Abstract
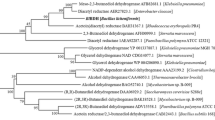
A new esterase gene abmbh, encoding a benzoate hydrolase which can enantioselectively hydrolyze l-menthyl benzoate to l-menthol, was recently identified from the genomic library of a soil isolate Acinetobacter sp. ECU2040. The abmbh gene contains a 1080-bp open reading frame encoding a protein of 360 amino acids with a calculated molecular mass of 40.7 kDa. The corresponding enzyme AbMBH was functionally expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3), purified, and characterized. The AbMBH displayed the maximum activity towards p-nitrophenyl butyrate at 50 °C, and an optimum pH of 8.5. A K M of 2.6 mM and a k cat of 0.26 s−1 were observed towards dl-menthyl benzoate. The AbMBH exhibited a moderate enantioselectivity (E = 27.5) towards dl-menthyl benzoate. It can also catalyze the enantioselective hydrolysis of a variety of racemic menthyl esters, including dl-menthyl acetate, dl-menthyl chloroacetate, and dl-menthyl butyrate.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clark, G. S. (1998). Menthol. Perfumer & Flavorist, 23, 33–46.
Clark, G. S. (2007). Aroma chemical profile: menthol. Perfumer & Flavorist, 32, 38–47.
Fleischer, J., Bauer, K., & Hopp, R. (1976). Separating optically pure d- and l-isomers of menthol, neomenthol and isomenthol. US Pat. 3943181.
Akutagawa, S. (1997). Enantioselective isomerization of allylamine to enamine: practical asymmetric synthesis of (−)-menthol by Rh–BINAP catalysts. Topics in Catalysis, 4, 271–274.
Noyori, R. (2003). Asymmetric catalysis: science and opportunities. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis, 345, 15–32.
Trasarti, A. F., Marchi, A. J., & Apesteguia, C. R. (2004). Highly selective synthesis of menthols from citral in a one-step process. Journal of Catalysis, 224, 484–488.
Vorlova, S., Bornscheuer, U. T., Gatfield, I., Hilmer, J. M., Bertram, H. J., & Schmid, R. D. (2002). Enantioselective hydrolysis of D, L-menthyl benzoate to L-(−)-menthol by recombinant Candida rugosa lipase LIP1. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis, 344, 1152–1155.
Yu, L. J., Xu, Y., Wang, X. Q., & Yu, X. W. (2007). Highly enantioselective hydrolysis of dl-menthyl acetate to l-menthol by whole-cell lipase from Burkholderia cepacia ATCC 25416. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 47, 149–154.
Zheng, G. W., Yu, H. L., Zhang, J. D., & Xu, J. H. (2009). Enzymatic production of l-menthol by a high substrate concentration tolerable esterase from newly isolated Bacillus subtilis ECU0554. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis, 351, 405–414.
Xu, J. H., Kawamoto, T., & Tanaka, A. (1995). High-performance continuous operation for enantioselective esterification of menthol by use of acid anhydride and free lipase in organic solvent. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 43, 639–643.
Lu, Z. X., Chu, Y., Han, Y. C., Wang, Y. H., & Liu, J. L. (2005). Enzymatic esterification of DL-menthol with propionic acid by lipase from Candida cylindracea. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 80, 1365–1370.
Brady, D., Reddy, S., Mboniswa, B., Steenkamp, L. H., Rousseau, A. L., Parkinson, C. J., Chaplin, J., Mitra, R. K., Moutlana, T., Marais, S. F., & Gardiner, N. S. (2012). Biocatalytic enantiomeric resolution of L-menthol from an eight isomeric menthol mixture through transesterification. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 75, 1–10.
Henke, E., & Bornscheuer, U. T. (2002). Esterases from Bacillus subtilis and B. stearothermophilus share high sequence homology but differ substantially in their properties. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 60, 320–326.
