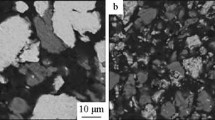
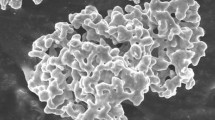
Abstract
Titanium and titanium alloys have a high strength to weight ratio and good corrosion resistance but also need longer time and have a higher cost on machining. Powder metallurgy offers a viable approach to produce near net-shape complex components with little or no machining. The Armstrong titanium powders are produced by direct reduction of TiCl4 vapor with liquid sodium, a process which has a relatively low cost. This paper presents a systematic research on powder characterization, mechanical properties, and sintering behavior and of Armstrong process powder metallurgy, and also discusses the sodium issue, and the advantages and disadvantages of Armstrong process powders.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
F.H. Froes, H. Friedrich, J. Kiese, and D. Bergoint, JOM 56, 40 (2004).
T.M. Zwitter, P. Nash, X. Xu, and C. Johnson, Report No. NETL–DE-FC26-08NT01913, Department of Energy, USA (2011).
X. Xu, P. Nash, Y. Yan, and T.M. Zwitter, Proceedings of 2011 International Conference on Powder Metallurgy & Particulate Materials (San Francisco: MPIF, 2011), p. 137.
Y. Yamamoto, W.H. Peter, and A.S. Sabau, Proceedings of 2010 International Conference on Powder Metallurgy & Particulate Materials (Ft. Lauderdale: MPIF, 2010), p. 24.
Metal Powder Industries Federation, Standard Test Methods for Metal Powders and Powder Metallurgy Products (Princeton: MPIF, 2002).
ASTM Committee ASTM E1409-08 Standard Test Method for Determination of Oxygen and Nitrogen in Titanium and Titanium Alloys by the Inert Gas Fusion Technique (2008).
ASTM Committee ASTM E1941-10 Standard Test Method for Determination of Carbon in Refractory and Reactive Metals and Their Alloys by Combustion Analysis (2010).
Y. Yamamoto, J.O. Kiggans, M.B. Clark, S.D. Nunn, A.S. Sabau, and W.H. Peter, Key Eng. Mater. 436, 103 (2010).
K. Araci, K. Akhtar, and D. Mangabhai, Proceedings of the 12th World Conference on Titanium (Beijing: Science Press, 2011), p. 135.
C. McCracken, PIM Int. 2, 55 (2008).
J.A. Roberts, ProQuest LLC, Master Thesis, Northern Ann Arbor, MI (2011).
W. Chen, Y. Yamamoto, and W.H. Peter, Key Eng. Mater. 436, 123 (2010).
X. Xu, P. Nash, Y. Yan, T.M. Zwitter, K. Akhtar, and K. Araci, Proceedings of the 12th World Conference on Titanium (Beijing: Science Press, 2011), p. 1709.
R. German, Powder Metallurgy and Particulate Materials Processing: The Processes, Materials, Products, Properties and Applications (MPIF: Princeton, 2005).
B. Peter, Defense Manufacturing Conference, Gee Whiz/Darpa Technology, unpublished research (2009).
J.D. Rivard, C.A. Blue, D.C. Harper, J.O. Kiggans, P.A. Menchhofer, J.R. Mayotte, L. Jacobsen, and D. Kogut, JOM 57, 58 (2005).
D. Eylon, W.A. Ernst, and D.P. Kramer, Ultra-fine Titanium Microstructure Development by Rapid Hot Compaction of Armstrong Process Powder for Improved Mechanical Properties and Superplasticity. http://www.itponline.com/docs/Eylon_Plansee_2009_TiPM_Paper.pdf. Accessed 4 Dec 2016.
X. Xu, Y. Han, C. Li, P. Nash, D. Mangabhai, and W. Lu, J. Mater. Res. 30, 1056 (2015).
W. H. Peter, C. A. Blue, S. Clive, B. Ernst, J. McKernan, J. Kiggans, J. Rivard, C. Yu, in Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference On Light Metals Technology (Saint-Sauveur, 2007), p. 24.
D. Cantin, P. Kean, N. Stone, R. Wilson, M. Gibson, M. Yousuff, D. Ritchie, and R. Rajakumar, Powder Metall. 54, 188 (2011).
G. Lutjering and J.C. Williams, Titanium (Berlin: Springer, 2007).
R. Boyer, G. Welsch, and E.W. Collings, Materials Properties Handbook: Titanium Alloys (Materials Park: ASM International, 1994).
V.A. Duz and V.S. Moxson, US Patent 7311873, US Patent and Trademark Office, published 25 December 2007.
V.A. Duz and V.S. Moxson, Sci. Technol. Powder Mater. Synth. Consol. Prop. 4, 2968 (2005).
D. Cantin, N. Stone, D. Alexander, M.A. Gibson, D. Ritchie, R. Wilson, M. Yousuff, R. Rajakumar, and K. Rogers, Mater. Sci. Forum 654–656, 807 (2010).
N. Stone, D. Cantin, M. Gibson, T. Kearney, S. Lathabai, D. Ritchie, R. Wilson, M. Yousuff, R. Rajakumar, and K. Rogers, Mater. Sci. Forum 618–619, 139 (2009).
O.M. Ivasishin, D. Eylon, V.I. Bondarchuk, and D.G. Savvakin, Defect Diffus. Forum 277, 177 (2008).
R. German, Sintering Theory and Practice (New York: Wiley, 1996).
X. Xu and P. Nash, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 607, 409 (2014).
K.S. Weil, Y. Hovanski, and C.A. Lavender, J. Alloys Compd. 473, 39 (2009).
S.D. Hill and R.V. Mrazek, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 5, 53 (1974).
C.W. Bale, J. Phase Equilibria 10, 138 (1989).
I. Becker, I. Hofmann, and F.A. Müller, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 27, 4547 (2007).
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the financial support provided by Cristal Metal Inc. and Thermal Processing Technology Center in USA. We also would like to acknowledge Honeywell for supplying the titanium powder for our research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Nash, P. & Mangabhai, D. Characterization and Sintering of Armstrong Process Titanium Powder. JOM 69, 770–775 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-016-2238-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-016-2238-x