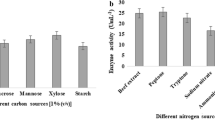
Abstract
In this study, the production and optimization of extracellular lipase from Kluyveromyces marxianus IFO 0288 was investigated by using optimized nutritional and cultural conditions in a yeast medium containing glucose as the carbon source in fully aerobic batch fermentation (150 rpm). The influence of four fermentation parameters (type of lipidic source, initial culture pH, temperature, and length of fermentation) on growth and lipase production was investigated and evaluated using the conventional “one variable at a time” approach and response surface methodology. An 18-fold increase in lipase production during 65 h of fermentation was obtained with optimized nutritional (0.5 % olive oil) and cultivation (pH 6.5, 35 °C) conditions by employing the conventional optimization method. By applying the response surface methodology technique the initial pH value of 6.4 and temperature of 32.5 °C were identified as optimal and led to further improvements (up to 18-fold) of extracellular lipase production. The results provide, for the first time, evidence that K. marxianus has the potential to be used as an efficient producer of extracellular lipase with prospective application in a variety of industrial and biotechnological areas.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gerritse, G., Hommes, R. W., & Quax, W. J. (1998). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 64, 2644–2651.
Houde, A., Kademi, A., & Leblanc, D. (2004). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 118, 155–170.
Maugard, T., Rejasse, B., & Legoy, M. D. (2002). Biotechnology Progress, 18, 424–428.
Patel, R. K., Mital, D., & Singh, S. (2005). Process Biochemistry, 40, 3569–3575.
Pandey, A., Benjamin, S., Soccol, C. R., Nigam, P., Krieger, N., & Soccol, V. T. (1999). Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry, 29, 119–131.
Deive, F. J., Costas, M., & Longo, M. A. (2003). Biotechnology Letters, 25, 1403–1406.
George, E., Tamerler, C., Martinez, A., Martinez, M. J., & Keshavarz, T. (1999). Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 74, 137–140.
Rathi, P., Sapna, B., Sexena, R., & Gupta, R. (2000). Biotechnology Letters, 22, 495–498.
He, Y. Q., & Tan, T. W. (2006). Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 43, 99–125.
Elibol, M. (2004). Process Biochemistry, 39, 1057–1062.
Kokkinou, M., Theodorou, L. G., & Papamichael, E. M. (2012). Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology, 55, 231–236.
Sharma, R., Chisti, Y., & Banerjee, U. C. (2001). Biotechnology Advances, 19, 627–662.
Khuri, A. I., & Cornell, J. A. (1996). Response surfaces: designs and analysis. New York: Marcel Dekker, ASQA.
Singh, A., Kuila, A., Yadav, G., & Banerjee, R. (2011). Food Technology and Biotechnology, 49, 322–328.
Design Expert (Statistical Package Software), trial v. 8.0.7.1, Stat-Ease Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA (2012) Available from: http://www.statease.com.
Fonseca, G. G., Heinzle, E., Wittmann, C., & Gombert, A. K. (2008). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 79, 339–354.
Lane, M. M., & Morrissey, J. P. (2010). Fungal Biology Reviews, 24, 17–26.
Benjamin, S., & Pandey, A. (1998). Yeast, 14, 1069–1087.
Vakhlu, J., & Kour, A. (2006). Electronic Journal of Biotechnology, 9, 69–85.
Soares, C. M. F., De Castro, H. F., Moraes, F. F., & Zanin, G. M. (1999). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 79, 745–757.
Garlapati, V. K., Vundavilli, P. R., & Banerjee, R. (2010). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 162, 1350–1361.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Prof. A. Koutinas of the Dept. of Chemistry, University of Patras, Greece for kindly providing the K. marxianus strain used in this work
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stergiou, PY., Foukis, A., Sklivaniti, H. et al. Experimental Investigation and Optimization of Process Variables Affecting the Production of Extracellular Lipase by Kluyveromyces marxianus IFO 0288. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 168, 672–680 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9808-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9808-3