Yu, L. J., Xu, Y., & Yu, X. W. (2009). Purification and properties of a highly enantioselective L-menthyl acetate hydrolase from Burkholderia cepacia. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 57, 27–33.
Ngo-Thi, M. T., Yin, J. G., Pan, J., Zheng, G. W., & Xu, J. H. (2013). Enantioselective hydrolysis of dl-menthyl benzoate by cell-free extract of newly isolated Acinetobacter sp. ECU2040. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 170, 1974–1981.
Qian, L., Liu, J. Y., Liu, J. Y., Yu, H. L., Li, C. X., & Xu, J. H. (2011). Fingerprint lipolytic enzymes with chromogenic p-nitrophenyl esters of structurally diverse carboxylic acids. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 73, 22–26.
Wang, B. Z., Guo, P., Hang, B. J., Li, L., He, J., & Li, S. P. (2009). Cloning of a novel pyrethroid-hydrolyzing carboxylesterase gene from Sphingobium sp. strain JZ-1 and characterization of the gene product. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75, 5496–5500.
Miller, S. A., Dykes, D. D., & Polesky, H. F. (1988). A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Research, 16, 1215.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Gao, L., Xu, J. H., Li, X. J., & Liu, Z. Z. (2004). Optimization of Serratia marcescens lipase production for enantioselective hydrolysis of 3-phenylglycidic acid ester. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 31, 525–530.
Arpigny, J. L., & Jaeger, K. E. (1999). Bacterial lipolytic enzymes: classification and properties. Biochemistry Journal, 343, 177–183.
Henke, E., Pleiss, J., & Bornscheuer, U. T. (2002). Activity of lipases and esterases towards tertiary alcohols: insights into structure-function relationships. Angew Chemical International Edition, 41, 3211–3213.
Kok, R. G., Christoffels, V. M., Vosman, B., & Hellingwerf, K. J. (1993). Growth-phase-dependent expression of the lipolytic system of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus BD413: cloning of a gene encoding one of the esterases. Journal of General Microbiology, 139, 2329–2342.
Kim, H. E., Lee, I. S., Kim, J. H., Hahn, K. W., Park, U. J., Han, H. S., & Park, K. R. (2003). Gene cloning, sequencing, and expression of an esterase from Acinetobacter lwoffii I6C-1. Current Microbiology, 46, 291–295.
Chao, Y. P., Fu, H. Y., Wang, Y. L., Huang, W. B., & Wang, J. Y. (2003). Molecular cloning of the carboxylesterase gene and biochemical characterization of the encoded protein from Pseudomonas citronellolis ATCC 13674. Research in Microbiology, 154, 521–526.
Wu, J., Liao, X. W., Yu, F. B., Wei, Z. B., & Yang, L. Y. (2013). Cloning of a dibutyl phthalate hydrolase gene from Acinetobacter sp. strain M673 and functional analysis of its expression product in Escherichia coli. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 97, 2483–2491.
Hotta, Y., Ezaki, S., Atomi, H., & Imanaka, T. (2002). Extremely stable and versatile carboxylesterase from a hyperthermophilic archaeon. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 3925–3931.
Manco, G., Giosue, E., D’Auria, S., Herman, P., Carrea, G., & Rossi, M. (2000). Cloning, overexpression, and properties of a new thermophilic and thermostable esterase with sequence similarity to hormone-sensitive lipase subfamily from the archaeon Archaeoglobus fulgidus. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 373, 182–192.
Suzuki, Y., Miyamoto, K., & Ohta, H. (2004). A novel thermostable esterase from the thermoacidophilic archaeon Sulfolobus tokodaii strain 7. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 236, 97–102.
Manco, G., Adinolfi, E., Pisani, F. M., Ottolina, G., Carrea, G., & Rossi, M. (1998). Overexpression and properties of a new thermophilic and thermostable esterase from Bacillus acidocaldarius with sequence similarity to hormone-sensitive lipase subfamily. Biochemistry Journal, 332, 203–212.
