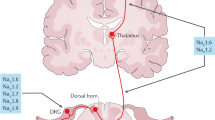
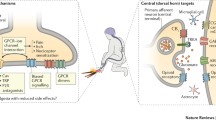
Abstract
This review focuses on the advances in the development of N-type calcium channel blockers as analgesic agents over the last 2 years. Firstly, it highlights the clinical progress with SNX-111 (Ziconotide; Elan Pharmaceuticals, Smithfield, RI) and then secondly, it outlines the various approaches being taken by researchers to design orally active, selective, small molecule modulators without the perceived disadvantages associated with SNX-111.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Brammar WJ: Voltage-gated calcium channels. In Ion Channel Facts Book, Volume 4: Voltage-Gated Channels. Edited by Conley EC, Brammar WJ. London: Academic Press; 1999:22–153. Excellent summary and reference source: nomenclature, expression, sequence analysis, structure and function, electrophysiology, pharmacology, and information retrieval.
Catterall WA: Neuronal Ca2}+ channels and neurotransmitter release. Neurosci Res Suppl 2000, 22:89–105.
Wang Y-X, Bowersox SS: Analgesic properties of ziconotide, a selective blocker of N-type neuronal calcium channels. CNS Drug Rev 2000, 6:1–20.
Heading C: Ziconotide neurex corporation. Curr Opin Cent Peripher Nerv Syst Invest Drugs 1999, 1:153–166.
Current Drugs Ltd. Ziconotide. The investigational drugs database drug report. Available at: http://www.currentdrugs. com. Accessed on August 2000. Excellent review on all aspects of the development of SNX-111.
Atanassoff PG, Hartmannsgruber MWB, Thrasher J, et al.: Ziconotide, a new N-type calcium channel blocker, administered intrathecally for acute postoperative pain. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2000, 25:274–278.
Lin Z, Haus S, Edgerton J, Lipscombe D: Identification of functionally distinct isoforms of the N-type Ca2}+ channel in rat sympathetic ganglia and brain. Neuron 1997, 18:153–166.
Lipscombe D, Schorge S, inventors; Brown University Research Foundation, assignee: A human N-type calcium channel splice variant isoform specific to the central nervous system and its therapeutic uses. US Patent WO9946383. September 16, 1999. Key disclosure of human brain N-type calcium channel isoform (ha1B+SFVG).
Gilmore J, Dell Colin, Bowman D, Lodge D: Neuronal calcium channels. Annu Rep Med Chem 1995, 30:51–60.
Cox B, Denyer JC: N-type calcium channel blockers in pain and stroke. Expert Opin Ther Pat 1998, 8:1237–1250. A comprehensive review of the previous 10 years on patent and open literature.
Norton RS, Pallaghy PK, Baell JB, et al.: Polypeptide omega-conotoxin GVIA as a basis for new analgesic and neuroprotective agents. Drug Dev Res 1999, 46:206–218.
Menzler S, Bikker JA, Horwell DC: Synthesis of a non-peptide analog of omega-conotoxin MVIIA. Tetrahedron Lett 1998, 39:7619–7622.
Menzler S, Bikker JA, Suman-Chauhan N, Horwell DC: Design and biological evaluation of non-peptide analogs of omegaconotoxin MVIIA. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2000, 10:345–347.
Guo Z-X, Cammidge AN, Horwell DC: Dendroid peptide structural mimetics of omega-conotoxin MVIIA based on a 2(1H)-quinolinone core. Tetrahedron 2000, 56:5045–5257.
Flinn JP, Pallaghy PK, Lew MJ, et al.: Roles of key functional groups in omega-conotoxin GVIA. Synthesis, structure and functional assay of selected peptide analogs. Eur J Biochem 1999, 262:447–455.
Flinn JP, Pallaghy PK, Lew MJ, et al.: Role of disulfide bridges in the folding, structure and biological activity of omegaconotoxin GVIA. Biochim Biophys Acta 1999, 1434:177–190.
Nielsen KJ, Schroeder T, Lewis R: Structure-activity relationships of omega-conotoxins at N-type voltage-sensitive calcium channels. J Mol Recognit 2000, 13:55–70. Comprehensive review of the structure-activity relationships of omega-conotoxins.
