Abstract
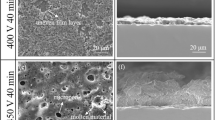
Based on the diffusion channel, the influence of Si content on the microstructure evolution of iron-based hot-dip Al-χSi coating was analyzed (χ=0, 1.5 wt%, 3.0 wt% and 7.0 wt%). The results show that the introduction of Si makes the reaction interface change from the lingual-tooth interface of hot-dip Al to the flat interface of hot-dip Al-Si. It also reduces the thickness of the alloy layer in the coating, especially the Fe2Al5 layer. When the Si content is 1.5 wt% or 3.0 wt%, the diffusion channel crosses the conjugate line of the two-phase region (FeAl3+liquid phase) into the FeAl3 single-phase region, and then moves to the region with higher Si content. Next, the diffusion channel cuts off the conjugate line of FeAl3 phase, τ1/τ9 phase, and Fe2Al5 phase, which promotes the form of τ1/τ9 phase. The formed τ1/τ9 phase inhibits the diffusion between Fe and Al atoms. When the Si content is 7.0 wt%, the diffusion channel passes through the two-phase region (liquid phase+τ5) and enters the τ5 single-phase region. The form of τ5 single-phase region has a strong inhibitory effect on the interatomic diffusion of Fe and Al, thereby reducing the thickness of the coating, especially the Fe2Al5 layer.
摘要
基于扩散通道,分析了Si含量对铁基热浸Al-χSi涂层微观结构演变的影响(χ=0,1.5 wt%,3.0 wt%,7.0 wt%)。结果表明,Si的引入使反应界面从热浸铝的舌状界面变为热浸Al-Si 的平坦界面,同时也减少了涂层中合金层的厚度,特别是Fe2Al5层。当Si 含量为1.5 wt%或3.0 wt%时,扩散通道穿过两相区(FeAl3+液相)的共轭线进入FeAl3 单相区,再移动到Si 含量较高的区域。然后,扩散通道切断FeAl3 相、τ1/τ9 相和Fe2Al5相的共轭线,从而促进了τ1/τ9 相的形成。由此产生的τ1/τ9 相抑制了Fe 原子和Al 原子之间的扩散。当Si 含量为7.0 wt%时,扩散通道穿过(液相+τ5)两相区,进入τ5 单相区。τ5 单相区对Fe 原子和Al原子间扩散有很强的抑制作用,从而减少了涂层的厚度,特别是Fe2Al5层。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
WANG Li-dong, TANG Di, WU Hui-bin, et al. Mechanical properties and CO2 corrosion behavior of Q125 grade oil tube steel used for ERW [J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2012, 43(6): 2165–2172. (in Chinese)
XIE Fei, WU Ming, CHEN Xu, et al. Effects of SO 2−4 on corrosion behavior of X80 pipeline steel in simulated Korla soil solution [J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2013, 44(1): 424–430. (in Chinese)
LIU Wei, LI Mou-cheng, LUO Qun, et al. Influence of alloyed magnesium on the microstructure and long-term corrosion behavior of hot-dip Al-Zn-Si coating in NaCl solution [J]. Corrosion Science, 2016, 104: 217–226. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2015.12.014.
LI Yang, JIANG Ying, LIU Bin, et al. Understanding grain refining and anti Si-poisoning effect in Al-10Si/Al-5Nb-B system [J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2021, 65: 190–201. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2020.04.075.
LIU Wei, LI Qian, LI Mou-cheng. Corrosion behaviour of hot-dip Al-Zn-Si and Al-Zn-Si-3Mg coatings in NaCl solution [J]. Corrosion Science, 2017, 121: 72–83. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2017.03.013.
KOBAYASHI S, YAKOU T K. Control of intermetallic compound layers at interface between steel and aluminum by diffusion-treatment [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2002, 338(1–2): 44–53. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(02)00053-9.
HUILGOL P, BHAT S, BHAT K U. Hot-dip aluminizing of low carbon steel using Al-7Si-2Cu alloy baths [J]. Journal of Coatings, 2013: 180740. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/180740.
