Abstract
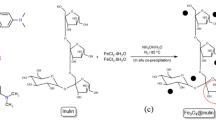
Excessive discharge of dye wastewater has brought serious harm to human health and the environment. In this paper, a magnetic absorbent, ferroferric oxide@β-cyclodextrin (Fe3O4@CD), was prepared for the efficient adsorption removal of basic fuchsin (BF) from dye wastewater, based on the special amphiphilicity of β-CD and the strong magnetism of Fe3O4. A series of influence factors including the initial dye concentration, adsorbent dosage, temperature and pH were investigated, as well as the adsorption mechanism. The results show that Fe3O4@CD has the best adsorption and removal effect on BF dye at room temperature and neutral pH, when the initial concentration of dye is 25 mg/L and the adsorbent dosage is 100 mg. The adsorption behavior conforms to the pseudo-second-order kinetics and the Langmuir adsorption isotherm, and the adsorption process is spontaneously endothermic. Fe3O4@CD adsorbed with BF dye can be rapidly separated under an external magnetic field and then easily regenerated by HCl treatment. After 5 times of recycling, the removal rate of the prepared magnetic composite on BF dye is kept above 75%. This work will provide an economic and eco-friendly technology for the treatment of the actual dye wastewater.
摘要
染料废水的过量排放给人类健康和环境带来了严重危害。本文基于β-CD的两亲性和纳米Fe3O4 的强磁性, 制备了磁性吸附剂Fe3O4@CD应用于染料废水中碱性品红的高效去除。考察了染料初始浓 度, 吸附剂用量, 温度, pH等系列因素对去除效果的影响及其吸附机理。研究表明, 在室温, 中性 pH值下, 当染料初始浓度为25 mg/L, 吸附剂用量为100 mg时, 所制备的Fe3O4@CD对BF的吸附去除 效果最佳; 其吸附行为符合准二级动力学和Langmuir 吸附等温模型, 且为自发吸热过程。Fe3O4@CD 吸附BF后在外加磁场下可快速分离再生, 循环使用5 次后碱性品红染料去除率保持在75%以上。研究 成果有望提供经济环保的实际染料废水处理新技术。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
GUPTA V K, MITTAL A, GAJBE V, MITTAL J. Adsorption of basic fuchsin using waste materials-bottom ash and deoiled soya-as adsorbents [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2008, 319(1): 30–39. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2007.09.091.
WANG Shao-mang, LI Ding-long, SUN Cheng, YANG Shao-gui, GUAN Yuan, HE Huan. Synthesis and characterization of g-C3N4/Ag3VO4 composites with significantly enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity for triphenylmethane dye degradation [J]. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2014, 144: 885–892. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.08.008.
PU Hong-yu, TANG Pei-xiao, ZHAO Lu-dan, SUN Qiao-mei, ZHAI Yuan-ming, LI Zhi-qiang, GAN Na, LIU Yuanyuan, REN Xiu-yun, LI Hui. Preparation of a carboxymethyl beta-cyclodextrin polymer and its rapid adsorption performance for basic fuchsin [J]. RSC Advances, 2020, 10(35): 20905–20914. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra10797e.
BESSASHIA W, BERREDJEM Y, HATTAB Z, BOUOUDINA M. Removal of Basic Fuchsin from water by using mussel powdered eggshell membrane as novel bioadsorbent: Equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies [J]. Environmental Research, 2020, 186: 109484. DOI: https://doi.org/10.10167/j.envres.2020.109484.
HUANG Jin, TAN Zhi-qiang, SU Hui-ming, GUO Yi-Wen, LIU Huang, LIAO Bo, LIU Qing-quan. Ferrocenyl building block constructing porous organic polymer for gas capture and methyl violet adsorption [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(4): 1247–1261. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4364-4.
CHEN S H, CHEOW Y L, NG S L, TING A S. Biodegradation of triphenylmethane dyes by non-white rot fungus penicillium simplicissimum: Enzymatic and toxicity studies [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research, 2019, 13(2): 273–282. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-019-00171-2.
NAUSHAD M, SHARMA G, ALOTHMAN Z A. Photodegradation of toxic dye using Gum Arabic-crosslinked-poly(acrylamide)/Ni(OH)2/FeOOH nanocomposites hydrogel [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 241: 118263. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118263.
