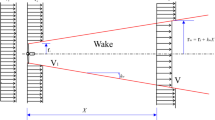
Abstract
This work bridges two research fields i.e. metaheuristics and wind farm layout design. Comparative performance of twelve metaheuristics (MHs) on wind farm layout optimisation (WFLO) was conducted. Four WFLO problems are proposed for benchmarking the various metaheuristics while the design problem is an attempt to simultaneously minimise wind farm cost and maximise wind farm totally produced power. Design variables are wind turbine placement with fixed and varied number of wind turbines. The Jansen’s wake model is used while two types of energy estimation with and without considering partially overshadowed wake areas are studied. The results obtained from using various MHs are statistically compared in terms of convergence and consistency while the best performer is obtained. Comparison results indicated that moth-flame optimisation (MFO) algorithm is the most efficient algorithms. The results obtained in this work are said to be the baseline for future study on WFLO using metahueristics.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reddy SR (2020) Wind farm layout optimization (WindFLO): an advanced framework for fast wind farm analysis and optimization. Appl Energy 269:115090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.115090
Khan MJ, Mathew L (2020) Comparative study of optimization techniques for renewable energy system. Arch Comput Methods Eng 27(2):351–360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-018-09306-8
Shu ZR, Li QS, Chan PW (2015) Investigation of offshore wind energy potential in Hong Kong based on Weibull distribution function. Appl Energy 156:362–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.07.027
Karad S, Thakur R (2019) Recent trends of control strategies for doubly fed induction generator based wind turbine systems: a comparative review. Arch Comput Methods Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-019-09367-3
Hewitt S, Margetts L, Revell A (2018) Building a digital wind farm. Arch Comput Methods Eng 25(4):879–899. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-017-9222-7
Shourangiz-Haghighi A, Haghnegahdar MA, Wang L, Mussetta M, Kolios A, Lander M (2020) State of the art in the optimisation of wind turbine performance using CFD. Arch Comput Methods Eng 27(2):413–431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-019-09316-0
Veisi AA, Shafiei Mayam MH (2017) Effects of blade rotation direction in the wake region of two in-line turbines using Large Eddy Simulation. Appl Energy 197:375–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.04.013
Gao X, Yang H, Lu L (2016) Optimization of wind turbine layout position in a wind farm using a newly-developed two-dimensional wake model. Appl Energy 174:192–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.04.098
Mosetti G, Poloni C, Diviacco B (1994) Optimization of wind turbine positioning in large windfarms by means of a genetic algorithm. J Wind Eng Ind Aerodyn 51(1):105–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-6105(94)90080-9
Wang Y, Liu H, Long H, Zhang Z, Yang S (2018) Differential evolution with a new encoding mechanism for optimizing wind farm layout. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 14(3):1040–1054. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2017.2743761
Eroğlu Y, Seçkiner SU (2012) Design of wind farm layout using ant colony algorithm. Renew Energy 44:53–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2011.12.013
Feng J, Shen WZ (2015) Solving the wind farm layout optimization problem using random search algorithm. Renew Energy 78:182–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2015.01.005
Bilbao M, Alba E (2009) Simulated annealing for optimization of wind farm annual profit. In: 2009 2nd International symposium on logistics and industrial informatics, pp 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/LINDI.2009.5258656
Chowdhury S, Zhang J, Messac A, Castillo L (2013) Optimizing the arrangement and the selection of turbines for wind farms subject to varying wind conditions. Renew Energy 52:273–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2012.10.017
Patel J, Savsani V, Patel V, Patel R (2017) Layout optimization of a wind farm to maximize the power output using enhanced teaching learning based optimization technique. J Clean Prod 158:81–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.04.132
Katic I, Højstrup J, Jensen NO (1987) A simple model for cluster efficiency. In: EWEC’86, vol. 1, p 5
Frandsen S et al (2006) Analytical modelling of wind speed deficit in large offshore wind farms. Wind Energy 9(1–2):39–53. https://doi.org/10.1002/we.189
Larsen GC (2009) A simple stationary semi-analytical wake model. Risø National Laboratory for Sustainable Energy, Technical University of Denmark
Ishihara T, Qian G-W (2018) A new Gaussian-based analytical wake model for wind turbines considering ambient turbulence intensities and thrust coefficient effects. J Wind Eng Ind Aerodyn 177:275–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jweia.2018.04.010
Bastankhah M, Porté-Agel F (2014) A new analytical model for wind-turbine wakes. Renew Energy 70:116–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2014.01.002
Xie S, Archer C (2015) Self-similarity and turbulence characteristics of wind turbine wakes via large-eddy simulation. Wind Energy 18(10):1815–1838. https://doi.org/10.1002/we.1792
Karaboga D, Basturk B (2007) A powerful and efficient algorithm for numerical function optimization: artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm. J Glob Optim 39:459–471. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10898-007-9149-x
Socha K, Dorigo M (2008) Ant colony optimization for continuous domains. Eur J Oper Res 185(3):1155–1173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2006.06.046
Storn R, Price K (1997) Differential evolution—a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces. J Glob Optim 11(4):341–359. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008202821328
