Abstract
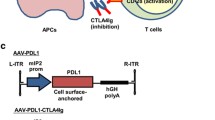
Diabetes mellitus affects 347 million people worldwide, and over 80 % of diabetes deaths occur in low- and middle-income countries. Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is characterized by the attacks of the body’s own immune system on the pancreatic β-cells. In this work, we present a new CTLA-4 Ig targeting at the surface of β-cell and prepare it from Escherichia coli aiming at clearing activated T cells around β-cells and avoiding all-round decline in systematic immunity. This fusion protein is composed of CTLA-4-Ig part and β-cell-targeting part, with properties of the therapeutic effect of CTLA-4-Ig and selective binding to β-cells. In preliminary biological activity assay, our results verified the feasibility of β-cell-targeting strategy and its activity of CTLA-4-Ig part. The fusion protein recognizes and binds specifically to CD80+ and CD86+ cells as well as β-cell, but not to control cells, displaying the potential to be used as a feasible and effective treatment of T1D with lessened side effect.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bengtson, L. G., Kucharska-Newton, A., Wruck, L. M., et al. (2014). Comparable ascertainment of newly-diagnosed atrial fibrillation using active cohort follow-up versus surveillance of centers for medicare and medicaid services in the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. PLoS One, 9, e94321.
Atkinson, M. A., & Eisenbarth, G. S. (2001). Type 1 diabetes: New perspectives on disease pathogenesis and treatment. Lancet, 358, 221–229.
van Belle, T. L., Coppieters, K. T., & von Herrath, M. G. (2011). Type 1 diabetes: Etiology, immunology, and therapeutic strategies. Physiological Reviews, 91, 79–118.
Jin, H., Li, C., Li, D., et al. (2013). Construction and characterization of a CTLA-4-targeted scFv-melittin fusion protein as a potential immunosuppressive agent for organ transplant. Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics, 67, 1067–1074.
Jain, N., Nguyen, H., Chambers, C., & Kang, J. (2010). Dual function of CTLA-4 in regulatory T cells and conventional T cells to prevent multiorgan autoimmunity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107, 1524–1528.
Egen, J. G., Kuhns, M. S., & Allison, J. P. (2002). CTLA-4: New insights into its biological function and use in tumor immunotherapy. Nature Immunology, 3, 611–618.
Schneider, H., Downey, J., Smith, A., et al. (2006). Reversal of the TCR stop signal by CTLA-4. Science, 313, 1972–1975.
Boni, A., Cogdill, A. P., Dang, P., et al. (2010). Selective BRAFV600E inhibition enhances T-cell recognition of melanoma without affecting lymphocyte function. Cancer Research, 70, 5213–5219.
Guo, J., Si, L., Kong, Y., et al. (2011). Phase II, open-label, single-arm trial of imatinib mesylate in patients with metastatic melanoma harboring c-Kit mutation or amplification. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 29, 2904–2909.
Salama, A. K., & Hodi, F. S. (2011). Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen-4. Clinical Cancer Research, 17, 4622–4628.
Ueberberg, S., Deutschbein, T., Klein, H. H., et al. (2011). Protection from diabetes development by single-chain antibody-mediated delivery of a NF-kappaB inhibitor specifically to beta-cells in vivo. American Journal of Physiology: Endocrinology and Metabolism, 301, E83–E90.
Ueberberg, S., Meier, J. J., Waengler, C., et al. (2009). Generation of novel single-chain antibodies by phage-display technology to direct imaging agents highly selective to pancreatic beta- or alpha-cells in vivo. Diabetes, 58, 2324–2334.
Ueberberg, S., Ziegler, D., Schechinger, W., et al. (2010). In vitro phage display in a rat beta cell line: A simple approach for the generation of a single-chain antibody targeting a novel beta cell-specific epitope. Diabetologia, 53, 1384–1394.
Yang, W., Lu, J., Weng, J., et al. (2010). Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China. New England Journal of Medicine, 362, 1090–1101.
Tian, J., Atkinson, M. A., Clare-Salzler, M., et al. (1996). Nasal administration of glutamate decarboxylase (GAD65) peptides induces Th2 responses and prevents murine insulin-dependent diabetes. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 183, 1561–1567.
Hagopian, W., Ferry, R. J., Jr, Sherry, N., et al. (2013). Teplizumab preserves C-peptide in recent-onset type 1 diabetes: Two-year results from the randomized, placebo-controlled Protege trial. Diabetes, 62, 3901–3908.
Herold, K. C., Gitelman, S. E., Willi, S. M., et al. (2013). Teplizumab treatment may improve C-peptide responses in participants with type 1 diabetes after the new-onset period: A randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia, 56, 391–400.
Orban, T., Bundy, B., Becker, D. J., et al. (2011). Co-stimulation modulation with abatacept in patients with recent-onset type 1 diabetes: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet, 378, 412–419.
Montes, V. N., & Hirsch, I. B. (2012). Treatment of LADA with etanercept. Diabetes Care, 35, e36.
Moran, A., Bundy, B., Becker, D. J., et al. (2013). Interleukin-1 antagonism in type 1 diabetes of recent onset: Two multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. Lancet, 381, 1905–1915.
Pescovitz, M. D., Greenbaum, C. J., Bundy, B., et al. (2014). B-lymphocyte depletion with rituximab and beta-cell function: Two-year results. Diabetes Care, 37, 453–459.
Deng, C., Xiang, Y. F., & Zhou, Z. G. (2013). Biologic therapies in type 1 diabetes: How far are they from us? Chinese Medical Journal (English), 126, 4003–4005.
Wong, F. S., & Wen, L. (2013). Therapy: Immunotherapy for T1DM: Targeting innate immunity. Nature Reviews Endocrinology, 9, 384–385.
Mayer, E., Holzl, M., Ahmadi, S., et al. (2013). CTLA4-Ig immunosuppressive activity at the level of dendritic cell/T cell crosstalk. International Immunopharmacology, 15, 638–645.
Acknowledgments
This project is supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation 20080441294.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, W., Li, L., Han, C. et al. Blockade of the Activation of T Cells Around β-Cell by the Targeted CTLA-4 Ig at the Surface of β-Cell. Cell Biochem Biophys 71, 913–918 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0282-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0282-0