SHARMA G, KUMAR A, SHARMA S, NAUSHAD M, DHIMAN P, VO D V N, STADLER F J. Fe3O4/ZnO/Si3N4 nanocomposite based photocatalyst for the degradation of dyes from aqueous solution [J]. Materials Letters, 2020, 278: 128359. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2020. 128359.
PIASKOWSKI K, SWIDERSKA-DABROWSKA R, ZARZYCKI P K. Dye Removal from water and wastewater using various physical, chemical, and biological processes [J]. Journal of AOAC International, 2018, 101(5): 1371–1384. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5740/jaoacint.18-0051.
JORFI S, BARZEGAR G, AHMADI M, SOLTANI R D C, HAGHIGHIFARD N A, TAKDASTAN A, SAEEDI R, ABTAHI M. Enhanced coagulation-photocatalytic treatment of Acid red 73 dye and real textile wastewater using UVA/synthesized MgO nanoparticles [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2016, 177: 111–118. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.04.005.
KHAN Z U H, KHAN A, CHEN Y, KHAN A, SHAH N S, MUHAMMAD N, MURTAZA B, TAHIR K, KHAN F U, WAN P. Photo catalytic applications of gold nanoparticles synthesized by green route and electrochemical degradation of phenolic Azo dyes using AuNPs/GC as modified paste electrode [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 725: 869–876. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.07.222.
GUPTA V K, SUHAS. Application of low-cost adsorbents for dye removal—A review [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2009, 90(8): 2313–2342. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2008.11.017.
AHMED D N, NAJI L A, FAISAL A A, AL-ANSARI N, NAUSHAD M. Waste foundry sand/MgFe-layered double hydroxides composite material for efficient removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solution [J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 2042. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-58866-y.
SHARMA G, ALOTHMAN Z A, KUMAR A, SHARMA S, PONNUSAMY S K, NAUSHAD M. Fabrication and characterization of a nanocomposite hydrogel for combined photocatalytic degradation of a mixture of malachite green and fast green dye [J]. Nanotechnology for Environmental Engineering, 2017, 2(1): 4. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41204-017-0014-y.
ALBADARIN A B, COLLINS M N, NAUSHAD M, SHIRAZIAN S, WALKER G, MANGWANDI C. Activated lignin-chitosan extruded blends for efficient adsorption of methylene blue [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 307: 264–272. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.089.
WAGN Jie, HOU Guang-ya, WU Lian-kui, CAO Hua-zhen, ZHENG Guo-qu, TANG Yi-ping. A novel adsorbent of three-dimensional ordered macro/mesoporous carbon for removal of malachite green dye [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(2): 388–402. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4304-3.
XIA Kai, LIU Xin, CHEN Zhao-jun, FANG Long, DU Hui, ZHANG Xiao-dong. Efficient and sustainable treatment of anionic dye wastewaters using porous cationic diatomite [J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2020, 113: 8–15. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2020.07.020.
LI Xiao-nan, LI Jing-hua, SHI Wei-lu, BAO Jian-feng, YANG Xian-yuan. A fenton-like nanocatalyst based on easily separated magnetic nanorings for oxidation and degradation of dye pollutant [J]. Materials, 2020, 13(2): 332. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13020332.
WU Shui-shen, LAN Dong-hui, ZHANG Xiao-wen, HUANG Yi, DENG Xin-hong, AU Chak-tong, YI Bing. Microwave hydrothermal synthesis, characterization and excellent uranium adsorption properties of CoFe2O4@rGO nanocomposite [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2021, 28(7): 1955–1965. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4744-4.
GOMEZ-PASTORA J, BRINGAS E, ORTIZ I. Recent progress and future challenges on the use of high performance magnetic nano-adsorbents in environmental applications [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 256: 187–204. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.06.119.
XU Piao, ZENG Guang-ming, HUANG Dan-lian, FENG Chong-ling, HU Shuang, ZHAO Mei-hua, LAI Cui, WEI Zhen, HUANG Chao, XIE Geng-xin, LIU Zhi-feng. Use of iron oxide nanomaterials in wastewater treatment: A review [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2012, 424: 1–10. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.02.023.
FAN Ji-xiang, CHEN Dong-yun, LI Na-jun, XU Qing-feng, LI Hua, HE Jing-hui, LU Jian-mei. Adsorption and biodegradation of dye in wastewater with Fe3O4@MIL-100 (Fe) core-shell bio-nanocomposites [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 191: 315–323. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.042.
JOSHI S, GARG V K, KATARIA N, KADIRVELU K. Applications of Fe3O4@AC nanoparticles for dye removal from simulated wastewater [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 236: 124280. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.07.011.
