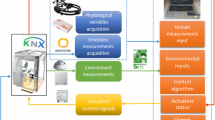
Abstract
Domotic integrates different technologies to facilitate the task in the home area. Domotic tools lead to the design and construction of interactive space with potential fields of use. Emotion Domotics is a research in which it is sought to create an interactive space for testing that its main objective is to react to the emotional state of the user in order to modify the environment until reaching the appropriate stage in which the user enters a state of comfort. It is also sought that this interactive space can be used to increase labor and learning efficiency. Another potential application of this interactive space is that it can be used as a tool to evaluate the user experience of products and services. However, to achieve the objective of this research, a communication system must be developed that integrates the available domotic technologies with biometric systems for the detection of emotions. This communication system is important for the progress of the research because it will also be the one that will control the environmental variables such as temperature, light intensity and hue, and humidity within the interactive space to create a scenario according to the user’s needs. Throughout this work, the development of the communication system for the interactive space will be presented, as well as the tests carried out to validate the effectiveness of the communication system.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abascal Carranza, C.M.: NORMA Oficial Mexicana NOM-015-STPS-2001, Condiciones térmicas elevadas o abatidas-Condiciones de seguridad e higiene. Technical report (2001)
Astarloa, A., Abej, S., Chamorro, F.: SoPC Implementation of the TP-KNX Protocol for Domotic Applications. In: 2008 International Conference on Advances in Electronics and Micro-electronics, vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 363–370 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/ENICS.2008.9
Barmaki, R.: Gesture assessment of teachers in an immersive rehearsal environment. Ph.D. thesis, University of Central Florida, United States of America (2016)
Basri, N.H., Noor, N.L.M., Adnan, W.A.W., Saman, F.M., Baharin, A.H.A.: Conceptualizing and understanding user experience. In: 2016 4th International Conference on User Science and Engineering (i-USEr), pp. 81–84 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/IUSER.2016.7857938
Berbano, A.E.U., Pengson, H.N.V., Razon, C.G.V., Tungcul, K.C.G., Prado, S.V.: Classification of stress into emotional, mental, physical and no stress using electroencephalogram signal analysis. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Signal and Image Processing Applications, ICSIPA 2017 pp. 11–14 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSIPA.2017.8120571
Bhemjibhaih, D.P., Sanjay, G.D., Sreejith, V., Prakash, B.: Brain-computer interface based home automation system for paralysed people. In: 2018 IEEE Recent Advances in Intelligent Computational Systems, RAICS 2018, pp. 230–233 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/RAICS.2018.8635060
Bujdei, C., Moraru, S.A.: Ensuring comfort in office buildings: designing a KNX monitoring and control system. In: Proceedings—2011 7th International Conference on Intelligent Environments, IE 2011, pp. 222–229 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/IE.2011.29
Cavalieri, S.: Analysing congestion in KNXnet/IP communication system. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology, pp. 244–249 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIT.2011.5754381
Cavalieri, S.: Estimating KNXnet/IP routing congestion. In: Proceedings—ISIE 2011: 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics pp. 1200–1205 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISIE.2011.5984329
Ekman, P., Friesen, W.V., Hager, J.C.: Facial Action Coding System, vol. 1. Research Nexus division of Network Information Research Corporation, Salt Lake City (2002)
Finsterwald, C., Alberini, C.M.: Stress and glucocorticoid receptor-dependent mechanisms in long-term memory: from adaptive responses to psychopathologies. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 112, 17–29 (2014)
Forlizzi, J., Battarbee, K.: Understanding experience in interactive systems. In: Proceedings of the 2004 Conference on Designing Interactive Systems Processes, Practices, Methods, and Techniques—DIS ’04, p. 261 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1145/1013115.1013152
González-Nalda, P., Etxeberria-Agiriano, I., Calvo, I., Otero, M.C.: A modular CPS architecture design based on ROS and Docker. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. 11(4), 949–955 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-016-0313-8
Hassenzahl, M.: User experience (UX): towards an experiential perspective on product quality. In: Proceedings of the 20th Conference on L’Interaction Homme-Machine, IHM ’08, pp. 11–15. ACM, New York (2008). https://doi.org/10.1145/1512714.1512717
Herrera Quintero, L.F.: Viviendas inteligentes (domótica). Revista Ingeniería e Investigación 25(2), 47–53 (2005)
IEEE standard for ethernet. IEEE Std 802.3-2015 (Revision of IEEE Std 802.3-2012) pp. 1–4017 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/IEEESTD.2016.7428776
Khowaja, S.A., Dahri, K.: Facial expression recognition using two-tier classification and its application to smart home automation system. In: 2015 International Conference on Emerging Technologies (ICET), pp. 1–6 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICET.2015.7389223
Kuo, C.-H., Huang, F.-G., Wang, K.-L., Chen, H.-W.: Design and implementation of Internet-based in-house healthcare and home automation systems, pp. 2944–2949 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/icsmc.2003.1244339
