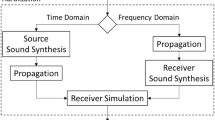
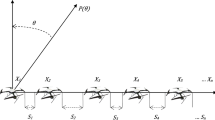
Abstract
Active noise control (ANC) techniques have been successfully investigated and implemented for the attenuation of stationary acoustic noise. Furthermore, adaptive methods for impulsive noise have been also presented in the literature, even though the considered statistical models are well suited only for a narrow class of impulsive disturbances that can be faced in realistic scenarios. In this paper, a preliminary study addressing the design of a non-adaptive deterministic ANC system for pulse signals is developed by avoiding any statistical assumption. The theory of Wave Field Synthesis is explicitly exploited in a destructive manner, that is, generating a canceling acoustic pressure field by means of arrays of secondary sources. An ad-hoc interactive software simulator implementing the proposed approach is realized and used to virtually explore the solution spaces of some test case scenarios. Simulations’ results considering linear and planar arrays in the case of free space propagation, as well as in the case of interaction with a hard ground, are presented and compared. Furthermore, the impact of different design solutions proposed to mitigate the impairments due to terrain reflections is evaluated.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The primary noise is considered quasi-stationary if the first and second order statistics vary relatively slow with respect to the adaptation time of the ANC system.
References
Akhtar, M.T., Mitsuhashi, W.: Improving performance of FxLMS algorithm for active noise control of impulsive noise. J. Sound Vib. 327(35), 647–656 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.jsv.2009.07.023
Akhtar, M.T., Mitsuhashi, W.: Improving robustness of filtered-x least mean p-power algorithm for active attenuation of standard symmetric-\(\alpha \)-stable impulsive noise. Applied Acoustics 72(9), 688–694 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.apacoust.2011.02.009
Alsyouf, I., Al-Alami, A., Saidam, A.: Implementing product design development methodology for assessing and improving the performance of products. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. (IJIDeM) 9(3), 225–234 (2015). doi:10.1007/s12008-015-0281-4
Attenborough, K., Li, K.M., Horoshenkov, K.: Predicting Outdoor Sound. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2006)
Bellomini, R., Luzzi, S., Carfagni, M., Borchi F, Governi, L., Bartalucci, C.: Life+2010 quadmap project (quiet areas definition and management in action plans): the methodology tested and optimized in pilot cases in Florence, Rotterdam and Bilbao (2014, January)
Berkhout, A.J., de Vries, D., Vogel, P.: Acoustic control by wave field synthesis. J. Acoust. Soc. Ame. 93(5), 2764–2778 (1993). doi:10.1121/1.405852
Carfagni, M., Bartalucci, C., Borchi, F., Governi, L., Petrucci, A., Weber, M., Aspuru, I., Bellomini, R., Gaudibert, P.: Life+2010 Quadmap Project (Quiet Areas Definition and Management in Action Plans): The New Methodology Obtained After Applying the Optimization Procedures, vol 3, pp 2576–2583 (2014)
Chaplin, G., Smith, R., Bramer, T.: Method and apparatus for reducing repetitive noise entering the ear. US Patent 4654871 (1987)
Di Gironimo, G., Marzano, A.: Design of an innovative assembly process of a modular train in virtual environment. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. (IJIDeM) 1(2), 85–97 (2007). doi:10.1007/s12008-007-0012-6
Douglas, S.C.: A family of normalized lms algorithms. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 1(3), 49–51 (1994). doi:10.1109/97.295321
Elliot, S., Nelson, P., Stothers, I., Boucher, C.: In-flight experiments on the active control of propeller-induced cabin noise. J. Sound Vib. 140(2), 219–238 (1990). doi:10.1016/0022-460X(90)90525-5
