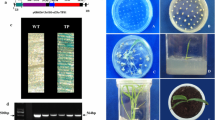
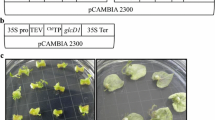
Abstract
Trehalose is a non-reducing disaccharide found in various organisms, including bacteria, fungi, invertebrates, and plants. It plays essential roles in diverse biological processes such as stress resistance, metabolism, and development in plants. Despite the important role of trehalose, it is challenging to increase trehalose levels because of its negative effects on plant growth and development. In this study, we tested several combinations of different promoters and trehalose biosynthetic genes to efficiently accumulate trehalose in potato plants. Transgenic potato plants expressing TPSP (trehalose-6-phosphate synthase/phosphatase) fusion gene under the control of Rd29A promoter increased trehalose content in response to high salt stress and did not show significant growth retardation. Although constitutive overexpression of plastid-targeted MTSH (maltooligosyltrehalose synthase/trehalohydrolase) fusion gene driven by CaMV 35S promoter remarkably accumulated trehalose, the transgenic potato plants showed a severely stunted phenotype. By contrast, stress-inducible expression of plastid-targeted MTSH under the control of Rd29A promoter led to trehalose accumulation without growth defects in response to high salt stress. Besides, tuber-specific expression of plastid-targeted MTSH driven by GBSS (granule-bound starch synthase) promoter specifically increased trehalose level in potato tubers without stunting growth. Consequently, we suggest that heterologous expression of TPSP and MTSH fusion genes driven by stress-inducible or tuber-specific promoters can be an effective strategy for accumulating trehalose in potato plants as well as minimizing its adverse effects on potato growth.




Similar content being viewed by others

References
Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (1995) Short protocols in molecular biology, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York
Avonce N, Mendoza-Vargas A, Morett E, Iturriaga G (2006) Insights on the evolution of trehalose biosynthesis. BMC Evol Biol 6:109
Chae K (1999) Development of trehalose-producing transgenic potato. The thesis for MS. Seoul National University
De Smet KA, Weston A, Brown IN, Young DB, Robertson BD (2000) Three pathways for trehalose biosynthesis in mycobacteria. Microbiol 146:199–208
Debast S, Nunes-Nesi A, Hajirezaei MR, Hofmann J, Sonnewald U, Fernie AR, Börnke F (2011) Altering trehalose-6-phosphate content in transgenic potato tubers affects tuber growth and alters responsiveness to hormones during sprouting. Plant Physiol 156:1754–1771
Diretto G, Tavazza R, Welsch R, Pizzichini D, Mourgues F, Papacchioli V, Beyer P, Giuliano G (2006) Metabolic engineering of potato tuber carotenoids through tuber-specific silencing of lycopene epsilon cyclase. BMC Plant Biol 6:13
Elbein AD (1974) The metabolism of alpha, alpha-trehalose. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem 30:227–256
Frison M, Parrou JL, Guillaumot D, Masquelier D, Francois J, Chaumont F, Batoko H (2007) The Arabidopsis thaliana trehalase is a plasma membrane-bound enzyme with extracellular activity. FEBS Lett 581:4010–4016
Garg AK, Kim J-K, Owens TG, Ranwala AP, Choi YD, Kochian LV, Wu RJ (2002) Trehalose accumulation in rice plants confers high tolerance levels to different abiotic stresses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:15898–15903
Ge LF, Chao DY, Shi M, Zhu MZ, Gao JP, Lin HX (2008) Overexpression of the trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase gene OsTPP1 confers stress tolerance in rice and results in the activation of stress responsive genes. Planta 228:191–201
Goddijn OJ, van Dun K (1999) Trehalose metabolism in plants. Trends Plant Sci 4:315–319
Goddijn OJ, Verwoerd TC, Voogd E, Krutwagen RW, de Graaf PT, van Dun K, Poels J, Ponstein AS, Damm B, Pen J (1997) Inhibition of trehalase activity enhances trehalose accumulation in transgenic plants. Plant Physiol 113:181–190
Granot D, Kelly G, Stein O, David-Schwartz R (2014) Substantial roles of hexokinase and fructokinase in the effects of sugars on plant physiology and development. J Exp Bot 65:809–819
Hoppmann V, Fiore SDI, Zimmermann S, Emans N, Rademacher T, Fischer R, Schillberg S (2002) The potato granule bound starch synthase chloroplast transit peptide directs recombinant proteins to plastids. J Plant Physiol 159:1061–1067
Jiang D, Chen W, Gao J, Yang F, Zhuang C (2019) Overexpression of the trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase OsTPP3 increases drought tolerance in rice. Plant Biotech Rep 13:285–292
Joo J, Choi HJ, Lee YH, Lee S, Lee CH, Kim CH, Cheong J-J, Choi YD, Song SI (2014) Over-expression of BvMTSH, a fusion gene for maltooligosyltrehalose synthase and maltooligosyltrehalose trehalohydrolase, enhances drought tolerance in transgenic rice. BMB Reports 47:27–32
