Abstract
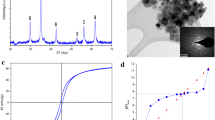
Interactions between metals and activated sludge can substantially affect the fate and transport of heavy metals in wastewater treatment plants. Therefore, it is important to develop a simple, fast and efficient method to elucidate the interaction. In this study, a modified titration method with a dynamic mode was developed to investigate the binding of Cu(II), a typical heavy metal, onto aerobic granules. The titration results indicated that pH and ionic strength both had a positive effect on the biosorption capacity of the granular sludge. The µ-XRF results demonstrated that the distribution of metals on the granular surface was heterogeneous, and Cu showed strong correlations and had the same “hot spots” positions with other metal ions (e.g., Ca, Mg, Fe etc.). Ion exchange and complexing were the main mechanisms for the biosorption of Cu(II) by aerobic granules. These results would be beneficial for better understanding of Cu(II) migration and its fate in wastewater treatment plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adav S S, Lee D J, Show K Y, Tay J H. Aerobic granular sludge: recent advances. Biotechnology Advances, 2008, 26(5): 411–423
Shi X Y, Sheng G P, Li X Y, Yu H Q. Operation of a sequencing batch reactor for cultivating autotrophic nitrifying granules. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(9): 2960–2964
Liu X W, Sheng G P, Yu H Q. Physicochemical characteristics of microbial granules. Biotechnology Advances, 2009, 27(6): 1061–1070
Luo J, Hao T, Wei L, Mackey H R, Lin Z, Chen G H. Impact of influent COD/N ratio on disintegration of aerobic granular sludge. Water Research, 2014, 62: 127–135
Yao L, Ye Z F, Tong M P, Lai P, Ni J R. Removal of Cr3+ from aqueous solution by biosorption with aerobic granules. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 165(1–3): 250–255
van LoosdrechtMC M, Brdjanovic D. Anticipating the next century of wastewater treatment. Science, 2014, 344(6191): 1452–1453
Wang X H, Song R H, Teng S X, GaoMM, Ni J Y, Liu F F, Wang S G, Gao B Y. Characteristics and mechanisms of Cu(II) biosorption by disintegrated aerobic granules. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 179(1–3): 431–437
Xu H, Liu Y, Tay J H. Effect of pH on nickel biosorption by aerobic granular sludge. Bioresource Technology, 2006, 97(3): 359–363
Benaïssa H, Elouchdi M A. Biosorption of copper (II) ions from synthetic aqueous solutions by drying bed activated sludge. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 194: 69–78
Sag Y, Tatar B, Kutsal T. Biosorption of Pb(II) and Cu(II) by activated sludge in batch and continuous-flow stirred reactors. Bioresource Technology, 2003, 87(1): 27–33
Luo H W, Chen J J, Sheng G P, Su J H, Wei S Q, Yu H Q. Experimental and theoretical approaches for the surface interaction between copper and activated sludge microorganisms at molecular scale. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4: 7078
Chen Y L, Hong X Q, He H, Luo H W, Qian T T, Li R Z, Jiang H, Yu H Q. Biosorption of Cr (VI) by Typha angustifolia: mechanism and responses to heavy metal stress. Bioresource Technology, 2014, 160: 89–92
Gonzalez-Gil G, Holliger C. Aerobic granules: microbial landscape and architecture, stages, and practical implications. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2014, 80(11): 3433–3441
Gai L H, Wang S G, Gong W X, Liu X W, Gao B Y, Zhang H Y. Influence of pH and ionic strength on Cu(II) biosorption by aerobic granular sludge and biosorption mechanism. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology (Oxford, Oxfordshire), 2008, 83(6): 806–813
Xu H, Liu Y. Mechanisms of Cd2+, Cu2+ and Ni2+ biosorption by aerobic granules. Separation and Purification Technology, 2008, 58 (3): 400–411
Mungasavalli D P, Viraraghavan T, Jin Y C. Biosorption of chromium from aqueous solutions by pretreated Aspergillus niger: batch and column studies. Colloids and Surfaces A-Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2007, 301(1–3): 214–223
Wan C, Yang X, Lee D J, Zhang Q, Li J, Liu X. Formation of filamentous aerobic granules: role of pH and mechanism. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2014, 98(19): 8389–8397
Liu X M, Sheng G P, Luo H W, Zhang F, Yuan S J, Xu J, Zeng R J, Wu J G, Yu H Q. Contribution of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) to the sludge aggregation. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(11): 4355–4360
Stumm W, Morgan J J. Aquatic Chemistry: An Introduction Emphasizing Chemical Equilibria in Natural Waters. New York, NY: Wiley-Interscience, 1981, 599–684
Ren T T, Liu L, Sheng G P, Liu X W, Yu H Q, Zhang MC, Zhu J R. Calcium spatial distribution in aerobic granules and its effects on granule structure, strength and bioactivity. Water Research, 2008, 42 (13): 3343–3352
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, H., Wang, L., Tong, Z. et al. Approaching the binding between Cu(II) and aerobic granules by a modified titration and µ-XRF. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 10, 362–367 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-015-0803-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-015-0803-0