Abstract
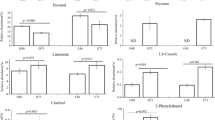
The volatile flavor characteristics of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) fillets thawed by magnetic nanoparticles plus microwave thawing (MNPMT) were compared with those of fresh samples thawed by chill storage thawing (CST) and microwave thawing (MT). The strategies of headspace solid-phase microextraction (HS-SPME), gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC-MS), gas chromatography-olfactometry (GC-O), aroma extract dilution analysis (AEDA), and sensory evaluation were applied to analyze the aroma-active compounds. The results of GC-MS showed that 24 kinds of volatile compounds existed in largemouth bass fillets. Orthogonal partial least squares discriminate analysis (OPLS-DA) (R2Y = 0.979, R2Y = 0.98, Q2 = 0.695) showed ethanol, hexanal, 2,6,10,14-tetramethyl-pentadecane, and (E)-9-octadecenoic acid were responsible for the flavor differences in MNPMT, MT, and CST. In GC-O measurement, 14 kinds of volatile compounds were detected, and MNPMT had similar aroma-active compounds with the fresh sample. The grassy (score = 1.58) and leafy (score = 0.75) odors were weak in MT, but the fishy odors (score = 1.5) were strong. All results showed the MNPMT samples had less changes in aroma composition compared with the fresh sample.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alasalvar, C., Taylor, K. D. A., & Shahidi, F. (2005). Comparison of volatiles of cultured and wild sea bream (Sparus aurata) during storage in ice by dynamic headspace analysis gas chromatography mass spectrometry. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 53(7), 2616–2622.
Campañone, L. A., & Zaritzky, N. E. (2010). Mathematical modeling and simulation of microwave thawing of large solid foods under different operating conditions. Food & Bioprocess Technology, 3(6), 813–825.
Cao, M. J., Cao, A. L., Wang, J., Cai, L. Y., Regenstein, J., Ruan, Y. J., et al. (2018a). Effect of magnetic nanoparticles plus microwave or far-infrared thawing on protein conformation changes and moisture migration of red seabream (Pagrus major) fillets. Food Chemistry, 266, 498–507.
Cao, J. X., Zhou, C. Y., Wang, Y., Sun, Y. Y., & Pan, D. D. (2018b). The effect of oxidation on the structure of G-actin and its binding ability with aroma compounds in carp grass skeletal muscle. Food Chemistry, 240, 346–353.
Casaburi, A., Nasi, A., Ferrocino, I., Monaco, R. D., Mauriello, G., Villani, F., et al. (2011). Spoilage-related activity of Carnobacterium maltaromaticum strains in air-stored and vacuum-packed meat. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 77(20), 7382–7393.
Domínguez, R., Gómez, M., Fonseca, S., & Lorenzo, J. M. (2014). Effect of different cooking methods on lipid oxidation and formation of volatile compounds in foal meat. Meat Science, 97(2), 223–230.
Etheridge, M. L., Xu, Y., Rott, L., Choi, J., Glasmacher, B., & Bischof, J. (2014). RF heating of magnetic nanoparticles improves the thawing of cryopreserved biomaterials. Technology, 2(3), 229–242.
Feng, Y., Cai, Y., Sun-Waterhouse, D., Cui, C., Su, G., Lin, L., & Zhao, M. (2015). Approaches of aroma extraction dilution analysis (AEDA) for headspace solid phase microextraction and gas chromatography-olfactometry (HS-SPME-GC-O): altering sample amount, diluting the sample or adjusting split ratio. Food Chemistry, 187, 44–52.
Fu, X., Lin, Q., Xu, S., & Wang, Z. (2015). Effect of drying methods and antioxidants on the flavor and lipid oxidation of silver carp slices. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 61(1), 251–257.
Hempfling, K., Fastowski, O., Kopp, M., Pour Nikfardjam, M., & Engel, K. H. (2013). Analysis and sensory evaluation of gooseberry (Ribes uva crispa L.) volatiles. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 61(26), 6240–6249.
