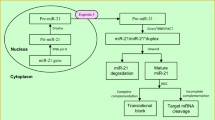
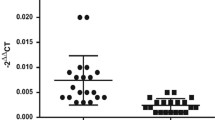
Abstract
Hypertension (HTN) is a chronic medical condition that commonly affects the aging population worldwide. The prevalence of HTN is increasing in developing countries and is one of the leading causes of death in older individuals. HTN results from a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors. Besides, HTN can result in various other health complications such as stroke and chronic kidney diseases, if not treated. Although various studies have explained the underlying mechanisms in the pathogenesis of HTN, limited information is available on their biomarkers. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are RNA molecules that have been recognized as key regulators for HTN. miR-21 is a common microRNA that is has been reported to be significantly upregulated in HTN individuals. Hence, miR-21 can be a potential therapeutic target for HTN. The number of studies related to miR-21 on hypertension is limited. Therefore, the main thrust of this paper is to provide an overview of the current clinical evidence and significance of miR-21 in HTN.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: •• Of major importance
•• Wei LK, Au A, Teh LK, Lye HS. Recent advances in the genetics of hypertension. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;956:561–581.
•• Sarkar T, Singh NP. Epidemiology and genetics of hypertension. J Assoc Physicians India. 2015;63(9):61–98.
•• Yip W, Wong TY, Jonas JB, Zheng Y, Lamoureux EL, Nangia V, Sabanayagam C. Prevalence, awareness, and control of hypertension among Asian Indians living in urban Singapore and rural India. J Hypertens. 2013;31(8):1539–46.
•• Gkaliagkousi E, Gavriilaki E, Triantafyllou A, Douma S. Clinical significance of endothelial dysfunction in essential hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2015;17(11):85.
•• Krishnan R, Mani P, Sivakumar P, Gopinath V, Sekar D. Expression and methylation of circulating microRNA-510 in essential hypertension. Hypertens Res. 2016; doi:10.1038/hr.2016.147.
•• Kontaraki JE, Marketou ME, Zacharis EA, Parthenakis FI, Vardas PE. MicroRNA-9 and microRNA-126 expression levels in patients with essential hypertension: potential markers of target-organ damage. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2014;8(6):368–75.
•• Sekar D, Basam V, Krishnan R, Mani P, Sivakumar P, Gopinath V. Methylation dependent miR-510 in prostate cancer: a novel upcoming candidate for prostate cancer. Gene Reports. 2016;4:70–3.
•• Cengiz M, Yavuzer S, Kılıçkıran Avcı B, Yürüyen M, Yavuzer H, Dikici SA, Karataş ÖF, Özen M, Uzun H, Öngen Z. Circulating miR-21 and eNOS in subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with hypertension. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2015;37(8):643–9.
•• Parikh VN, Park J, Nikolic I, Channick R, Yu PB, De Marco T, Hsue PY, Chan SY. Brief report: coordinated modulation of circulating miR-21 in HIV, HIV-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension, and HIV/hepatitis C virus coinfection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2015;70(3):236–41.
•• Kontaraki JE, Marketou ME, Parthenakis FI, Maragkoudakis S, Zacharis EA, Petousis S, Kochiadakis GE, Vardas PE. Hypertrophic and antihypertrophic microRNA levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and their relationship to left ventricular hypertrophy in patients with essential hypertension. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2015;9(10):802–10.
•• Cengiz M, Karatas OF, Koparir E, Yavuzer S, Ali C, Yavuzer H, Kirat E, Karter Y, Ozen M. Differential expression of hypertension-associated microRNAs in the plasma of patients with white coat hypertension. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94(13):e693.
•• Bienertova-Vasku J, Novak J, Vasku A. MicroRNAs in pulmonary arterial hypertension:pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2015;9(3):221–34.
•• Boucherat O, Potus F, Bonnet S. microRNA and pulmonary hypertension. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;888:237–52.
•• Meloche J, Paulin R, Provencher S, Bonnet S. Therapeutic potential of microRNA modulation in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2015;13(3):331–40.
•• Iannone L, Zhao L, Dubois O, Duluc L, Rhodes CJ, Wharton J, Wilkins MR, Leiper J, Wojciak-Stothard B. miR-21/DDAH1 pathway regulates pulmonary vascular responses to hypoxia. Biochem J. 2014;462(1):103–12.
