62:31–40
Yung S, Zhang Q, Zhang CZ, Chan KW, Lui SL, Chan TM (2009) Anti-DNA antibody induction of protein kinase C phosphorylation and fibronectin synthesis in human and murine lupus and the effect of mycophenolic acid. Arthritis Rheum 60:2071–2082
Weston BS, Wahab NA, Roberts T, Mason RM (2001) Bacitracin inhibits fibronectin matrix assembly by mesangial cells in high glucose. Kidney Int 60:1756–1764
Murphy-Ullrich JE, Oberley TD, Mosher DF (1986) Serologic and pathologic studies of mice immunized with homologous fibronectin. Am J Pathol 125:182–190
Fujii H, Nakatani K, Arita N, Ito MR, Terada M, Miyazaki T, Yoshida M, Ono M, Fujiwara T, Saiga K, Ota T, Ohtani H, Lockwood M, Sasaki T, Nose M (2003) Internalization of antibodies by endothelial cells via fibronectin implicating a novel mechanism in lupus nephritis. Kidney Int 64:1662–1670
Atta MS, Powell RJ, Hopkinson ND, Todd I (1994) Human anti-fibronectin antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus: occurrence and antigenic specificity. Clin Exp Immunol 96:20–25
Carsons S (1987) High levels of fibronectin fragments in the plasma of a patient with active systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 14:1052–1054
Nishinarita S, Yamamoto M, Takizawa T, Hayakawa J, Karasaki M, Sawada S (1990) Increased plasma fibronectin in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol 9:214–219
Nowling TK, Gilkeson GS (2011) Mechanisms of tissue injury in lupus nephritis. Arthritis Res Ther 13:250
Strutz F, Neilson EG (2003) New insights into mechanisms of fibrosis in immune renal injury. Springer Semin Immunopathol 24:459–476
Baelde HJ, Eikmans M, van Vliet AI, Bergijk EC, de Heer E, Bruijn JA (2004) Alternatively spliced isoforms of fibronectin in immune-mediated glomerulosclerosis: the role of TGFbeta and IL-4. J Pathol 204:248–257
van Vliet AI, van Alderwegen IE, Baelde HJ, de Heer E, Bruijn JA (2002) Fibronectin accumulation in glomerulosclerotic lesions: self-assembly sites and the heparin II binding domain. Kidney Int 61:481–489
Bergijk EC, Baelde HJ, De Heer E, Killen PD, Bruijn JA (1995) Specific accumulation of exogenous fibronectin in experimental glomerulosclerosis. J Pathol 176:191–199
Ronda N, Cravedi P, Benozzi L, Lunghi P, Bonati A, Allegri L, Carnevali ML, Caserta C, Borghetti A, Buzio C (2005) Early proinflammatory activation of renal tubular cells by normal and pathologic IgG. Nephron Exp Nephrol 100:e77–84
Nagafuchi H, Suzuki N, Mizushima Y, Sakane T (1993) Constitutive expression of IL-6 receptors and their role in the excessive B cell function in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol 151:6525–6534
Finck BK, Chan B, Wofsy D (1994) Interleukin 6 promotes murine lupus in NZB/NZW F1 mice. J Clin Invest 94:585–591
Tesch GH, Maifert S, Schwarting A, Rollins BJ, Kelley VR (1999) Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1-dependent leukocytic infiltrates are responsible for autoimmune disease in MRL-Fas(lpr) mice. J Exp Med 190:1813–1824
Rovin BH, Lu L, Zhang X (2002) A novel interleukin-8 polymorphism is associated with severe systemic lupus erythematosus nephritis. Kidney Int 62:261–265
Iwata Y, Wada T, Furuichi K, Sakai N, Matsushima K, Yokoyama H, Kobayashi K (2003) p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase contributes to autoimmune renal injury in MRL-Fas lpr mice. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:57–67
Molad Y, Amit-Vazina M, Bloch O, Yona E, Rapoport MJ (2009) Increased ERK and JNK activities correlate with disease activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus patients. Ann Rheum Dis 69:175–180
Border WA (1994) Transforming growth factor-beta and the pathogenesis of glomerular diseases. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 3:54–58