WANG C J, CHEN S M. The high-temperature oxidation behavior of hot-dipping Al-Si coating on low carbon steel [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2006, 200(22–23): 6601–6605. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2005.11.031.
GLASBRENNER H, BORGSTEDT H U. Preparation and characterization of Al2O3/Fe.xAly layers on MANET steel [J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 1994, 212–215: 1561–1565. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3115(94)91090-1.
SERRA E, GLASBRENNER H, PERUJO A, et al. Hot-dip aluminum deposit as a permeation barrier for MANET steel [J]. Fusion Engineering and Design, 1998, 41: 149–155.
KITAJIMA Y, HAYASHI S, NISHIMOTO T, et al. Rapid formation of α -Al2O3 scale on an Fe-Al alloy by pure-metal coatings at 900 °C [J]. Oxidation of Metals, 2010, 73(3–4): 375–388. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-009-9184-8.
BOUAYAD A, GEROMETTA C, BELKEBIR A, et al. Kinetic interactions between solid iron and molten aluminium [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 363(1–2): 53–61. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(03)00469-6.
TAKATA N, NISHIMOTO M, KOBAYASHI S, et al. Morphology and formation of Fe-Al intermetallic layers on iron hot-dipped in Al-Mg-Si alloy melt [J]. Intermetallics, 2014, 54: 136–142. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2014.06.003.
LEMMENS B, CORLU B, STRYCKER J, et al. The effect of Si on the intermetallics formation during hot dip aluminizing [J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2014, 922: 429–434. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.922.429.
AN J, LIU Y, LU Yao, et al. The formation of reacted film and its influence on tribological properties of extruded Al-Si-Cu-20-25Pb alloy under dry sliding [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2003, 38: 1975–1982. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A%3A1023529220567.
LI Zhi-wei, RUAN Rui-wen, XI Shi-heng, et al. The influence of Al on the surface properties of the hot-dip galvanized melt [J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Materials Science Edition, 2022, 37: 117–122. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-022-2507-1.
CHANG Y Y, TSAUR C C, ROCK J C. Microstructure studies of an aluminide coating on 9Cr-1Mo steel during high temperature oxidation [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2006, 200(22–23): 6588–6593. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2005.11.038.
GLASBRENNER H, STEIN-FECHNER K, KONYS J. Scale structure of aluminised F82H-mod.steel after HIP treatment [J]. Fusion Engineering and Design, 2000, 51–52: 105–110. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0920-3796(00)00383-5.
AWAN G H, HASAN F U. The morphology of coating/substrate interface in hot-dip-aluminized steels [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 472(1–2): 157–165. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.03.013.
BAHADUR A, MOHANTY O N. Structural studies of hot dip aluminized coatings on mild steel [J]. Materials Transactions JIM, 1991, 32(11): 1053–1061. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans1989.32.1053.
PINT B A, ZHANG Y, TORTORELLI P F, et al. Evaluation of iron-aluminide CVD coatings for high temperature corrosion protection [J]. Materials at High Temperatures, 2001, 18(3): 185–192. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1179/mht.2001.021.
ZHANG Y, PINT B A, GARNER G W, et al. Effect of cycle length on the oxidation performance of iron aluminide coatings [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2004, 188–189: 35–40. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2004.07.090.
AGÜERO A, MUELAS R, GUTIéRREZ M, et al. Cyclic oxidation and mechanical behaviour of slurry aluminide coatings for steam turbine components [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2007, 201(14): 6253–6260. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2006.11.033.
LUO Qun, LI Jian-ding, LI Bo, et al. Kinetics in Mg-based hydrogen storage materials: Enhancement and mechanism [J]. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys, 2019, 7(1): 58–71. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jma.2018.12.001.
LI Zhi-wei, PENG Hao-ping, LIU Ya, et al. Synergy of ball-milling and pre-oxidation on microstructure and corrosion resistance of hot-dip zinc coating of nodular cast iron [J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2022, 16: 1402–1412. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.12.052.
PANG Yue-peng, SUN Dong-ke, GU Qin-fen, et al. Comprehensive determination of kinetic parameters in solidstate phase transitions: An extended Jonhson-Mehl-Avrami-Kolomogorov model with analytical solutions [J]. Crystal Growth & Design, 2016, 16(4): 2404–2415.