•• Parikh VN, Jin RC, Rabello S, Gulbahce N, White K, Hale A, Cottrill KA, Shail RS, Waxman AB, Zhang YY, Maron BA, Hartner JC, Fujiwara Y, Orkin SH, Haley KJ, Barabasi AL, Loscalzo J, Chan SY, MicroRNA-21 integrates pathogenic signaling to control pulmonary hypertension:results of a network bioinformatics approach Circulation. 2012 Mar 27;125(12):1520–32.
•• Yang S, Banerjee S, Ad F, Cui H, Xie N, Abraham E, Liu G. miR-21 regulates chronic hypoxia induced pulmonary vascular remodeling. AM J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012;302(6):L521–9.
•• Green DE, Murphy TC, Kang BY, Searles CD, Hart CM. PPAR gamma ligands attenuates hypoxia-induced proliferation in human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells through modulation of microRNA-21. PLoS One. 2015 Jul 24;10(7):e0133391.
•• Li H, Zhang X, Wang F, Zhou L, Yin Z, Fan J, Nie X, Wang P, Fu XD, Chen C, Wang DW. MicroRNA-21 lowers blood pressure in spontaneous hypertensive rats by upregulating mitochondrial translation. Circulation. 2016;134(10):734–51.
•• Wang G, Wu L, Chen Z, Sun J. Identification of crucial miRNAs and the targets in renal cortex of hypertensive patients by expression profiles. Ren Fail. 2016;2:1–8.
•• Joshi SR, Dhagia V, Gairhe S, Edwards JG, McMurtry IF, Gupte SA. MicroRNA-140 is elevated and mitofusin-1 is downregulated in the right ventricle of the Sugen5416/hypoxia/normoxia model of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016;311(3):H689–98.
•• Solayman MH, Langaee T, Patel A, El-Wakeel L, El-Hamamsy M, Badary O, Johnson JA. Identification of suitable endogenous normalizers for qRT-PCR analysis of plasma microRNA expression in essential hypertension. Mol Biotechnol. 2016;58(3):179–87.
•• Yan M, Chen C, Gong W, Yin Z, Zhou L, Chaugai S, Wang DW. MiR-21-3p regulates cardiac hypertrophic response by targeting histone deacetylase-8. Cardiovasc Res. 2015;105(3):340–52.
•• White K, Dempsie Y, Caruso P, Wallace E, McDonald RA, Stevens H, Hatley ME, Van Rooij E, Morrell NW, MacLean MR, Baker AH. Endothelial apoptosis in pulmonary hypertension is controlled by a microRNA/programmed cell death 4/caspase-3 axis. Hypertension. 2014;64(1):185–94.
•• Parikh VN, Jin RC, Rabello S, Gulbahce N, White K, Hale A, Cottrill KA, Shaik RS, Waxman AB, Zhang YY, Maron BA, Hartner JC, Fujiwara Y, Orkin SH, Haley KJ, Barabási AL, Loscalzo J, Chan SY. MicroRNA-21 integrates pathogenic signaling to control pulmonary hypertension: results of a network bioinformatics approach. Circulation. 2012;125(12):1520–32.
•• Denby L, Ramdas V, McBride MW, Wang J, Robinson H, McClure J, Crawford W, Lu R, Hillyard DZ, Khanin R, Agami R, Dominiczak AF, Sharpe CC, Baker AH. MiR-21 and miR-214 are consistently modulated during renal injury in rodent models. Am J Pathol. 2011;179(2):661–72.
•• Sekar D, Venugopal B, Sekar P, Ramalingam K. Role of microRNA 21 in diabetes and associated/related diseases. Gene. 2016;582:14–8.
•• Sekar D, Krishnan R, Thirugnanasambantham K, Rajasekaran B, Islam VI, Sekar P. Significance of microRNA 21 in gastric cancer. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2016;40(5):538–45.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to our Chancellor Dr.P.Shamaraju, REVA university, Bangalore for giving moral support and motivation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest relevant to this manuscript.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Resistant Hypertension
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sekar, D., Shilpa, B.R. & Das, A.J. Relevance of microRNA 21 in Different Types of Hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep 19, 57 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11906-017-0752-z
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11906-017-0752-z