Border WA, Noble NA (1994) Transforming growth factor beta in tissue fibrosis. N Engl J Med 331:1286–1292
Yamamoto T, Noble NA, Cohen AH, Nast CC, Hishida A, Gold LI, Border WA (1996) Expression of transforming growth factor-beta isoforms in human glomerular diseases. Kidney Int 49:461–469
Yamamoto K, Loskutoff DJ (2000) Expression of transforming growth factor-beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the plasma and tissues of mice with lupus nephritis. Lab Investig 80:1561–1570
Peterson KS, Huang JF, Zhu J, D'Agati V, Liu X, Miller N, Erlander MG, Jackson MR, Winchester RJ (2004) Characterization of heterogeneity in the molecular pathogenesis of lupus nephritis from transcriptional profiles of laser-captured glomeruli. J Clin Invest 113:1722–1733
Pankov R, Yamada KM (2002) Fibronectin at a glance. J Cell Sci 115:3861–3863
Ren L, Blanchette JB, White LR, Clark SA, Heffner DJ, Tibbles LA, Muruve DA (2005) Soluble fibronectin induces chemokine gene expression in renal tubular epithelial cells. Kidney Int 68:2111–2120
Hayman EG, Pierschbacher MD, Ruoslahti E (1985) Detachment of cells from culture substrate by soluble fibronectin peptides. J Cell Biol 100:1948–1954
Chan TM, Li FK, Tang CS, Wong RW, Fang GX, Ji YL, Lau CS, Wong AK, Tong MK, Chan KW, Lai KN (2000) Efficacy of mycophenolate mofetil in patients with diffuse proliferative lupus nephritis. Hong Kong-Guangzhou Nephrology Study Group. N Engl J Med 343:1156–1162
Chan TM, Tse KC, Tang CS, Mok MY, Li FK (2005) Long-term study of mycophenolate mofetil as continuous induction and maintenance treatment for diffuse proliferative lupus nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:1076–1084
Ginzler EM, Dooley MA, Aranow C, Kim MY, Buyon J, Merrill JT, Petri M, Gilkeson GS, Wallace DJ, Weisman MH, Appel GB (2005) Mycophenolate mofetil or intravenous cyclophosphamide for lupus nephritis. N Engl J Med 353:2219–2228
Allison AC (2005) Mechanisms of action of mycophenolate mofetil. Lupus 14(Suppl 1):s2–8
Allison AC, Eugui EM (2000) Mycophenolate mofetil and its mechanisms of action. Immunopharmacology 47:85–118
Mohacsi PJ, Tuller D, Hulliger B, Wijngaard PL (1997) Different inhibitory effects of immunosuppressive drugs on human and rat aortic smooth muscle and endothelial cell proliferation stimulated by platelet-derived growth factor or endothelial cell growth factor. J Heart Lung Transplant 16:484–492
Morath C, Reuter H, Simon V, Krautkramer E, Muranyi W, Schwenger V, Goulimari P, Grosse R, Hahn M, Lichter P, Zeier M (2008) Effects of mycophenolic acid on human fibroblast proliferation, migration and adhesion in vitro and in vivo. Am J Transplant 8:1786–1797
Chang HW, Wu VC, Wu KD, Huang HY, Hsieh BS, Chen YM (2010) In rat renal fibroblasts, mycophenolic acid inhibits proliferation and production of the chemokine CCL2, stimulated by tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Br J Pharmacol 160:1611–1620
Baer PC, Gauer S, Hauser IA, Scherberich JE, Geiger H (2000) Effects of mycophenolic acid on human renal proximal and distal tubular cells in vitro. Nephrol Dial Transplant 15:184–190
Dubus I, Vendrely B, Christophe I, Labouyrie JP, Delmas Y, Bonnet J, Combe C (2002) Mycophenolic acid antagonizes the activation of cultured human mesangial cells. Kidney Int 62:857–867
Badid C, Vincent M, McGregor B, Melin M, Hadj-Aissa A, Veysseyre C, Hartmann DJ, Desmouliere A, Laville M (2000) Mycophenolate mofetil reduces myofibroblast infiltration and collagen III deposition in rat remnant kidney. Kidney Int 58:51–61
Deng Y, Tsao BP (2014) Advances in lupus genetics and epigenetics. Curr Opin Rheumatol 26:482–492