LUO Qun, GUO Yan-lin, LIU Bin, et al. Thermodynamics and kinetics of phase transformation in rare earth-magnesium alloys: A critical review [J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2020, 44: 171–190. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2020.01.022.
EI-MAHALLAWY N A, TAHA M A, SHADY M A, et al. Analysis of coating layer formedon steel strips during aluminising by hot dipping in Al-Si baths [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 1997, 13(10): 832–840. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1179/mst.1997.13.10.832.
AKDENIZ M V, MEKHRABOV A O, YILMAZ T. The role of Si addition on the interfacial interaction in Fe-Al diffusion layer [J]. Scripta Metallurgica et Materialia, 1994, 31(12): 1723–1728. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0956-716X(94)90471-5.
HAN Wei, YIN Fu-cheng, SU Xu-ping. Effect of silicon on the growth kinetics of Fe2Al5 in Fe/Al solid state diffusion reaction [J]. Journal of Materials and Heat Treatment. 2010, 31(6): 28–32. (in Chinese)
RICHARDS R W, JONES R D, CLEMENTS P D, et al. Metallurgy of continuous hot dip aluminizing [J]. International Materials Reviews, 2013, 39(5): 191–212. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1179/imr.1994.39.5.191.
ROBERT F M. Metals handbook [M]. 9th Edition American Society of Metals, 1983.
NICHOLLS, JOHN E. Hot-dipped aluminum coatings [J]. Anti-corrosion Methods and Materials, 1964, 11(10): 16–21.
CHENG W J, WANG C J. Effect of silicon on the formation of intermetallic phases in aluminide coating on mild steel [J]. Intermetallics, 2011, 19(10): 1455–1460. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2011.05.013.
DURANDET Y, STREZOV L, EBRILL N. Formation of Al-Zn-Si coating on low carbon steel substrates [C]// 4th International Conference on Zinc and Zinc Alloy Coated Steel Sheet. Makuhari, Chiba, Japan: The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan, 1998: 147–152.
LI Zhi-wei, PENG Hao-ping, WANG Jian-hua, et al. Effect of ball-milling pretreatment on microstructure and corrosion of hot-dip galvanized coating [J]. Materials Characterization, 2022, 192: 112177. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/jmatchar2002.112117.
DU Yong, SCHUSTER J C, LIU Zi-kui, et al. A thermodynamic description of the Al-Fe-Si system over the whole composition and temperature ranges via a hybrid approach of CALPHAD and key experiments [J]. Intermetallics, 2008, 16(4): 554–570. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2008.01.003.
XIA Yuan, YAO Mei, ZHANG Rui-ping. Influencing factors on the growth law of hot-dip aluminum coating on A3 steel [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 1996, 1: 74–78. (in Chinese)
WEI Han. The influence of Si on the growth kinetics of Fe2Al5 phase during the Fe-Al reaction [D]. Xiangtan: Xiangtan University, 2009. (in Chinese)
GHOSH G. Aluminum-iron-silicon [J]. Landolt-Bornstein New Series, 2008, 4: 359–409.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item
Projects(51971039, 51671037) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(19KJA530001) supported by the Natural Science Research Project of Higher Education of Jiangsu, China; Project(KYCX21_2868) supported by the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province, China
Contributors
SU Xu-ping provided the research concept and edited the manuscript. PENG Hao-ping wrote the first draft and reviewed the literature. MA Ming and XI Shi-heng conducted experiments and data analysis. PENG Hao-ping and LIU Ya summarized the experimental reaction mechanism. LEI Yun and SU Wei revised and edited the manuscript. All authors revised the final draft.
Conflict of interest
PENG Hao-ping, MA Ming, XI Shi-heng, LIU Ya, LEI Yun, SU Wei and SU Xu-ping declare that they have no conflicts of interest that would affect the work of the report.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, Hp., Ma, M., Xi, Sh. et al. Influence of Si content on interface reaction of iron-based hot-dip aluminizing on Fe sheet. J. Cent. South Univ. 29, 3581–3591 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-022-5025-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-022-5025-6