Abstract
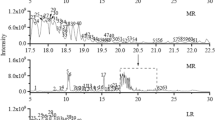
Apostichopus japonicus is an important invertebrate that is widely used as a tonic food in Asian countries. The purpose of this study is to purify and identify a class of compound, the saponins, from the body wall of A. japonicus, and to establish a new method to determine the quantity of saponins in the sea cucumber. In this study, the saponins of A. japonicus, cladoloside A (CA), were obtained from 80% ethanol extract by column chromatography for the first time and were characterized using the spectral method. The resulting purified saponins were then profiled using 1HNMR, 13CNMR, and ESI-MS, which revealed the CA molecular formula of C53H82O2 and contained a triterpenoid backbone, a methylglucopyranosyl moiety, a quinovopyranosyl, and two xylopyranosyls. A method for the quantitative determination of CA, comprising microwave-assisted extraction, high-performance liquid chromatography, and diode array detector method, was established. Extraction efficiency was optimized by changing microwave power, extraction solvent, volume, time, and temperature. Results showed that under the optimum conditions (extraction time of 10 min, temperature of 45°C, and solvent of 25 mL 70% ethanol under 400 W), the detection limit of CA was 0.0015 mg mL−1, and the recoveries of CA from samples at spiking levels of 10, 20, and 50 µg g−1 ranged from 90.1%–104%. The proposed method was successfully applied to analyze the saponins in different tissues of A. japonicus collected in different seasons. The method developed in this study can provide quantitative technical support for the quality control of A. japonicus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexandra, S. S., Anatoly, I. K., Sergey, A. A., Pelageya, V. A., Pavel, S. D., Ekaterina, A. Y., et al., 2014. Triterpene glycosides from the sea cucumber Cladolabes schmeltzii. II. Structure and biological action of cladolosides A1–A6. Natural Product Communications, 9 (10): 1421–1428.
Avilov, S. A., and Stonik, V. A., 1988. New triterpenen glycosides from the holothurian Cladolabes sp.. Chemistry of Natural Compounds, 24 (5): 656, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00633413.
Ganzler, K., Salgó, A., and Valkó, K., 1986. Microwave extraction, a novel sample preparation method for chromatography. Journal of Chromatography A, 371: 299–306, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(01)94714-4.
Gao, Z. Y., Wang, R., Guo, F. J., Jia, Q., and Li, Y. M., 2014. Determination total saponin content in sea cucumbers. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 20 (15): 89–92 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Guillaume, C., Karim, M., Dina, L. S., Corentin, D., Marie, D., Igor, E., et al., 2016. Chemical characterization of saponins contained in the body wall and the Cuvierian tubules of the sea cucumber Holothuria (Platyperona) sanctori (Delle Chiaje, 1823). Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 68: 119–127, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2016.06.005.
Guo, S. S., Yang, L. M., Zhang, Y. M., Yang, L., and Han, M., 2015. Determination of contents of total saponins and monomer saponins in Panax ginseng by micro-assisted extraction method. Food Chemistry, 36 (2): 1–6, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-011-0280-z.
Liu, H. L., Kong, X., Chen, J. W., and Zhang, H. B., 2018. De novo sequencing and transcriptome analysis of Stichopus horrens to reveal genes related to biosynthesis of triterpenoids. Aquaculture, 491: 358–367, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.01.012.
Magali, H. E., Roberto, A. E., Francisco, A. S., and Yves, S., 2015. Biological and taxonomic perspective of triterpenoid glycosides of sea cucumbers of the family Holothuriidae (Echinodermata, Holothuroidea). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, Part B, 180: 16–39, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2014.09.007.
Menchinskaya, E. S., Pislyagin, E. A., Kovalchyk, S. N., Davydova, V. N., Silchenko, A. S., Avilov, S. A., et al., 2013. Antitumor activity of cucumarioside A2-2. Chemotherapy, 59: 181–191, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1159/000354156.
Menéndez, J., Arenillas, A., Fidalgo, B., Fernández, Y., Zubizarreta, L., Calvo, E. G., et al., 2010. Microwave heating processes involving carbon materials. Fuel Processing Technology, 91: 1–8, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2009.08.021.
Van, D. S., Caulier, G., Todesco, M., Gerbaux, P., Fournier, I., Wisztorski, M., et al., 2011. The triterpenoid glycosides of Holothuria forskali, usefulness and efficiency as achemical defense mechanism against predatory fish. Journal of Experimental Biology, 214: 1347–1356, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.050930.
Xu, C., Zhang, R., and Wen, Z. Z., 2018. Bioactive compounds and biological functions of sea cucumbers as potential functional foods. Journal of Functional Foods, 49: 73–84, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2018.08.009.
Xue, C. H., Yu, L. F., Dong, P., Xu, J., Li, Z. J., and Xue, Y., 2010. Isolation and identification of three triterpene glycosides from sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus Selenka of Qingdao. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 40 (8): 60–65 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yu, S., Gao, J., Hao, J. W., and He, T. T., 2016. Study on ultrasonic-assisted extraction of Pulsatilla chinensis total saponin by response surface methodology. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 55 (20): 5348–5351 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yu, S. R., Ye, X. W., Huang, H. C., Peng, R., Su, Z. H., Lian, X. Y., et al., 2015. Bioactive sulfated saponins from sea cucumber Holothuria moebii. Planta Medica, 81: 152–159, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1383404.
Zhang, R., Wang, Y. H., Liu, Y. F., Yang, J., Jiang, T. F., and Lv, Z. H., 2013. Isolation, preparation and analysis of triterpene glycoside Holotoxin A1 in Apostichopus japonicus. Chinese Journal of Marine Drugs, 4 (8): 8–14 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang, Y., Li, H. J., Dou, H. T., He, Z. F., Wu, H. J., Sun, Z. G., et al., 2013. Optimization of nobiletin extraction assisted by microwave from orange byproduct using response surface methodology. Food Science and Biotechnology, 22: 153–159, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-013-0061-5.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2018YFD0900105), the Entrepreneurship Program for High-Level Talent of Dalian (No. 2018RD10), the Liaoning Revitalization Talents Program (No. XLYC1907109), and the Liaoning Key Research and Development Program (No. 2018228004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, G., Wang, X., Ge, K. et al. Isolation, Identification, and Quantitative Determination of Saponin in Apostichopus japonicus by HPLC-DAD. J. Ocean Univ. China 21, 473–478 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-022-4854-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-022-4854-0