Huang, X., Xin, J., & Zhao, J. (2011). A novel technique for rapid evaluation of fish freshness using colorimetric sensor array. Journal of Food Engineering, 105(4), 632–637.
Huang, L., Wu, Z., Chen, X., Weng, P., & Zhang, X. (2018). Characterization of flavour and volatile compounds of fermented squid using electronic nose and HPMS in combination with GC-MS. International Journal of Food Properties, 21(1), 760–770.
Iglesias, J., Medina, I., Bianchi, F., Careri, M., Mangia, A., & Musci, M. (2009). Study of the volatile compounds useful for the characterisation of fresh and frozen-thawed cultured gilthead sea bream fish by solid-phase microextraction gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Chemistry, 115(4), 1473–1478.
Jamilah, B., Mohamed, A., Abbas, K. A., Abdul Rahman, R., & Karim, R. (2009). A review on the effect of animal diets and presence of selected natural antioxidants on lipid oxidation of meat. Journal of Food Agriculture & Environment, 7(2), 76–81.
Jørgensen, L. V., Huss, H. H., & Dalgaard, P. (2001). Significance of volatile compounds produced by spoilage bacteria in vacuum-packed cold-smoked salmon (Salmo salar) analyzed by GC-MS and multivariate regression. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry, 49(5), 2376–2381.
Leygonie, C., Britz, T. J., & Hoffman, L. C. (2012). Impact of freezing and thawing on the quality of meat: review. Meat Science, 91(2), 93–98.
Li, Y., Jia, W., Zhang, C. H., Li, X., Wang, J. Z., Zhang, D. Q., & Mu, G. F. (2014). Fluctuated low temperature combined with high-humidity thawing to reduce physicochemical quality deterioration of beef. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 7(12), 3370–3380.
López-García, M. M., Ramilnovo, L. A., Vázquez-Odériz, M. L., & Romero-Rodríguez, M. A. (2014). Development of a quality index method for freshness assessment of thawed Greenland halibut (Reinhardtius hippoglossoides) stored at chilling temperature. Food & Bioprocess Technology, 7(6), 1847–1852.
Lv, T., Wang, Y., Pan, D., Cao, J., Zhang, X., Sun, Y., Chen, Y., & Liu, Y. (2017). Effect of trypsin treatments on the structure and binding capacity of volatile compounds of myosin. Food Chemistry, 214, 710–716.
Min, S. G., Hong, G. P., Chun, J. Y., & Park, S. H. (2016). Pressure ohmic thawing: a feasible approach for the rapid thawing of frozen meat and its effects on quality attributes. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 9(4), 564–575.
Neff, M. R., Bhavsar, S. P., Ni, F. J., Carpenter, D. O., Drouillard, K., Fisk, A. T., & Arts, M. T. (2014). Risk-benefit of consuming Lake Erie fish. Environmental Research, 134, 57–65.
Palmeri, G., Turchini, G. M., Caprino, F., Keast, R., Moretti, V. M., & Silva, S. S. D. (2008). Biometric, nutritional and sensory changes in intensively farmed Murray cod (Maccullochella peelii peelii, Mitchell) following different purging times. Food Chemistry, 107(4), 1605–1615.
Pham, A. J., Schilling, M. W., Mikel, W. B., Williams, J. B., Martin, J. M., & Coggins, P. C. (2008). Relationships between sensory descriptors, consumer acceptability and volatile flavor compounds of American dry-cured ham. Meat Science, 80(3), 728–737.
Piveteau, F., Le, G. S., Gandemer, G., Baud, J. P., Prost, C., & Demaimay, M. (2000). Aroma of fresh oysters Crassostrea gigas: composition and aroma notes. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry, 48(10), 4851–4857.
Podduturi, R., Petersen, M. A., Mahmud, S., Rahman, M. M., & Nog, J. (2017). Potential contribution of fish feed and phytoplankton to the content of volatile terpenes in cultured Pangasius (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) and tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry, 65(18), 3730–3736.
