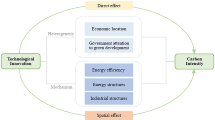
Abstract
The Chinese economy traces an outstanding economics growth and development by utilizing its natural resources and cheap labor force along with environmental problems. China is focusing on policies related to technology for people’s well-being. Despite this, about 2 million Chinese are going to die yearly due to air pollution regarding the Global Air Quality Report of the World Health Organization. The marginal impact of technology innovation and adoption is inaudible in the Chinese pollution equation. Therefore, this study analysis spotlights on nexuses of technology innovation and adoption CO2 emission for the Chinese economy, respectively. The marginal impacts infer that technology innovation and trade openness are mitigating the CO2 emission, whereas technology adoption and GDP enrich the CO2 emission in the Chinese context. Lag periods of technology innovation and adoption also have significant linkage with CO2 emission. Hence, an increase in technology innovation will help lessen the CO2 emission. The introduction of green energy and efficient ICT equipment is needed to tackle environmental degradation. The policy-makers can put a carbon tax on inefficient industrial processes and products for sustainable development.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ICT:
-
Information and telecommunication technologies
- TI:
-
Technology innovation
- TA:
-
Technology adoption
- LMIC:
-
Lower middle-income countries
- CO2 :
-
Carbon dioxide emission
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- JB:
-
Jarque-Bera test
- CUSUMSQ:
-
Cumulative sum of squares of recursive residuals
- ARDL:
-
Autoregressive distributive lag model
- GDP:
-
Gross domestic product
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
- WDI:
-
World Development Indicator
- ADF:
-
Augmented Dicky-Fuller
- PP:
-
Phillips-Perron
- CUSUM:
-
Cumulative sum of recursive residuals
References
Aghaei M, Rezagholizadeh M (2017) The impact of information and communication technology (ICT) on economic growth in the OIC countries. Econ Environ Stud 17:255–276
Ahmed Z, Wang Z, Mahmood F, Hafeez M, Ali N (2019a) Does globalization increase the ecological footprint? Empirical evidence from Malaysia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:18565–18582
Ahmed Z, Wang Z, Ali S (2019b) Investigating the non-linear relationship between urbanization and CO2 emissions: an empirical analysis. Air Qual Atmos Health 12:945–953. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-019-00711-x
Albiman M, Sulong Z (2016) The role of ICT use to the economic growth in Sub Saharan African region (SSA). J Sci Technol Policy Manag 7:306–329
Al-Mulali U, Saboori B, Ozturk I (2015a) Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Vietnam. Energy Policy 76:123–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2014.11.019
Al-Mulali U, Sheau-Ting L, Ozturk I (2015b) The global move toward Internet shopping and its influence on pollution: an empirical analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:9717–9727
Añón Higón D, Gholami R, Shirazi F (2017) ICT and environmental sustainability: a global perspective. Telematics Inform 34:85–95
Apergis N, Ozturk I (2015) Testing environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Asian countries. Ecol Indic 52:16–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.11.026
Asongu SA, Le Roux S, Biekpe N (2017) Enhancing ICT for environmental sustainability in sub-Saharan Africa. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 127:209–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2017.09.022
Asongu SA, Le Roux S, Biekpe N (2018) Enhancing ICT for environmental sustainability in sub-Saharan Africa. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 127:209–216
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Shahbaz M, Ponz-Tienda JL, Cantos-Cantos JM (2017) Energy innovation in the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC): a theoretical approach. In: Carbon footprint and the industrial life cycle (243–268). Springer, Cham
Ben M, Ben S (2015) The environmental Kuznets curve, economic growth, renewable and non-renewable energy, and trade in Tunisia. Renew Sust Energ Rev 47:173–185
Charfeddine L, Al-malk AY, Al K (2018) Is it possible to improve environmental quality without reducing economic growth: evidence from the Qatar economy. Renew Sust Energ Rev 82:25–39
Coroama VC, Hilty LM, Heiri E, Horn FM (2013) The direct energy demand of internet data flows. J Ind Ecol 17:680–688
das Neves Almeida TA, García-Sánchez IM (2017) Sociopolitical and economic elements to explain the environmental performance of countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(3):3006–3026
Engle RF, Yoo BS (1987) Forecasting and testing in co-integrated systems. J Econom 35(1):143–159
EPI Rank (2018) Environmental Performance Index by Yale University. https://epi.envirocenter.yale.edu. Accessed 10 Mar 2019
Hafeez M, Chunhui Y, Strohmaier D, Ahmed M, Jie L (2018) Does finance affect environmental degradation: evidence from One Belt and One Road Initiative region? Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:9579–9592. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1317-7
Hafeez M, Yuan C, Khelfaoui I, Sultan Musaad OA, Waqas Akbar M, Jie L (2019a) Evaluating the energy consumption inequalities in the one belt and one road region: implications for the environment. Energies 12:1358
Hafeez M, Yuan C, Shahzad K, Aziz B, Iqbal K, Raza S (2019b) An empirical evaluation of financial development-carbon footprint nexus in One Belt and Road region. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:25026–25036
Hafeez M, Yuan C, Yuan Q, Zhuo Z, Stromaier D (2019c) A global prospective of environmental degradations: economy and finance. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:25898–25915