Chung SA, Brown EE, Williams AH, Ramos PS, Berthier CC, Bhangale T, Alarcon-Riquelme ME, Behrens TW, Criswell LA, Graham DC, Demirci FY, Edberg JC, Gaffney PM, Harley JB, Jacob CO, Kamboh MI, Kelly JA, Manzi S, Moser-Sivils KL, Russell LP, Petri M, Tsao BP, Vyse TJ, Zidovetzki R, Kretzler M, Kimberly RP, Freedman BI, Graham RR, Langefeld CD (2014) Lupus nephritis susceptibility loci in women with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Am Soc Nephrol 25:2859–2870
Ge Y, Brown MG, Wang H, Fu SM (2012) Genetic approach to study lupus glomerulonephritis. Methods Mol Biol 900:271–290
Liu K, Li QZ, Yu Y, Liang C, Subramanian S, Zeng Z, Wang HW, Xie C, Zhou XJ, Mohan C, Wakeland EK (2007) Sle3 and Sle5 can independently couple with Sle1 to mediate severe lupus nephritis. Genes Immun 8:634–645
Sanchez E, Nadig A, Richardson BC, Freedman BI, Kaufman KM, Kelly JA, Niewold TB, Kamen DL, Gilkeson GS, Ziegler JT, Langefeld CD, Alarcon GS, Edberg JC, Ramsey-Goldman R, Petri M, Brown EE, Kimberly RP, Reveille JD, Vila LM, Merrill JT, Anaya JM, James JA, Pons-Estel BA, Martin J, Park SY, Bang SY, Bae SC, Moser KL, Vyse TJ, Criswell LA, Gaffney PM, Tsao BP, Jacob CO, Harley JB, Alarcon-Riquelme ME, Sawalha AH (2011) Phenotypic associations of genetic susceptibility loci in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 70:1752–1757
Freedman BI, Langefeld CD, Andringa KK, Croker JA, Williams AH, Garner NE, Birmingham DJ, Hebert LA, Hicks PJ, Segal MS, Edberg JC, Brown EE, Alarcon GS, Costenbader KH, Comeau ME, Criswell LA, Harley JB, James JA, Kamen DL, Lim SS, Merrill JT, Sivils KL, Niewold TB, Patel NM, Petri M, Ramsey-Goldman R, Reveille JD, Salmon JE, Tsao BP, Gibson KL, Byers JR, Vinnikova AK, Lea JP, Julian BA, Kimberly RP (2014) End-stage renal disease in African Americans with lupus nephritis is associated with APOL1. Arthritis Rheumatol 66:390–396
Chung SA, Taylor KE, Graham RR, Nititham J, Lee AT, Ortmann WA, Jacob CO, Alarcon-Riquelme ME, Tsao BP, Harley JB, Gaffney PM, Moser KL, Petri M, Demirci FY, Kamboh MI, Manzi S, Gregersen PK, Langefeld CD, Behrens TW, Criswell LA (2011) Differential genetic associations for systemic lupus erythematosus based on anti-dsDNA autoantibody production. PLoS Genet 7:e1001323
Waters ST, Fu SM, Gaskin F, Deshmukh US, Sung SS, Kannapell CC, Tung KS, McEwen SB, McDuffie M (2001) NZM2328: a new mouse model of systemic lupus erythematosus with unique genetic susceptibility loci. Clin Immunol 100:372–383
Deng Y, Tsao BP (2010) Genetic susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus in the genomic era. Nat Rev Rheumatol 6:683–692
Fu Q, Zhao J, Qian X, Wong JL, Kaufman KM, Yu CY, Mok MY, Harley JB, Guthridge JM, Song YW, Cho SK, Bae SC, Grossman JM, Hahn BH, Arnett FC, Shen N, Tsao BP (2011) Association of a functional IRF7 variant with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 63:749–754
Li P, Cao C, Luan H, Li C, Hu C, Zhang S, Zeng X, Zhang F, Zeng C, Li Y (2011) Association of genetic variations in the STAT4 and IRF7/KIAA1542 regions with systemic lupus erythematosus in a Northern Han Chinese population. Hum Immunol 72:249–255
Waters ST, McDuffie M, Bagavant H, Deshmukh US, Gaskin F, Jiang C, Tung KS, Fu SM (2004) Breaking tolerance to double stranded DNA, nucleosome, and other nuclear antigens is not required for the pathogenesis of lupus glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med 199:255–264
Chang YK, Yang W, Zhao M, Mok CC, Chan TM, Wong RW, Lee KW, Mok MY, Wong SN, Ng IO, Lee TL, Ho MH, Lee PP, Wong WH, Lau CS, Sham PC, Lau YL (2009) Association of BANK1 and TNFSF4 with systemic lupus erythematosus in Hong Kong Chinese. Genes Immun 10:414–420
Wandstrat A, Wakeland E (2001) The genetics of complex autoimmune diseases: non-MHC susceptibility genes. Nat Immunol 2:802–809