Lee, W.S., Hong, S.H.: KNX—zigbee gateway for home automation. In: 4th IEEE Conference on Automation Science and Engineering, CASE 2008, pp. 750–755 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/COASE.2008.4626433
Lopez-Aguilar, A.A., Navarro-Tuch, S.A., Bustamante-Bello, M.R., Izquierdo-Reyes, J., Curiel-Ramirez, L.A.: Interpretation and emulation for telegrams of the KNX Standard on MATLAB Simulink. In: 2018 International Conference on Mechatronics, Electronics and Automotive Engineering (ICMEAE), pp. 129–133 (2018)
Lozada, M.A.C., De La Rosa, R.F.: Simulation platform for domotic systems. In: 2014 IEEE Colombian Conference on Communications and Computing, COLCOM 2014—Conference Proceedings (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/ColComCon.2014.6860413
Lozano Alarcon, J.: Norma Oficial Mexicana NOM-025-STPS-2008, Condiciones de iluminación en los centros de trabajo. Technical report (2008)
Mandler, G.: The Psychology of Facial Expression. Studies in Emotion and Social Interaction. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1997). https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511659911
Navarro-Tuch, S.A., Bustamante-Bello, M.R., Izquierdo-Reyes, J., Avila-Vazquez, R., Ramirez-Mendoza, R., Pablos-Hach, J.L., Gutiérrez-Martínez, Y.: Emotional Domotics: inhabitable home automation system for emotion modulation. In: Intelligent Systems and Applications, pp. 218–241 (2018)
Navarro-Tuch, S.A., Bustamante-Bello, M.R., Molina, A., Izquierdo-Reyes, J., Avila-Vazquez, R., Pablos-Hach, J.L., Gutiérrez-Martínez, Y.: Inhabitable space control for the creation of healthy interactive spaces through emotional domotics. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. 12(4), 1337–1347 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-017-0410-3
Navarro-Tuch, S.A., Lopez-Aguilar, A.A., Bustamante-Bello, M.R., Molina, A., Izquierdo-Reyes, J., Curiel Ramirez, L.A.: Emotional domotics: a system and experimental model development for UX implementations. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-019-00598-z
Ning, H.N.H., Ya-Hu, W.Y.H.W., Yi, T.Y.T.: Research of KNX device node and development based on the bus interface module. In: 2010 29th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), pp. 4346–4350 (2010)
Ou, C.z., Lin, B.s.: Brain computer interface-based smart environmental control system. In: 2012 Eighth International Conference on Intelligent Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing, pp. 281–284 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/IIH-MSP.2012.74
Seifried, S., Gridling, G., Kastner, W.: KNX IPv6: design issues and proposed architecture. In: IEEE International Workshop on Factory Communication Systems—Proceedings, WFCS (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/WFCS.2017.7991951
Shin, D.H.: Quality of experience: beyond the user experience of smart services. Total Qual. Manag. Bus. Excell. 26(7–8), 919–932 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/14783363.2014.912037
Shojaeilangari, S., Yau, W.Y., Nandakumar, K., Li, J., Teoh, E.K.: Robust representation and recognition of facial emotions using extreme sparse learning. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 24(7), 2140–2152 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2015.2416634
Sita, I.V.: Train comfort, access and security using KNX and LOGO! controllers. In: Electrical Systems for Aircraft, Railway and Ship Propulsion, ESARS (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/ESARS.2012.6387411
Stanley, R.O., Burrows, G.D.: Psychogenic heart disease- stress and the heart: a historical perspective. Stress Health J. Int. Soc. Investig. Stress 24(3), 181–187 (2008)
Tarallo, A., Mozzillo, R., Di Gironimo, G., De Amicis, R.: A cyber-physical system for production monitoring of manual manufacturing processes. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. 12(4), 1235–1241 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-018-0493-5
Thenmozhi, R., Kabali, B., Kapali, S.C.: Effect of administrative stress on mental health in a group ofoffice workers-Across sectional study. In: 2014 International Conference on Science Engineering and Management Research, ICSEMR 2014, pp. 1–3 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSEMR.2014.7043570
Tokkonen, H., Saariluoma, P.: How user experience is understood? In: 2013 Science and Information Conference, pp. 791–795 (2013)
Vuppalapati, C., Khan, M.S., Raghu, N., Veluru, P., Khursheed, S.: A system to detect mental stress using machine learning and mobile development. Proc. Int. Conf. Mach. Learn. Cybernet. 1, 161–166 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMLC.2018.8527004
Withanage, C., Otto, K.: A comparison of the popular home automation technologies. In: 2014 IEEE Innovative Smart Grid Technologies—Asia (ISGT ASIA), pp. 600–605 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISGT-Asia.2014.6873860
Acknowledgements
Eng. Maribel Pacheco Ramos, Eng. Ernesto Pacheco, Eng. Rimack Quiñones, Tronik Edificios Inteligentes SA de CV. CPM - Colegio y Proyectos en Microelectrónica SC. This research is being supported by Centro de Investigación en Microsistemas y Biodiseño (CIMB) at Tecnológico de Monterrey, Campus Ciudad de México. This research is done by the help of Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACYT), México, by the scholarship 886598.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lopez-Aguilar, A.A., Bustamante-Bello, M.R., Navarro-Tuch, S.A. et al. Communication system development for emotional domotics interactive space. Int J Interact Des Manuf 14, 727–736 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-019-00624-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-019-00624-0