CHATTERJEE S, GUHA N, KRISHNAN S, SINGH A K, MATHUR P, RAI D K. Selective and recyclable congo red dye adsorption by spherical Fe3O4 nanoparticles functionalized with 1, 2, 4, 5-benzenetetracarboxylic acid [J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 111. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-57017-2.
YU Si-yuan, WANG Jin-bao, CUI Jian-lan. Preparation of a novel chitosan-based magnetic adsorbent CTS@SnO2@Fe3O4 for effective treatment of dye wastewater [J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2020, 156: 1474–1482. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.11.194.
JIN Lin-feng, CHAI Li-yuan, SONG Ting-ting, YANG Wei-chun, WANG Hai-ying. Preparation of magnetic Fe3O4@Cu/Ce microspheres for efficient catalytic oxidation co-adsorption of arsenic(III) [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(4): 1176–1185. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4358-2.
NING Jing-heng, WANG Yu-fang, WU Qi, ZHANG Xue-feng, LIN Xian-fu, ZHAO Hong-bin. Novel supramolecular assemblies of repulsive DNA-anionic porphyrin complexes based on covalently modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes and cyclodextrins [J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(27): 21153–21160. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra15741a.
DUAN Hui-ling, MOU Zhao-li, WANG Jun, MA Shi-yao, ZHAN Han-ying, ZHANG Zhi-qi. Magnetically modified porous β-cyclodextrin polymers for dispersive solid-phase extraction high-performance liquid chromatography analysis of sudan dyes [J]. Food Analytical Methods, 2019, 12(6): 1429–1438. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-019-01476-w.
RAJ V, SARATHI A, CHANDRAKALA T, DHANALAKSHMI S, SUDHA R, RAJASEKARAN K. Guest-host interactions in the alkaline bleaching of triphenylmethane dyes catalysed by β-cyclodextrin [J]. Journal of Chemical Sciences, 2009, 121: 529–534. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-009-0064-1.
LIU Jin-shui, LIU Guo-ning, LIU Wen-xiu. Preparation of water-soluble beta-cyclodextrin/poly(acrylic acid)/graphene oxide nanocomposites as new adsorbents to remove cationic dyes from aqueous solutions [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 257: 299–308. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.07.021.
TAKAAL, FOSSO-KANKEU E, PILLAY K, MBIANDA X Y. Metal nanoparticles decorated phosphorylated carbon nanotube/cyclodextrin nanosponge for trichloroethylene and Congo red dye adsorption from wastewater [J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2020, 8(3): 103602. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103602.
LIU Xiao-dong, YAN Liang, YIN Wen-yan, ZHOU Liang-jun, TIAN Gan, SHI Jun-xin, YANG Zhi-yong, XIAO De-bao, GU Zhan-jun, ZHAO Yu-liang. A magnetic graphene hybrid functionalized with beta-cyclodextrins for fast and efficient removal of organic dyes [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(31): 12296–12303. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ta00753k.
QU Jian-hua, YUAN Yi-hang, MENG Qing-juan, ZHANG Guang-shan, DENG Feng-xia, WANG Lei, TAO Yue, JIANG Zhao, ZHANG Ying. Simultaneously enhanced removal and stepwise recovery of atrazine and Pb (II) from water using beta-cyclodextrin functionalized cellulose: Characterization, adsorptive performance and mechanism exploration [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 400: 123142. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123142.
LIU Qi-ming, ZHOU Yi, LU Jian, ZHOU Yan-bo. Novel cyclodextrin-based adsorbents for removing pollutants from wastewater: A critical review [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 241: 125043. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125043.
NING Jing-heng, WANG Min, LUO Xin, HU Qiong-can, HOU Rong, CHEN Wei-wei, CHEN Dong-er, WANG Jian-hui, LIU Jun. SiO2 stabilized magnetic nanoparticles as a highly effective catalyst for the degradation of basic fuchsin in industrial dye wastewaters [J]. Molecules, 2018, 23(10): 2573–2589. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102573.
ZHU Chun-shan, ZHANG Xiao-yuan, WANG Qiu-ju, ZHANG Rui-li, WANG Ting. Thermo/pH dual responsive beta-cyclodextrin magnetic microspheres for anti-cancer drug controlled release [J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2015, 213: 21–22. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.05.032.