Rhee, J. K., Ahn, D. G., Kim, Y. G., & Oh, J. W. (2005). New thermophilic and thermostable esterase with sequence similarity to the hormone-sensitive lipase family, cloned from a metagenomic library. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71, 817–825.
Zheng, G. W., Pan, J., Yu, H. L., Ngo-Thi, M. T., Li, C. X., & Xu, J. H. (2010). An efficient bioprocess for enzymatic production of L-menthol with high ratio of substrate to catalyst using whole cells of recombinant E. coli. Journal of Biotechnology, 150, 108–114.
Chen, C. S., Fujimoto, Y. F., Girdaukas, G., & Sih, C. J. (1982). Quantitative analyses of biochemical kinetic resolutions of enantiomers. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 104, 7294–7299.
Barnier, J. P., Blanco, L., Guibejampel, E., & Rousseau, G. (1989). Preparation of (R)-veratryl- and (R)-(3-methoxybenzyl)succinates. Tetrahedron, 45, 5051–5058.
Manco, G., Carrea, G., Giosue, E., Ottolina, G., Adamo, G., & Rossi, M. (2002). Modification of the enantioselectivity of two homologous thermophilic carboxylesterases from Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius and Archaeoglobus fulgidus by random mutagenesis and screening. Extremophiles, 6, 325–331.
Valinger, G., Hermann, M., Wagner, U. G., & Schwab, H. (2007). Stability and activity improvement of cephalosporin esterase EstB from Burkholderia gladioli by directed evolution and structural interpretation of muteins. Journal of Biotechnology, 129, 98–108.
Ema, T., Kamata, S., Takeda, M., Nakano, Y., & Sakai, T. (2010). Rational creation of mutant enzyme showing remarkable enhancement of catalytic activity and enantioselectivity toward poor substrates. Chemical Communication, 46, 5440–5442.
Jochens, H., Aerts, D., & Bornscheuer, U. T. (2010). Thermostabilization of an esterase by alignment-guided focused directed evolution. Protein Engineering, Design & Selection, 23, 903–909.
Godinho, L. F., Reis, C. R., van Merkerk, R., Poelarends, G. J., & Quax, W. J. (2012). An esterase with superior activity and enantioselectivity towards 1,2-O-isopropylideneglycerol esters obtained by protein design. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis, 354, 3009–3015.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31200050 and 21276082) and Ministry of Science and Technology, People’s Republic of China (Nos. 2011AA02A210 and 2011CB710800).
Ethical Statement
This manuscript is original and has not been published and will not be submitted elsewhere for publication. No data has been fabricated or manipulated (including images) to support our conclusions. No data, text, or theories by others are presented as if they were our own.
The submission has been received explicitly from all co-authors. And authors whose names appear on the submission have contributed sufficiently to the scientific work and therefore share collective responsibility and accountability for the results.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
Effect of pH on AbMBH activity. The relative activity was determined using dl-menthyl benzoate as the substrate. Enzyme assay was performed in different buffers (100 mM) within a pH range of 6.0–10.0 (potassium phosphate, 6.0–8.5; Tris–HCl, 8.0–9.0; Na2CO3–NaHCO3, 9.0–10.0) at 30°C. Relative activity was expressed as a percentage of maximum activity under the experimental conditions. (DOC 42 kb)
Fig. S2
Effect of temperature on AbMBH activity. Relative activity was expressed as a percentage of maximum activity under the experimental conditions. (DOC 42 kb)
Fig. S3
Effect of temperature on AbMBH stability. Diamond, 30 °C (inserted graph); circle, 40 ºC; and square, 50 °C. Samples were withdrawn at different time intervals to estimate the residual activity using the standard assay. Residual activity was expressed as a percentage of the activity measured initially without any pre-incubation. (DOC 36 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, JG., Xu, GC., Zheng, GW. et al. Cloning and Characterization of an Enantioselective l-Menthyl Benzoate Hydrolase from Acinetobacter sp. ECU2040. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 176, 1102–1113 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1632-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1632-0