Elliott, S.J., Nelson, P.A.: Active noise control. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 10(4), 12–35 (1993). doi:10.1109/79.248551
Khan, O., Huang, P., Untz, S.: Display technology application assessment for virtual systems. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. (IJIDeM) 1(4), 243–251 (2007). doi:10.1007/s12008-007-0023-3
Kuntz A, Rabenstein R (2004) An approach to global noise control by wave field synthesis. In: Signal Processing Conference, 2004 12th European, pp 1999–2002
Kuo, S.M., Morgan, D.: Active Noise Control Systems: Algorithms and DSP Implementations, 1st edn. Wiley, New York (1995)
Kuo, S.M., Morgan, D.R.: Active noise control: a tutorial review. Proc. IEEE 87(6), 943–973 (1999). doi:10.1109/5.763310
Leahy, R., Zhou, Z., Hsu, Y.C. Adaptive filtering of stable processes for active attenuation of impulsive noise. In: International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1995 (ICASSP-95), vol. 5, pp. 2983–2986. (1995). doi:10.1109/ICASSP.1995.479472
Manolakis, D.G., Ingle, V.K., Kogon, S.M.: Statistical and Adaptive Signal Processing: Spectral Estimation, Signal Modeling. Adaptive Filtering and Array Processing, Artech House Inc, Norwood (2005)
Quinlan, D.A.: Application of active control to axial flow fans. Noise Control Eng. J. 39(3), 95–101 (1992). doi:10.3397/1.2827822
Schroeder, M., Rossing, T.D., Dunn, F., Hartmann, W.M., Campbell, D.M., Fletcher, N.H.: Springer Handbook of Acoustics, 1st edn. Springer, Berlin (2007)
Start. E. W.: Direct sound enhancement by wave field synthesis. PhD thesis, TU Delft (1997)
Sun, G., Li, M., Lim, T.C.: A family of threshold based robust adaptive algorithms for active impulsive noise control. Appl. Acoust. 97, 30–36 (2015a). doi:10.1016/j.apacoust.2015.04.003
Sun, G., Li, M., Lim, T.: C.: Enhanced filtered-x least mean M-estimate algorithm for active impulsive noise control. Appl Acoust 90, 31–41 (2015b). doi:10.1016/j.apacoust.2014.10.012
Sun, X., Kuo, S.M., Meng, G.: Adaptive algorithm for active control of impulsive noise. J. Sound Vib. 291(12), 516–522 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.jsv.2005.06.011
Thanigai, P., Kuo, S., Yenduri, R.: Nonlinear active noise control for infant incubators in neo-natal intensive care units. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 2007 (ICASSP 2007), vol. 1, pp. I-109-I-112. (2007). doi:10.1109/ICASSP.2007.366628
Treeby, B.E., Rendell, A.P., Cox, B.T.: Modeling nonlinear ultrasound propagation in heterogeneous media with power law absorption using a k-space pseudospectral method. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 131(6), 4324–4336 (2012)
Uberti, S., Copeta, A., Baronio, G., Motyl, B.: An eco-innovation and technical contaminated approach for designing a low environmental impact off-road motorcycle. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. (IJIDeM). (2017). doi:10.1007/s12008-017-0382-3
Widrow, B., Stearns, S.D.: Adaptive Signal Processing. Prentice-Hall Inc, Upper Saddle River (1985)
Wu, L., Qiu, X.: An m-estimator based algorithm for active impulse-like noise control. Appl. Acoust. 74(3), 407–412 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.apacoust.2012.06.019
Wu, L., He, H., Qiu, X.: An active impulsive noise control algorithm with logarithmic transformation. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 19(4), 1041–1044 (2011). doi:10.1109/TASL.2010.2061227
Zanolin, M., Podini, P., Farina, A., De Stabile, S., Vezzoni, P.: Active control of noise by wave field synthesis. In: Audio Engineering Society Convention 108 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lapini, A., Borchi, F., Carfagni, M. et al. Simulation and design of active control systems for acoustic pulse noise. Int J Interact Des Manuf 12, 573–584 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-017-0409-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-017-0409-9