Prost, C., Hallier, A., Cardinal, M., Serot, T., & Courcoux, P. (2004). Effect of storage time on raw sardine (Sardina pilchardus) flavor and aroma quality. Journal of Food Science, 69(5), S198–S204.
Salum, P., Guclu, G., & Selli, S. (2017). Comparative evaluation of key aroma-active compounds in raw and cooked red mullet (Mullus barbatus) by aroma extract dilution analysis. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 65(38), 8402–8408.
Sánchez-Escalante, A., Torrescano, G., Djenane, D., Beltrán, J. A., & Roncalés, P. (2003). Stabilisation of colour and odour of beef patties by using lycopene-rich tomato and peppers as a source of antioxidants. Journal of the Science of Food & Agriculture, 83(3), 187–194.
Tran, V. H., Chan, H. P., Thurston, M., Jackson, P., Lewis, C., Yates, D., et al. (2010). Breath analysis of lung cancer patients using an electronic nose detection system. IEEE Sensors Journal, 10(9), 1514–1518.
Wang, J., He, Z. F., Li, H. J., & Liu, Y. N. (2013). Determination of flavour compounds in rabbit meat by HS-SPME/GC-MS. Food Science, 34(14), 212–217.
Wang, T., Zhao, G., Liang, X. M., Xu, Y., Li, Y., Tang, H., Jiang, R., & Gao, D. (2014). Numerical simulation of the effect of super paramagnetic nanoparticles on microwave rewarming of cryopreserved tissues. Cryobiology, 68(2), 234–243.
Wu, Y., Li, B., Zhu, X. J., Wei, Y., Yang, X. Q., & Chen, S. J. (2016). Comparison of nutrient composition of cultured sea bass and cultured fresh-water bass, Lateolabrax japonicas and Micropterus salmoides. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 37(2), 348–359.
Xu, Y., Liu, Y., Jiang, C., Zhang, C., Li, X., Zhu, D., & Li, J. (2014). Determination of volatile compounds in turbot (Psetta maxima) during refrigerated storage by headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 94(12), 2464–2471.
Yan, S. U., Liu, Y., Zhou, T., & Xia, Y. (2015). Effect of freeze-thaw cycles on the changes in volatile compounds of chansi rabbit, a traditional Chinese cured rabbit meat product. Food Science, 6(16), 158–162.
Yang, Q. L., Lou, X. W., Wang, Y., Pan, D. D., Sun, Y. Y., & Cao, J. X. (2016). Effect of pH on the interaction of volatile compounds with the myofibrillar proteins of duck meat. Poultry Science, pew413.
Zhang, B., Deng, S. G., & Lin, H. M. (2012). Changes in the physical and chemical and volatile flavor characteristics of Scomberomorus niphonius during chilled and frozen storage. Advanced Materials Research, 573–574(5), 1057–1063.
Zhang, L., Li, Q., Jia, S., Huang, Z., & Luo, Y. (2017). Effect of different stunning methods on antioxidant status, in vivo, myofibrillar protein oxidation, and the susceptibility to oxidation of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) fillets during 72 h postmortem. Food Chemistry, 246, 121–128.
Zhou, F., Zhao, M., Su, G., & Sun, W. (2014). Binding of aroma compounds with myofibrillar proteins modified by a hydroxyl-radical-induced oxidative system. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 62(39), 9544–9552.
Zhu, F., Zhang, D., He, Y., Liu, F., & Sun, D. W. (2013). Application of visible and near infrared hyperspectral imaging to differentiate between fresh and frozen–thawed fish fillets. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 6(10), 2931–2937.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFD0901106), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31401478), the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province of China (20170540006), and the Open Fund of the Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Food Nutrition and Human Health (20171003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, L., Cao, M., Cao, A. et al. The Effect of Magnetic Nanoparticles Plus Microwave Thawing on the Volatile Flavor Characteristics of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) Fillets. Food Bioprocess Technol 12, 1340–1351 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-019-02299-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-019-02299-7