Atkinson RA, Kieffer B, Dejaegere A, et al.: Structural and dynamic characterization of omega-conotoxin MVIIA: the binding loop exhibits slow conformational exchange. Biochemistry 2000, 39:3908–3919.
Sato K, Raymond C, Martin-Moutot N, et al.: Binding of ala-scanning analogs of omega-conotoxin MVIIC to N- and P/Q-type calcium channels. FEBS Lett 2000, 469:147–150.
Sato K, Raymond C, Martin-Moutot N, et al.: Binding of six chimeric analogs of omega-conotoxin MVIIA and MVIIC to N- and P/Q-type calcium channels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2000, 269:254–256.
Yuen P-W, Schelkun RM, Szoke B, et al.: Synthesis and structure activity relationship of substituted quinoline and isoquinoline derivatives as N-type calcium channel blockers. Presented at the 214th American Chemical Society National Meeting, Las Vegas, NV, September 7–11, 1997:MEDI-005.
Yuen PW, Schelkun RM, Szoke B, Tarczy-Hornoch K: Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of substituted 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolines as N-type calcium channel blockers. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 1998, 8:2415–2418.
Yuen PW, Schelkun RM, Malone TC, et al.: Synthesis and biological activity of substituted bis-(4-hydroxyphenyl) methanes as N-type calcium channel blockers. Presented at the 214th American Chemical Society National Meeting, Las Vegas, NV, September 7–11, 1997:MEDI-007.
Schelkun RM, Yuen P-W, Malone TC, et al.: Synthesis and biological activity of substituted bis(4-hydroxyphenyl) methanes as N-type calcium channel blockers. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 1999, 9:2447–2452.
Kornberg BE, Nikam SS, Stoehr S, et al.: Synthesis and biological evaluation of substituted a-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl) benzeneethanamine derivatives as novel N-type calcium channel blockers. Presented at the 219th American Chemical Society National Meeting, San Francisco, CA, March 26–30, 2000:MEDI-260.
Hu L-Y, Ryder TR, Rafferty MF, et al.: N,N-dialkyl-dipeptidylamines as novel N-type calcium channel blockers. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 1999, 9:907–912.
Song Y, Sercel AD, Ingals S, et al.: Novel N-type calcium channel antagonists: SAR studies of PD 0151307 analogs. Presented at the 218th American Chemical Society National Meeting, New Orleans, LA, August 22–26,1999:MEDI-264.
Hu LY, Ryder TR, Rafferty MF, et al.: Synthesis of a series of 4-benzyloxyaniline analogs as neuronal N-type calcium channel blockers with improved anticonvulsant and analgesic properties. J Med Chem 1999, 42:4239–4249.
Hu L-Y, Ryder TR, Nikam SS, et al.: Synthesis and biological evaluation of substituted 4-(OBz)phenylalanine derivatives as novel N-type calcium channel blockers. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 1999, 9:1121–1126.
Hu LY, Ryder TR, Rafferty MF, et al.: Structure-activity relationship of N-methyl-N-aralkyl-peptidylamines as novel N-type calcium channel blockers. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 1999, 9:2151–2156.
Ryder TR, Hu LY, Rafferty MF, et al.: Multiple parallel synthesis of N,N-dialkyldipeptidylamines as N-type calcium channel blockers. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 1999, 9:1813–1818.
Rafferty MF, Song Y, inventors; Warner-Lambert Company, assignee: Preparation of reduced dipeptide analogs as calcium channel antagonists. US Patent WO0006559. February 10, 2000.
Ryder TR, Hu LY, Rafferty MF, et al.: Structure-activity relationship at the leucine side chain in a series of N, N-dialkyldipeptidyl-amines as N-type calcium channel blockers. Drug Des Discov 2000, 16:317–322.
Ryder TR, Hu LY, Rafferty MF, et al.: Synthesis and biological activity of 4-aminopiperidine derivatives as N-type calcium channel antagonists. Med Chem Res 2000, 10:11–8.
Ryder TR, Hu LY, Rafferty MF, et al.: Structure-activity relationship at the proximal phenyl group in a series of non-peptidyl N-type calcium channel antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 1999, 9:2453–2458.
