Abstract
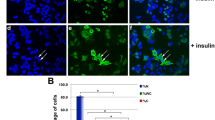
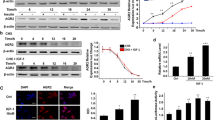
Under normal physiological conditions, IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor-1) has important biological effects. However, many studies have found that IGF-1 is closely related to the occurrence and development of breast cancer. But up to now, the cellular properties of IGF-1 have not been systematically explored in breast cancer cell. It is well-known that the cellular properties and behaviors of IGF-1/IGF-1R are closely related to its biological functions. In the current study, we used the breast cancer cell line as a model to explore the biological characteristics of IGF-1/IGF-1R, and found that IGF-1/IGF-1R can be internalized into the cytoplasm. In addition, we also found that IGF-1R can also enter cell nuclei under the mediation of IGF-1. Further research found that the nuclear-localized IGF-1R has important potential biological effects, which is closely associated to the proliferation of breast cancer cell, this may be achieved by regulating IGF-1R-mediated intracellular signaling. The current research has laid the foundation for investigating the relationship between IGF-1/IGF-1R system and the occurrence and development of breast cancer.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feng, Z., & Levine, A. J. (2010). The regulation of energy metabolism and the IGF-1/mTOR pathways by the p53 protein. Trends in Cell Biology, 20(7), 427–434.
Ascenzi, F., Barberi, L., Dobrowolny, G., Villa Nova Bacurau, A., Nicoletti, C., Rizzuto, E., & Musarò, A. (2019). Effects of IGF-1 isoforms on muscle growth and sarcopenia. Aging Cell, 18(3), e12954.
Rigiracciolo, D. C., Nohata, N., Lappano, R., Cirillo, F., Talia, M., Scordamaglia, D., & Maggiolini, M. (2020). IGF-1/IGF-1R/FAK/YAP transduction signaling prompts growth effects in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells. Cells, 9(4), 1010.
Forbes, B. E., Blyth, A. J., & Wit, J. M. (2020). Disorders of IGFs and IGF-1R signaling pathways. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 518, 1110354
Delafontaine, P., Song, Y. H., & Li, Y. (2004). Expression, regulation, and function of IGF-1, IGF-1R, and IGF-1 binding proteins in blood vessels. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 24(3), 435–444.
Troncoso, R., Ibarra, C., Vicencio, J. M., Jaimovich, E., & Lavandero, S. (2014). New insights into IGF-1 signaling in the heart. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism, 25(3), 128–137.
Shuang, T., Fu, M., Yang, G., Wu, L., & Wang, R. (2018). The interaction of IGF-1/IGF-1R and hydrogen sulfide on the proliferation of mouse primary vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochemical Pharmacology, 149, 143–152.
Baserga, R., Peruzzi, F., & Reiss, K. (2003). The IGF-1 receptor in cancer biology. International Journal of Cancer, 107(6), 873–877.
AsghariHanjani, N., & Vafa, M. (2019). The role of IGF-1 in obesity, cardiovascular disease, and cancer. Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran, 33, 56.
Jentzsch, T., Robl, B., Husmann, M., Bode-Lesniewska, B., & Fuchs, B. (2014). Worse prognosis of breast cancer patients expressing IGF-1 on a tissue microarray. Anticancer Research, 34(8), 3881–3889.
Tang, W., Feng, X., Zhang, S., Ren, Z., Liu, Y., Yang, B., & Ge, N. (2015). Caveolin-1 confers resistance of hepatoma cells to anoikis by activating IGF-1 pathway. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 36(3), 1223–1236.
Foti, M., Ahmed Moukil, M., Dudognon, P., & Carpentier, J. L. (2004). Insulin and IGF-1 receptor trafficking and signalling. In Biology of IGF-1: its interaction with insulin in health and malignant states: Novartis Foundation Symposium 262 (Vol. 262, pp. 125–147). Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Armakolas, N., Armakolas, A., Antonopoulos, A., Dimakakos, A., Stathaki, M., & Koutsilieris, M. (2016). The role of the IGF-1 Ec in myoskeletal system and breast cancer pathophysiology. Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology, 108, 137–145.
Burrow, S., Andrulis, I. L., Pollak, M., & Bell, R. S. (1998). Expression of insulin-like growth factor receptor, IGF-1, and IGF-2 in primary and metastatic breast cancer. Journal of Surgical Oncology, 69(1), 21–27.
Zhang, W., Lee, J. C., Kumar, S., & Gowen, M. (1999). ERK Pathway Mediates the Activation of Cdk2 in IGF-1–Induced Proliferation of Human Breast cancer MG-63 Cells. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, 14(4), 528–535.
Crudden, C., Song, D., Cismas, S., Trocmé, E., Pasca, S., Calin, G. A., & Girnita, L. (2019). Below the surface: IGF-1R therapeutic targeting and its endocytic journey. Cells, 8(10), 1223.
Anisimov, V. N., & Bartke, A. (2013). The key role of growth hormone–insulin–IGF-1 signaling in aging and cancer. Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology, 87(3), 201–223.
Tentori, L., & Graziani, G. (2007). Doping with growth hormone/IGF-1, anabolic steroids or erythropoietin: is there a cancer risk? Pharmacological Research, 55(5), 359–369.
Tentori, L., & Graziani, G. (2007). Doping with growth hormone/IGF-1, anabolic steroids or erythropoietin: is there a cancer risk? Pharmacological Research, 55.5, 359–369.
Pemberton, L. F., Blobel, G., & Rosenblum, J. S. (1998). Transport routes through the nuclear pore complex. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 10(3), 392–399.
Cronshaw, J. M., Krutchinsky, A. N., Zhang, W., Chait, B. T., & Matunis, M. J. (2002). Proteomic analysis of the mammalian nuclear pore complex. The Journal of Cell Biology, 158(5), 915–927.
Packham, S., Warsito, D., Lin, Y., Sadi, S., Karlsson, R., Sehat, B., & Larsson, O. (2015). Nuclear translocation of IGF-1R via p150 Glued and an importin-β/RanBP2-dependent pathway in cancer cells. Oncogene, 34(17), 2227–2238.
Moloney, A. M., Griffin, R. J., Timmons, S., OConnor, R., Ravid, R., O, & Neill, C. (2010). Defects in IGF-1 receptor, insulin receptor and IRS-1/2 in Alzheimer’s disease indicate possible resistance to IGF-1 and insulin signalling. Neurobiology of Aging, 31(2), 224–243.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Jilin Scientific and Technological Development Program [grant no. 20190905003SF], [grant no. 20190701060GH]; China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Grant [grant no. 2019M651216].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, B., Lv, Z., Cui, C. et al. IGF-1R Transported to the Cell Nuclei to Regulate the Proliferation of Breast Cancer Cells. Cell Biochem Biophys 79, 801–813 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-021-00989-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-021-00989-8