Kasuga M, Liu Q, Miura S, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1999) Improving plant drought, salt, and freezing tolerance by gene transfer of a single stress-inducible transcription factor. Nat Biotechnol 17:287–291
Kaushik JK, Bhat R (2003) Why is trehalose an exceptional protein stabilizer? An analysis of the thermal stability of proteins in the presence of the compatible osmolyte trehalose. J Biol Chem 278:26458–26465
Kim YH, Kwon TK, Park S, Seo HS, Cheong J-J, Kim CH, Kim J-K, Lee JS, Choi YD (2000) Trehalose synthesis by sequential reactions of recombinant maltooligosyltrehalose synthase and maltooligosyltrehalose trehalohydrolase from Brevibacterium helvolum. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:4620–4624
Kortstee AJ, Vermeesch AM, de Vries BJ, Jacobsen E, Visser RG (1996) Expression of Escherichia coli branching enzyme in tubers of amylose-free transgenic potato leads to an increased branching degree of the amylopectin. Plant J 10:83–90
Lee S-B, Kwon H-B, Kwon S-J, Park S-C, Jeong M-J, Han S-E, Byun M-O, Daniell H (2003) Accumulation of trehalose within transgenic chloroplasts confers drought tolerance. Mol Breed 11:1–13
Liu Q, Kasuga M, Sakuma Y, Abe H, Miura S, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1998) Two transcription factors, DREB1 and DREB2, with an EREBP/AP2 DNA binding domain separate two cellular signal transduction pathways in drought- and low-temperature-responsive gene expression, respectively, in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 10:1391–1406
Lunn JE, Delorge I, Figueroa CM, Van Dijck P, Stitt M (2014) Trehalose metabolism in plants. Plant J 79:544–567
Maruta K, Nakada T, Kubota M, Chaen H, Sugimoto T, Kurimoto M, Tsujisaka Y (1995) Formation of trehalose from maltooligosaccharides by a novel enzymatic system. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 59:1829–1834
Maruta K, Hattori K, Nakada T, Kubota M, Sugimoto T, Kurimoto M (1996) Cloning and sequencing of trehalose biosynthesis genes from Arthrobacter sp. Q36. Biochimi Biophys Acta 1289:10–13
Miranda JA, Avonce N, Suarez R, Thevelein JM, Van Dijck P, Iturriaga G (2007) A bifunctional TPS-TPP enzyme from yeast confers tolerance to multiple and extreme abiotic-stress conditions in transgenic Arabidopsis. Planta 226:1411–1421
Ohtake S, Wang YJ (2011) Trehalose: current use and future applications. J Pharm Sci 100:2020–2053
Paul MJ, Gonzalez-Uriarte A, Griffiths CA, Hassani-Pak K (2018) The role of trehalose 6-phosphate in crop yield and resilience. Plant Physiol 177:12–23
Pellny TK, Ghannoum O, Conroy JP, Schluepmann H, Smeekens S, Andralojc J, Krause KP, Goddijn O, Paul MJ (2004) Genetic modification of photosynthesis with E. coli genes for trehalose synthesis. Plant Biotechnol J 2:71–82
Ponnu J, Wahl V, Schmid M (2011) Trehalose-6-phosphate: connecting plant metabolism and development. Front Plant Sci 2:70
Schluepmann H, Pellny T, van Dijken A, Smeekens S, Paul M (2003) Trehalose 6-phosphate is indispensable for carbohydrate utilization and growth in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:6849–6854
Schluepmann H, Berke L, Sanchez-Perez GF (2012) Metabolism control over growth: a case for trehalose-6-phosphate in plants. J Exp Bot 63:3379–3390
Seo HS, Koo YJ, Lim JY, Song JT, Kim CH, Kim JK, Lee JS, Choi YD (2000) Characterization of a bifunctional enzyme fusion of trehalose-6-phosphate synthetase and trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase of Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:2484–2490
Sheerman S, Bevan MW (1988) A rapid transformation method for Solanum tuberosum using binary Agrobacterium tumefaciens vectors. Plant Cell Rep 7:13–16
Stiller I, Dulai S, Kondrak M, Tarnai R, Szabo L, Toldi O, Banfalvi Z (2008) Effects of drought on water content and photosynthetic parameters in potato plants expressing the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Planta 227:299–308
Strommer J, Grenerson R, Vayada M (1993) Isolation and characterization of plant mRNA. In: Methods in plant molecular biology and biotechnology. CRC press, Florida
Yadav UP, Ivakov A, Feil R, Duan GY, Walther D, Giavalisco P, Piques M, Carillo P, Hubberten HM, Stitt M, Lunn JE (2014) The sucrose-trehalose 6-phosphate (Tre6P) nexus: specificity and mechanisms of sucrose signalling by Tre6P. J Exp Bot 65:1051–1068
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Creative-Pioneering Researchers Program through Seoul National University and a Grant from the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 Program (PJ013399) of Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shim, J.S., Seo, JS., Seo, J.S. et al. Heterologous expression of bacterial trehalose biosynthetic genes enhances trehalose accumulation in potato plants without adverse growth effects. Plant Biotechnol Rep 13, 409–418 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-019-00554-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-019-00554-z