Deapen D, Escalante A, Weinrib L, Horwitz D, Bachman B, Roy-Burman P, Walker A, Mack TM (1992) A revised estimate of twin concordance in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 35:311–318
Bird A (2007) Perceptions of epigenetics. Nature 447:396–398
Beckerman P, Ko YA, Susztak K (2014) Epigenetics: a new way to look at kidney diseases. Nephrol Dial Transplant 29:1821–1827
Youngson NA, Whitelaw E (2008) Transgenerational epigenetic effects. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 9:233–257
Dwivedi RS, Herman JG, McCaffrey TA, Raj DS (2011) Beyond genetics: epigenetic code in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 79:23–32
Reddy MA, Natarajan R (2015) Recent developments in epigenetics of acute and chronic kidney diseases. Kidney Int 88:250–261
Jeffries MA, Sawalha AH (2015) Autoimmune disease in the epigenetic era: how has epigenetics changed our understanding of disease and how can we expect the field to evolve? Expert Rev Clin Immunol 11:45–58
Li E, Bestor TH, Jaenisch R (1992) Targeted mutation of the DNA methyltransferase gene results in embryonic lethality. Cell 69:915–926
Bird AP, Wolffe AP (1999) Methylation-induced repression - belts, braces, and chromatin. Cell 99:451–454
Esteller M (2008) Epigenetics in cancer. N Engl J Med 358:1148–1159
Zeisberg EM, Zeisberg M (2013) The role of promoter hypermethylation in fibroblast activation and fibrogenesis. J Pathol 229:264–273
Illingworth RS, Bird AP (2009) CpG islands--'a rough guide'. FEBS Lett 583:1713–1720
Reik W (2007) Stability and flexibility of epigenetic gene regulation in mammalian development. Nature 447:425–432
Weber M, Hellmann I, Stadler MB, Ramos L, Paabo S, Rebhan M, Schubeler D (2007) Distribution, silencing potential and evolutionary impact of promoter DNA methylation in the human genome. Nat Genet 39:457–466
Bestor TH (2005) Transposons reanimated in mice. Cell 122:322–325
Bechtel W, McGoohan S, Zeisberg EM, Muller GA, Kalbacher H, Salant DJ, Muller CA, Kalluri R, Zeisberg M (2010) Methylation determines fibroblast activation and fibrogenesis in the kidney. Nat Med 16:544–550
Tampe B, Tampe D, Muller CA, Sugimoto H, LeBleu V, Xu X, Muller GA, Zeisberg EM, Kalluri R, Zeisberg M (2014) Tet3-mediated hydroxymethylation of epigenetically silenced genes contributes to bone morphogenic protein 7-induced reversal of kidney fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 25:905–912
Graff JR, Herman JG, Lapidus RG, Chopra H, Xu R, Jarrard DF, Isaacs WB, Pitha PM, Davidson NE, Baylin SB (1995) E-cadherin expression is silenced by DNA hypermethylation in human breast and prostate carcinomas. Cancer Res 55:5195–5199
Corn PG, Smith BD, Ruckdeschel ES, Douglas D, Baylin SB, Herman JG (2000) E-cadherin expression is silenced by 5' CpG island methylation in acute leukemia. Clin Cancer Res 6:4243–4248
Wing MR, Devaney JM, Joffe MM, Xie D, Feldman HI, Dominic EA, Guzman NJ, Ramezani A, Susztak K, Herman JG, Cope L, Harmon B, Kwabi-Addo B, Gordish-Dressman H, Go AS, He J, Lash JP, Kusek JW, Raj DS (2014) DNA methylation profile associated with rapid decline in kidney function: findings from the CRIC study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 29:864–872
Altorok N, Sawalha AH (2013) Epigenetics in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Rheumatol 25:569–576
Kondo Y, Shen L, Cheng AS, Ahmed S, Boumber Y, Charo C, Yamochi T, Urano T, Furukawa K, Kwabi-Addo B, Gold DL, Sekido Y, Huang TH, Issa JP (2008) Gene silencing in cancer by histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation independent of promoter DNA methylation. Nat Genet 40:741–750
Tachibana M, Sugimoto K, Nozaki M, Ueda J, Ohta T, Ohki M, Fukuda M, Takeda N, Niida H, Kato H, Shinkai Y (2002) G9a histone methyltransferase plays a dominant role in euchromatic histone H3 lysine 9 methylation and is essential for early embryogenesis. Genes Dev 16:1779–1791
