Abstract
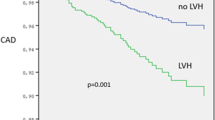
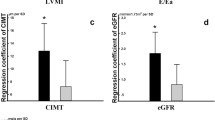
We evaluated the temporal association between aortic arterial stiffness and subclinical target organ damage, including renal function decline, left ventricular geometric remodeling, and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in patients with mild hypertension. Automatic pulse wave velocity (PWV) measuring system was applied to examine carotid-femoral PWV (CFPWV) reflecting aortic arterial stiffness in 644 essential hypertensive patients. Clinical data were collected, and cardiac structure and function were assessed by echocardiography. CFPWV was significantly and positively associated with left ventricular mass index (r = 0.153, P = 0.018), relative wall thickness (r = 0.235, P < 0.001), and left atrial diameter (r = 0.192, P = 0.003), and negatively with E/A ratio (r = −0.361, P < 0.001) and creatinine clearance (r = −0.248, P < 0.001). Logistic regression analysis demonstrated that CFPWV remained significantly correlated with renal function decline (P = 0.011), left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (P = 0.009) and left ventricular geometric remodeling (P = 0.020). Higher CFPWV was independently associated with greater burden of subclinical disease in renal impairment, left ventricular geometric remodeling and diastolic dysfunction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Laurent, S., Cockcroft, J., Van Bortel, L., Boutouyrie, P., Giannattasio, C., Hayoz, D., et al. (2006). European Network for non-invasive investigation of large arteries. Expert consensus document on arterial stiffness: methodological issues and clinical applications. European Heart Journal, 27, 2588–2605.
Laurent, S., Boutouyrie, P., Asmar, R., Gautier, I., Laloux, B., Guize, L., et al. (2001). Aortic stiffness is an independent predictor of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in hypertensive patients. Hypertension, 37, 1236–1241.
Asmar, R., Rudnichi, A., Blacher, J., London, G. M., & Safar, M. E. (2001). Pulse pressure and aortic pulse wave are markers of cardiovascular risk in hypertensive populations. American Journal of Hypertension, 14, 91–97.
Asmar, R., Benetos, A., Topouchian, J., Laurent, P., Pannier, B., Brisac, A. M., et al. (1995). Assessment of arterial distensibility by automatic pulse wave velocity measurement: Validation and clinical application studies. Hypertension, 26, 485–490.
Ni, Y., Wang, H., Hu, D., & Zhang, W. (2003). The relationship between pulse wave velocity and pulse pressure in Chinese patients with essential hypertension. Hypertension Research, 26, 871–874.
Devereux, R. B., Lutas, E. M., Casale, P. N., Kligfield, P., Eisenberg, R. R., Hammond, I. W., et al. (1984). Standardization of M-mode echocardiographic left ventricular anatomic measurements. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 4, 1222–1230.
Ganau, A., Devereux, R. B., Roman, M. J., De Simone, G., Pickering, T. G., Saba, P. S., et al. (1992). Patterns of left ventricular hypertrophy and geometric remodeling in essential hypertension. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 19, 1500–1508.
O’Rourke, M. F., & Safar, M. E. (2005). Relationship between aortic stiffness and microvascular disease in brain and kidney: Cause and logic of therapy. Hypertension, 46, 200–204.
Gusbeth-Tatomir, P., & Covic, A. (2007). Causes and consequences of increased arterial stiffness in chronic kidney disease patients. Kidney and Blood Pressure Research, 30, 90–107.
Ohya, Y., Iseki, K., Iseki, C., Miyage, T., Kinjo, K., & Takishita, S. (2006). Increased pulse wave velocity is associated with low creatinine clearance and proteinuria in a screened cohort. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 47, 790–797.
Tomiyama, H., Tanaka, H., Hashimoto, H., Matsumoto, C., Odaira, M., Yamada, J., et al. (2010). Arterial stiffness and declines in individuals with normal renal function/early chronic kidney disease. Atherosclerosis, 212, 345–350.
Schillaci, G., Mannarino, M. R., Pucci, G., Pirro, M., Helou, J., Savarese, G., et al. (2007). Age-specific relationship of aortic pulse wave velocity with left ventricular geometry and function in hypertension. Hypertension, 49, 317–321.
Lantelme, P., Laurent, S., Besnard, C., Bricca, G., Vincent, M., Legedz, L., et al. (2008). Arterial stiffness is associated with left atrial size in hypertensive patients. Archives of Cardiovascular Diseases, 101, 35–40.
Weber, T. (2010). Systolic and diastolic function as related to arterial stiffness. Artery Research, 4, 122–127.
Roman, M. J., Ganau, A., Saba, P. S., Pini, R., Pickering, T. G., & Devereux, R. B. (2000). Impact of arterial stiffening on left ventricular structure. Hypertension, 36, 489–494.
Argues, S., Roux, E., & Luccioni, R. (2007). Current clinical applications of spectral tissue Doppler echocardiography (E/E’ ratio) as a noninvasive surrogate for left ventricular diastolic pressures in the diagnosis of heart failure with preserved left ventricular systolic function. Cardiovascular Ultrasound, 5, 16.
Botev, R., Mallié, J. P., Couchoud, C., Schück, O., Fauvel, J. P., Wetzels, J. F., et al. (2009). Estimating glomerular filtration rate: Cockcroft-Gault and modification of diet in renal disease formulas compared to renal inulin clearance. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 4, 899–906.
Shlipak, M. G., Katz, R., & Sarnak, M. J. (2006). Cystatin C and prognosis for cardiovascular and kidney outcomes in elderly persons without chronic kidney disease. Annals of Internal Medicine, 145, 237–246.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jing Tan and Yinghua Pei equally contributed to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, J., Pei, Y., Hua, Q. et al. Aortic Pulse Wave Velocity is Associated with Measures of Subclinical Target Organ Damage in Patients with Mild Hypertension. Cell Biochem Biophys 70, 167–171 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-9876-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-9876-9