ZHAN Fang-ke, WANG Ran, YIN Juan-juan, HAN Zeng-sheng, ZHANG Lun, JIAO Ti-feng, ZHOU Jing-xin, ZHANG Le-xin, PENG Qiu-ming. Facile solvothermal preparation of Fe3O4-Ag nanocomposite with excellent catalytic performance [J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(2): 878–883. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra08516a.
MARIAN E, DUTEANU N, VICAS L, RUSU G, JURCA T, MURESAN M, MICLE O, HANGAN A C, STAN R L, IONESCU C, SEVASTRE B, PÁLL E. Synthesis, characterization of inclusion compounds of amygdalin with β-cyclodextrin and sod-like activity and cytotoxicity on hela tumor cells [J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2020, 13(8): 6828–6837. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2020.06.035.
HO Y S, OFOMAJA A E. Pseudo-second-order model for lead ion sorption from aqueous solutions onto palm kernel fiber [J]. Journal of Hazardous materials, 2006, 129(1–3): 137–142. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.08.020.
HO Y S. Citation review of Lagergren kinetic rate equation on adsorption reactions [J]. Scientometrics, 2004, 59(1): 171–177. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:SCIE.0000013305.99473.cf.
WONG S, TUMARI H H, NGADI N, MOHAMED W B, HASSAN O, MAT R, AMIN N A S. Adsorption of anionic dyes on spent tea leaves modified with polyethyleneimine (PEI-STL) [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 206: 394–406. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.09.201.
LI Xia, NIE Xiao-juan, ZHU Yu-nuo, YE Wen-chao, JIANG Yu-lin, SU Shi-long, YAN Bi-ting. Adsorption behaviour of eriochrome Black T from water onto a cross-linked β-cyclodextrin polymer [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2019, 578: 123582. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.123582.
HAI N T, YOU Sheng-jie, HOSSEINI-BANDEGHARAEI A, CHAO Huan-ping. Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: A critical review [J]. Water Research, 2017, 120: 88–116. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.04.014.
HAGHTALAB A, NABIPOOR M, FARZAD S. Kinetic modeling of the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis in a slurry phase bubble column reactor using Langmuir-Freundlich isotherm [J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2012, 104: 73–79. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2011.07.005.
LYU Jia-fei, ZHANG Nan, LIU Hong-xu, ZENG Zhou-liang-zi, ZHANG Jing-shuang, BAI Peng, GUO Xiang-hai. Adsorptive removal of boron by zeolitic imidazolate framework: Kinetics, isotherms, thermodynamics, mechanism and recycling [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2017, 187: 67–75. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.05.059.
ZHAO Yong-hua, GENG Jin-tao, CAI Jie-chuan, CAI Yu-fu, CAO Chun-yan. Adsorption performance of basic fuchsin on alkali-activated diatomite [J]. Adsorption Science & Technology, 2020, 38(5): 151–167. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0263617420922084.
RAZMI F A, NGADI N, WONG S, INUWA I M, OPOTU L A. Kinetics, thermodynamics, isotherm and regeneration analysis of chitosan modified pandan adsorbent [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 231: 98–109. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.228.
LI Qian, YUE Qin-yan, SU Yuan, GAO Bao-yu, SUN Hong-jian. Equilibrium, thermodynamics and process design to minimize adsorbent amount for the adsorption of acid dyes onto cationic polymer-loaded bentonite [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2010, 158(3): 489–497. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.01.033.
Funding
Project(2017YFC1600306) supported by the National Key R&D Program of China; Project(21505005) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2018JJ2424) supported by the Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China; Project(2019IC21) supported by the International Cooperative Project for “Double First-Class”, China
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Contributors
NING Jing-heng designed the experiments and provided financial supports; CHEN Dong-er and HU Qiong-can performed the experiments; LIU Yong-le, HUANG Shou-en, WEI Jia-qian, WEI Rui and SUN Chang analyzed the data and contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; NING Jing-heng and CHEN Dong-er wrote the paper; WANG Fa-xiang revised the paper; all authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflict of interest
NING Jing-heng, CHEN Dong-er, LIU Yong-le, HUANG Shou-en, WANG Fa-xiang, WEI Rui, HU Qiong-can, WEI Jia-qian and SUN Chang declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ning, Jh., Chen, De., Liu, Yl. et al. Efficient adsorption removal and adsorption mechanism of basic fuchsin by recyclable Fe3O4@CD magnetic microspheres. J. Cent. South Univ. 28, 3666–3680 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4845-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4845-0