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1995) Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of ICNN’95 international conference on neural networks, vol. 4, pp 1942–1948. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICNN.1995.488968
Rao RV, Savsani VJ, Vakharia DP (2011) Teaching–learning-based optimization: a novel method for constrained mechanical design optimization problems. Comput Aided Des 43(3):303–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cad.2010.12.015
Hansen N, Müller SD, Koumoutsakos P (2003) Reducing the time complexity of the derandomized evolution strategy with covariance matrix adaptation (CMA-ES). Evol Comput 11(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1162/106365603321828970
Mirjalili S (2015) Moth-flame optimization algorithm: a novel nature-inspired heuristic paradigm. Knowl-Based Syst 89:228–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2015.07.006
Mirjalili S (2016) SCA: a sine cosine algorithm for solving optimization problems. Knowl-Based Syst 96:120–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2015.12.022
Mirjalili S, Lewis A (2016) The whale optimization algorithm. Adv Eng Softw 95:51–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2016.01.008
Askarzadeh A (2016) A novel metaheuristic method for solving constrained engineering optimization problems: crow search algorithm. Comput Struct 169:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2016.03.001
Mirjalili S, Gandomi AH, Mirjalili SZ, Saremi S, Faris H, Mirjalili SM (2017) Salp Swarm algorithm: a bio-inspired optimizer for engineering design problems. Adv Eng Softw 114:163–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2017.07.002
Saremi S, Mirjalili S, Lewis A (2017) Grasshopper optimisation algorithm: theory and application. Adv Eng Softw 105:30–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2017.01.004
Wu X, Hu W, Huang Q, Chen C, Jacobson MZ, Chen Z (2020) Optimizing the layout of onshore wind farms to minimize noise. Appl Energy 267:114896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.114896
Shakoor R, Hassan MY, Raheem A, Wu Y-K (2016) Wake effect modeling: a review of wind farm layout optimization using Jensen׳s model. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 58:1048–1059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.12.229
Sethi JK, Deb D, Malakar M (2011) Modeling of a wind turbine farm in presence of wake interactions. In: 2011 international conference on energy, automation and signal, pp 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEAS.2011.6147144
Weisstein EW (2020) Circle-circle intersection. https://mathworld.wolfram.com/Circle-CircleIntersection.html. Accessed July 30 2020
Paul S, Rather ZH (2019) A new bi-level planning approach to find economic and reliable layout for large-scale wind farm. IEEE Syst J 13(3):3080–3090. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSYST.2019.2891996
Parada L, Herrera C, Flores P, Parada V (2017) Wind farm layout optimization using a Gaussian-based wake model. Renew Energy 107:531–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.02.017
Tao S, Kuenzel S, Xu Q, Chen Z (2019) Optimal micro-siting of wind turbines in an offshore wind farm using Frandsen–Gaussian wake model. IEEE Trans Power Syst 34(6):4944–4954. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRS.2019.2916906
Chen Y, Li H, Jin K, Song Q (2013) Wind farm layout optimization using genetic algorithm with different hub height wind turbines. Energy Convers Manage 70:56–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2013.02.007
Vasel-Be-Hagh A, Archer CL (2017) Wind farm hub height optimization. Appl Energy 195:905–921. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.03.089
Abdulrahman M, Wood D (2017) Investigating the Power-COE trade-off for wind farm layout optimization considering commercial turbine selection and hub height variation. Renew Energy 102:267–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2016.10.038
Chen K, Song MX, Zhang X, Wang SF (2016) Wind turbine layout optimization with multiple hub height wind turbines using greedy algorithm. Renew Energy 96:676–686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2016.05.018
Duan B, Wang J, Gu H (2014) Modified genetic algorithm for layout optimization of multi-type wind turbines. In: 2014 American control conference, pp 3633–3638. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACC.2014.6859416
Romanuke VV (2019) Iterative power maximization by one-half cost dichotomy for optimizing wind farm deployment. KPI Sci News. https://doi.org/10.20535/kpi-sn.2019.4.177315
Charhouni N, Sallaou M, Mansouri K (2019) Realistic wind farm design layout optimization with different wind turbines types. Int J Energy Environ Eng 10(3):307–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40095-019-0303-2
MirHassani SA, Yarahmadi A (2017) Wind farm layout optimization under uncertainty. Renew Energy 107:288–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.01.063
Turner SDO, Romero DA, Zhang PY, Amon CH, Chan TCY (2014) A new mathematical programming approach to optimize wind farm layouts. Renew Energy 63:674–680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2013.10.023
Zhang J, Sanderson AC (2009) JADE: adaptive differential evolution with optional external archive. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 13(5):945–958. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2009.2014613
Tanabe R, Fukunaga A (2013) Evaluating the performance of SHADE on CEC 2013 benchmark problems. In: 2013 IEEE congress on evolutionary computation, pp 1952–1959. https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC.2013.6557798
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the support from the Thailand Research Fund (RTA6180010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kunakote, T., Sabangban, N., Kumar, S. et al. Comparative Performance of Twelve Metaheuristics for Wind Farm Layout Optimisation. Arch Computat Methods Eng 29, 717–730 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-021-09586-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-021-09586-7