Abstract
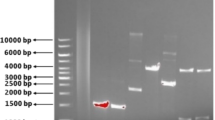
Prior studies disclosed that Aeromonas hydrophila NIU01 was a biodecolorization and bioelectricity bacterium which was isolated from a cross-strait of Taiwan. However, enzymatic function, laccase, involved in this strain had never been reported. This first attempt is to explore its laccase activity, the molecular cloning and heterologous recombinant expression in Escherichia coli. A full-length novel gene of 1,647 bp, LacA, encoding of 549 amino acids was successfully cloned by polymerase chain reaction. The recombinant pET-15b(+)-NIU-LacA expression was compared in different E. coli strains. By applying Taguchi’s L9 in culture optimization, the soluble laccase increased to 22.7 %, in which the conditions were obtained at 22 °C with initial shaking speed at 200 rpm, addition of lactose of 0.2 mM and CuSO4 of 0.5 mM to the medium, and shaking off while cell mass reached to OD600nm of 1.5. NIU-LacA was strongly inhibited by chloride ion. The optimal temperature was 60 °C and the optimum pH for ABTS (2,2′-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzthiazolinesulfonic acid) and 2,6-DMP (2,6-dimethoxyphenol) were pH 2.1 and pH 7.5 which enzymatic activity was 274.6 and 44.8 U/L, respectively. Further study in structural modeling of NIU-LacA showed the C terminal domain was the major variance in the three most closely A. hydrophila strains.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thurston, C. (1994). The structure and function of fungal laccases. Microbiology, 140, 19–26.
Rodgers, C. J., Blanford, C. F., Giddens, S. R., Skamnioti, P., Armstrong, F. A., & Gurr, S. J. (2009). Designer laccases: a vogue for high-potential fungal enzymes? Trends in Biotechnology, 28(2), 63–72.
Jönsson, L. J., Palmqvist, E., Nilvebrant, N. O., & Hahn-Hägerdal, B. (1998). Detoxification of wood hydrolysates with laccase and peroxidase from the white-rot fungus Trametes versicolor. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 49(6), 691–697.
Larsson, S., Reimann, A., Nilvebrant, N. O., & Jonsson, L. J. (1999). Comparison of different methods for the detoxification of lignocellulose hydrolysate of spruce. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 77, 91–103.
Larsson, S., Cassland, P., & Jönsson, L. J. (2001). Development of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with enhanced resistance to phenolic fermentation inhibitors in lignocellulose hydrolysates by heterologous expression of laccase. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67(3), 1163–1170.
Yu, H. B., Kaur, R., Lim, S., Wang, X. H., & Leung, K. Y. (2007). Characterization of extracellular proteins produced by Aeromonas hydrophila AH-1. Proteomics, 7(3), 436–449.
Chen, K. C., Wu, J. Y., Liou, D. J., & Hwang, S. C. (2003). Decolorization of the textile dyes by newly isolated bacterial strains. Journal of Biotechnology, 101(1), 57–68.
Ren, S., Guo, J., Zeng, G., & Sun, G. (2006). Decolorization of triphenylmethane, azo, and anthraquinone dyes by a newly isolated Aeromonas hydrophila strain. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 72(6), 1316–1321.
Chen, B. Y., Lin, K. W., Wang, Y. M., & Yen, C. Y. (2009). Revealing interactive toxicity of aromatic amines to azo dye decolorizer Aeromonas hydrophila. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 166(1), 187–194.
Chen, B. Y., Chen, W. M., Kuo, H. Y., & Hsueh, C. C. (2009). Comparative assessment upon dye removal capability of indigenous bacterial strains from Lanyang Plain in northeast Taiwan. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 161(1), 526–533.
Chen, B. Y., Yen, C. Y., Chen, W. M., Chang, C. T., Wang, C. T., & Hu, Y. C. (2009). Exploring threshold operation criteria of biostimulation for azo dye decolorization using immobilized cell systems. Bioresource Technology, 100(23), 5763–5770.
Zhang, M. M., Chen, W. M., Chen, B. Y., Chang, C. T., Hsueh, C. C., Ding, Y., et al. (2010). Comparative study on characteristics of azo dye decolorization by indigenous decolorizers. Bioresource Technology, 101(8), 2651–2656.
Jeon, J. R., Baldrian, P., Murugesan, K., & Chang, Y. S. (2012). Laccase-catalysed oxidations of naturally occurring phenols: from in vivo biosynthetic pathways to green synthetic applications. Microbial Biotechnology, 5(3), 318–332.
Kyratsous, C. A., Silverstein, S. J., DeLong, C. R., & Panagiotidis, C. A. (2009). Chaperone-fusion expression plasmid vectors for improved solubility of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli. Gene, 440(1–2), 9–15.