Hu LY, Ryder TR, Rafferty MF, et al.: The discovery of [1-(4-dimethylamino-benzyl)-piperidin-4-yl]-[4-(3,3-dimethylbutyl)-phenyl]-(3-methyl-but-2-enyl)-amine, an N-type Ca+2 channel blocker with oral activity for analgesia. 2000, Bioorg Med Chem 8:1203–1212.
Grantham CJ, Main MJ, Cannell MB: Fluspirilene block of N-type calcium current in NGF-differentiated PC12 cells. Br J Pharmacol 1994, 111:483–488.
Song Y, Sercel AD, Ingals S, et al.: Novel N-type calcium channel antagonists: SAR studies on a series of benzhydrylalkyl amides and identification of PD 0176078 as a potent antagonist. Presented at the 218th American Chemical Society National Meeting, New Orleans, LA, August 22–26,1999:MEDI-265.
Song Y, Sercel AD, Ingals S, et al.: Novel N-type calcium channel antagonists: SAR studies on a series of benzhydrylpiperazines. Presented at the 218th American Chemical Society National Meeting, New Orleans, LA, August 22–26, 1999:MEDI-266.
Seko T, Kato M, inventors; Ono Pharmaceutical Co., assignee: Preparation and formulation of amino acid derivatives as N calcium channel inhibitors. US Patent WO9902146. January 21, 1999.
Seko T, Kato M, inventors; Ono Pharmaceutical Co., assignee: Preparation of amino acid derivatives as N type calcium channel inhibitors. US Patent WO0000470. January 6, 2000.
Seko T, Kato M, inventors; Ono Pharmaceutical Co., assignee: Preparation of amino acid derivatives as N-type calcium channel inhibitors. US Patent WO0004005. January 27, 2000.
Zamponi GW, inventor; Neuromed Technologies, assignee: Methods and compounds, to inactivate N-type calcium channels, therapeutic use, and screening method. US Patent WO0037059. June 29, 2000.
Marangos PJ, Sullivan BW, Wiemann T, et al., inventors; Cypros Pharmaceutical Corp., assignee: Preparation of neuroprotective poly-guanidino compounds which block presynaptic N and P/Q calcium channels. US Patent 6063819. May 16, 2000.
Deak F, Lasztoczi B, Pacher P, et al.: Inhibition of voltage-gated calcium channels by fluoxetine in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. Neuropharmacology 2000, 39:1029–1036.
Murakami M, Nakagawasai O, Fujii S, et al.: Antinociceptive effect of cilnidipine, a novel N-type calcium channel antagonist. Brain Res 2000, 868:123–127.
Ishii T: The effect of intrathecal infusion of cilnidipine, Ca 2}+ channel blocker on neuropathic pain in rats. Kyushu Shika Gakkai Zasshi 2000, 54:162–171.
Uneyama H, Niwa S, Onishi T, inventors; Ajinomoto Co., assignee: Preparation of 4-phenyldihydropyridine-3, 5-dicarboxylic acid esters as N-type calcium channel blockers. US Patent WO9849144. November 5, 1998.
Niwa S, Ohno S, Onishi T, Kito, et al., inventors; Ajinomoto Co., assignee: Preparation of dihydropyridine derivatives as N-type calcium channel blockers. US Patent WO9932446. July 1, 1999.
Niwa S, Ohno S, Takahara A, Kito M, inventors; Ajinomoto Co., assignee: Preparation of dihydropyridine derivatives and drug compositions containing the same. US Patent WO0024716. May 4, 2000.
Michne WF, Pierson ME Jr, inventors; Astra Aktiebolag (Publ), assignee: Preparation of 1,4-dihydropyrimidine-5-carboxylates as antagonists of N-type neuronal calcium channels. US Patent WO9901437. January 14, 1999.
Downs ES, Michne WF, Pierson ME Jr, inventors; Astra Aktiebolag (Publ), assignee: Preparation of dihydropyrimidinecarboxylates as N-type neuronal calcium channel antagonists. US Patent WO9901438. January 14, 1999.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cox, B. Calcium channel blockers and pain therapy. Current Review of Pain 4, 488–498 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-000-0073-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-000-0073-8