Irifuku T, Doi S, Sasaki K, Doi T, Nakashima A, Ueno T, Yamada K, Arihiro K, Kohno N, Masaki T (2015) Inhibition of H3K9 histone methyltransferase G9a attenuates renal fibrosis and retains klotho expression. Kidney Int
Marumo T, Hishikawa K, Yoshikawa M, Hirahashi J, Kawachi S, Fujita T (2010) Histone deacetylase modulates the proinflammatory and -fibrotic changes in tubulointerstitial injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 298:F133–141
Mishra N, Reilly CM, Brown DR, Ruiz P, Gilkeson GS (2003) Histone deacetylase inhibitors modulate renal disease in the MRL-lpr/lpr mouse. J Clin Invest 111:539–552
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136:215–233
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Lujambio A, Calin GA, Villanueva A, Ropero S, Sanchez-Cespedes M, Blanco D, Montuenga LM, Rossi S, Nicoloso MS, Faller WJ, Gallagher WM, Eccles SA, Croce CM, Esteller M (2008) A microRNA DNA methylation signature for human cancer metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:13556–13561
Tampe B, Zeisberg M (2014) Contribution of genetics and epigenetics to progression of kidney fibrosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 29 Suppl 4:iv72-79
Chandrasekaran K, Karolina DS, Sepramaniam S, Armugam A, Wintour EM, Bertram JF, Jeyaseelan K (2012) Role of microRNAs in kidney homeostasis and disease. Kidney Int 81:617–627
Wang Q, Wang Y, Minto AW, Wang J, Shi Q, Li X, Quigg RJ (2008) MicroRNA-377 is up-regulated and can lead to increased fibronectin production in diabetic nephropathy. FASEB J 22:4126–4135
Zhou H, Hasni SA, Perez P, Tandon M, Jang SI, Zheng C, Kopp JB, Austin H 3rd, Balow JE, Alevizos I, Illei GG (2013) miR-150 promotes renal fibrosis in lupus nephritis by downregulating SOCS1. J Am Soc Nephrol 24:1073–1087
Wang B, Komers R, Carew R, Winbanks CE, Xu B, Herman-Edelstein M, Koh P, Thomas M, Jandeleit-Dahm K, Gregorevic P, Cooper ME, Kantharidis P (2012) Suppression of microRNA-29 expression by TGF-beta1 promotes collagen expression and renal fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 23:252–265
Sole C, Cortes-Hernandez J, Felip ML, Vidal M, Ordi-Ros J (2015) miR-29c in urinary exosomes as predictor of early renal fibrosis in lupus nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 30:1488–1496
Wang W, Mou S, Wang L, Zhang M, Shao X, Fang W, Lu R, Qi C, Fan Z, Cao Q, Wang Q, Fang Y, Ni Z (2015) Up-regulation of Serum MiR-130b-3p Level is Associated with Renal Damage in Early Lupus Nephritis. Sci Rep 5:12644
Ryan MJ, Johnson G, Kirk J, Fuerstenberg SM, Zager RA, Torok-Storb B (1994) HK-2: an immortalized proximal tubule epithelial cell line from normal adult human kidney. Kidney Int 45:48–57
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the RGC General Research Fund (HKU 7604/10M, HKU 7607/12M, and 17126814) and Merit Award, the University of Hong Kong Small Project Funding (201007176285), UGC Matching Grant Schemes (Phases IV, V, and VI), the Estate of the late Mr. Chan Wing Hei, and kind donations from Mr. G. King and Mr. C.S. Yung. S. Yung is supported by the Wai Hung Charitable Foundation Limited and the “Yu Chiu Kwong Chair in Medicine” Endowment Fund awarded to T.M. Chan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
S. Yung and T.M. Chan declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yung, S., Chan, T.M. Molecular and Immunological Basis of Tubulo-Interstitial Injury in Lupus Nephritis: a Comprehensive Review. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol 52, 149–163 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-016-8533-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-016-8533-z