Arnold, K., Bordoli, L., Kopp, J., & Schwede, T. (2006). The SWISS-MODEL workspace: a web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics, 22(2), 195–201.
Wu, J., Kim, K. S., Lee, J. H. & Lee, Y. C (2010). Cloning, expression in Escherichia coli, and enzymatic properties of laccase from Aeromonas hydrophila WL-11. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 22(4), 635–640.
Richards, G. P., Watson, M. A., & Parveen, S. (2005). Development of a simple and rapid fluorogenic procedure for identification of vibrionaceae family members. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71(7), 3524–3527.
Zheng, X., Ng, I. S., Ye, C., Chen, B. Y., & Lu, Y. (2012). Copper ion-stimulated McoA-laccase production and enzyme characterization in Proteus hauseri ZMd44. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering. doi:10.1016/j.jbiosc.2012.10.012.
Bukh, C., & Bjerrum, M. J. (2010). The reversible depletion and reconstitution of a copper ion in Coprinus cinereus laccase followed by spectroscopic techniques. Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry, 104(10), 1029–1037.
Galhaup, C., Goller, S., Peterbauer, C. K., Strauss, J., & Haltrich, D. (2002). Characterization of the major laccase isoenzyme from Trametes pubescens and regulation of its synthesis by metal ions. Microbiology, 148(7), 2159–2169.
Stajic, M., Persky, L., Hadar, Y., Friesem, D., Duletic-Lausevic, S., Wasser, S. P., et al. (2006). Effect of copper and manganese ions on activities of laccase and peroxidases in three Pleurotus species grown on agricultural wastes. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 128(1), 87–96.
Durao, P., Chen, Z., Fernandes, A. T., Hildebrandt, P., Murgida, D. H., Todorovic, S., et al. (2008). Copper incorporation into recombinant CotA laccase from Bacillus subtilis: characterization of fully copper loaded enzymes. Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry, 13, 183–193.
Salony, Garg, N., Baranwal, R., Chhabra, M., Mishra, S., Chaudhuri, T. K., et al. (2008). Laccase of Cyathus bulleri: structural, catalytic characterization and expression in Escherichia coli. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1784(2), 259–268.
Ye, M., Li, G., Liang, W. Q., & Liu, Y. H. (2010). Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel metagenome-derived multicopper oxidase with alkaline laccase activity and highly soluble expression. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 87(3), 1023–1031.
Martins, L. O., Soares, C. M., Pereira, M. M., Teixeira, M., Costa, T., Jones, G. H., et al. (2002). Molecular and biochemical characterization of a highly stable bacterial laccase that occurs as a structural component of the Bacillus subtilis endospore coat. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277(21), 18849–18859.
Shleev, S., Christenson, A., Serezhenkov, V., Burbaev, D., Yaropolov, A., Gorton, L., et al. (2005). Electrochemical redox transformations of T1 and T2 copper sites in native Trametes hirsuta laccase at gold electrode. Biochemical Journal, 385(3), 745–754.
Fang, Z., Li, T., Wang, Q., Zhang, X., Peng, H., Fang, W., et al. (2011). A bacterial laccase from marine microbial metagenome exhibiting chloride tolerance and dye decolorization ability. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 89(4), 1103–1110.
Fang, Z. M., Li, T. L., Chang, F., Zhou, P., Fang, W., Hong, Y. Z., et al. (2012). A new marine bacterial laccase with chloride-enhancing, alkaline-dependent activity and dye decolorization ability. Bioresource Technology, 111, 36–41.
Bertrand, T., Jolivalt, C., Briozzo, P., Caminade, E., Joly, N., Madzak, C., et al. (2002). Crystal structure of a four-copper laccase complexed with an arylamine: insights into substrate recognition and correlation with kinetics. Biochemistry, 41(23), 7325–7333.
Kerr, I. D., Berridge, G., Linton, K. J., Higgins, C. F., & Callaghan, R. (2003). Definition of the domain boundaries is critical to the expression of the nucleotide-binding domains of P-glycoprotein. European Biophysics Journal, 32(7), 644–654.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the financial support by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2011121017), the Chinese National Natural Science Foundation (21206141), and the Fujian Provincial Department of Science and Technology (2012I0009). The authors also sincerely appreciate Professor Bor-Yann Chen who supports the bacterium and initiates the academic connection program between Xiamen University (China) and National I-Lan University (Taiwan).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ng, IS., Zhang, X., Zhang, Y. et al. Molecular Cloning and Heterologous Expression of Laccase from Aeromonas hydrophila NIU01 in Escherichia coli with Parameters Optimization in Production. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 169, 2223–2235 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0128-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0128-z