Hajko V, Sebri M, Al-Saidi M, Balsalobre-Lorente D (2018) The energy-growth nexus: history, development, and new challenges. In: The economics and econometrics of the energy-growth nexus (1–46). Academic Press
Hamidi A, Ramavandi B (2020) Evaluation and scientometric analysis of researches on air pollution in developing countries from 1952 to 2018. Air Qual Atmos Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-020-00836-4
Houghton J (2010) ICT and the environment in developing countries: opportunities and developments. Dev Dimens ICTs Dev Improv Policy Coherence 6:149
Ioannides YM, Overman HG, Rossi-Hansberg E, Schmidheiny K (2008) The effect of information and communication technologies on urban structure. Econ Policy 23:202–242
ITU (2018) Statistics. https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-D/Statistics/Pages/stat/default.aspx. Accessed 10 Mar 2019
ITU (2018a) Environmental Sustainability and Climate Change. https://www.itu.int/en/action/climate/Pages/stat/default.aspx. Accessed 10 Mar 2019
Jayakar K, Park EA (2013) Broadband availability and employment: an analysis of county-level data from the National Broadband Map. J Inf Policy 3:181–200
Johansen S (1988) Statistical analysis of cointegration vectors. J Econ Dyn Control 12(2–3):231–254
Khan N, Baloch MA, Saud S, Fatima T (2018) The effect of ICT on CO2 emissions in emerging economies: does the level of income matters? Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:22850–22860
Landrigan PJ, Fuller R, Acosta N, Adeyi O, Arnold R, Basu NN et al (2018) The Lancet Commission on pollution and health. Lancet 391(10119):462–512
Lennerfors TT, Fors P, van Rooijen J (2015) ICT and environmental sustainability in a changing society. Inf Technol People 28:758–774
Liu J, Yuan C, Hafeez M, Yuan Q (2018) The relationship between environment and logistics performance: evidence from Asian countries. J Clean Prod 204:282–291
Miao Z, Baležentis T, Tian Z, Shao S, Geng Y, Wu R (2019) Environmental performance and regulation effect of China’s atmospheric pollutant emissions: evidence from “three regions and ten urban agglomerations”. Environ Resour Econ 74:211–242
Mundial B (2018) World Development Indicators (WDI). Recuperado de https://databank.worldbank.org/ddp/home.do
Naser M, Afzal I, Gow J (2016) Electricity consumption and information and communication technology in the next eleven emerging economies. Int J Energy Econ Policy 6:381–388
Pesaran MH, Shin Y, Smith RJ (2001) Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. J Appl Econ 16(3):289–326
Pradhan RP, Arvin M, Nair M, Bennett S, Bahmani S (2017) ICT-finance- growth nexus: empirical evidence from the Next-11 countries. Cuad Econ 40:115–134
Qi X, Han Y, Kou P (2020) Population urbanization, trade openness and carbon emissions: an empirical analysis based on China. Air Qual Atmos Health 13:519–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-020-00808-8
Raheem ID, Tiwari AK, Balsalobre-Lorente D (2020) The role of ICT and financial development in CO2 emissions and economic growth. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:1912–1922
Rauf A, Liu X, Amin W, Ozturk I, Rehman OU, Hafeez M (2018) Testing EKC hypothesis with energy and sustainable development challenges: a fresh evidence from belt and road initiative economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:1–15
Saboori B, Sulaiman J, Mohd S (2012) Economic growth and CO2 emissions in Malaysia: a cointegration analysis of the environmental Kuznets curve. Energy Policy 51:184–191
Salam S, Hafeez M, Mahmood MT, Akbar K (2019) The dynamic relation between technology adoption, technology innovation, human capital and economy: comparison of lower-middle-income countries. Interdiscipl Descript Complex Syst 17(1-B):146–161
Sassi S, Goaied M (2013) Financial development, ICT diffusion and economic growth: lessons from MENA region. Telecommun Policy 37:252–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.telpol.2012.12.004
Wang Y, Sanchez-Rodrigues V, Leighton E (2015) The use of ICT in road freight transport for CO2 reduction—an exploratory study of the UK’s grocery retail industry. Int J Logist Manag 26:2–29
Yakunina RP, Bychkov GA (2015) Correlation analysis of the components of the human development index across countries. Proc Econ Finan 24:766–771
Yao X, Yasmeen R, Li Y, Hafeez M, Padda IUH (2019) Free trade agreements and environment for sustainable development: a gravity model analysis. Sustainability 11:597
Yasmeen R, Li Y, Hafeez M, Ahmad H (2018) The trade-environment nexus in light of governance: a global potential. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:34360–34379
Yasmeen R, Li Y, Hafeez M (2019) Tracing the trade–pollution nexus in global value chains: evidence from air pollution indicators. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:5221–5233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3956-0
Yuelan P, Akbar MW, Hafeez M, Ahmad M, Zia Z, Ullah S (2019) The nexus of fiscal policy instruments and environmental degradation in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:28919–28932. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06071-4
Zivot E, Andrews DWK (2002) Further evidence on the great crash, the oil-price shock, and the unit-root hypothesis. J Bus Econ Stat 20:25–44
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the respected Editor Professor Yong S. Chung and anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions and comments to improve manuscript quality.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 118 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xinmin, W., Hui, P., Hafeez, M. et al. The nexus of environmental degradation and technology innovation and adoption: an experience from dragon. Air Qual Atmos Health 13, 1119–1126 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-020-00868-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-020-00868-w