Abstract
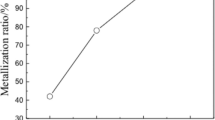
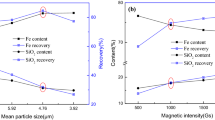
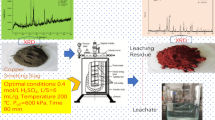
Approximately 2.0–3.0 t of copper slag (CS) containing 35%–45% iron is generated for every ton of copper produced during the pyrometallurgical process from copper concentrate. Therefore, the recovery of iron from CS utilizes a valuable metal and alleviates the environmental stress caused by stockpile. In this paper, a new method has been developed to realize the enrichment of iron in CS through the selective removal of silica. The thermodynamic analyses and experimental results show that the iron in CS can be fully reduced into metallic iron by carbothermic reduction at 1473 K for 60 min. The silica was converted into free quartz solid solution (QSS) and cristobalite solid solution (CSS). QSS and CSS are readily soluble, whereas metallic iron is insoluble, in NaOH solution. Under optimal leaching conditions, a residue containing 87.32% iron is obtained by decreasing the silica content to 6.02% in the reduction roasted product. The zinc content in the residue is less than 0.05%. This study lays the foundation for the development of a new method to comprehensively extract silicon and iron in CS while avoiding the generation of secondary tailing.
摘要
以铜精矿为原料,采用火法冶炼工艺每生产1.0 t 金属铜将产生2.0~3.0 t 含铁35%~45%的铜渣。 因此,从铜渣中回收铁不仅能实现有价金属的提取,还能减少其因堆存而带来的环境问题。本文提出 了一种通过选择性脱硅而实现铜渣中铁富集的新方法。热力学计算及实验结果表明,铜渣中的铁在 1473 K 碳热还原60 min 可被完全还原为金属铁,此时氧化硅转变为游离的石英固溶体和方石英固溶 体。石英固溶体和方石英固溶体均易溶于碱溶液而金属铁不溶于碱溶液。在最佳浸出条件下,铜渣还 原焙烧产物中的氧化硅可降低至6.02%,同时获得含铁87.32%的浸出渣。浸出渣中锌含量低于0.05%。 本研究为铜渣中硅和铁综合提取新技术的开发奠定基础,并避免二次尾矿的产生。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
FENG Yan, YANG Qi-xing, CHEN Qiu-song, KERO J, ANDERSSON A, AHMED H, ENGSTRÖM F, SAMUELSSON C. Characterization and evaluation of the pozzolanic activity of granulated copper slag modified with CaO [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 232: 1112–1120. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.06.062.
HOLLAND K, ERIÇ R H, TASKINEN P, JOKILAAKSO A. Upgrading copper slag cleaning tailings for re-use [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2019, 133: 35–42. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2018.12.026.
CHUN T, MU G, DI Z, LONG H, NING C, LI D. Recovery of iron from copper slag by carbothermic reduction and magnetic separation in the presence of CaO [J]. Archives of Metallurgy and Materials, 2018, 63(1): 299–305. DOI: https://doi.org/10.24425/118941.
SHEN Hui-ting, FORSSBERG E. An overview of recovery of metals from slags [J]. Waste Management, 2003, 23(10): 933–949.
ALP I, DEVECI H, SÜNGÜN H. Utilization of flotation wastes of copper slag as raw material in cement production [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 159: 390–395.
GORAI B, JANA R K. Characteristics and utilisation of copper slag—A review [J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2003, 39: 299–313.
KIM B S, JO S K, SHIN D Y, LEE J C, JEONG S B. A physico-chemical separation process for upgrading iron from waste copper slag [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2013, 124: 124–127.
TSUNAZAWA Y, LIU Chang-zhi, TOI R, OKURA T, TOKORO C. Crystal formation and growth by slow cooling for recovery of magnetite particles from copper smelting slag [J]. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy, 2019, 128(4): 248–255. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/25726641.2018.1483793.
GUO Zheng-qi, ZHU De-qing, PAN Jian, WU Teng-jiao, ZHANG Feng. Improving beneficiation of copper and iron from copper slag by modifying the molten copper slag [J]. Metals, 2016, 6(4): 86. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/met6040086.
NADIROV R, SYZDYKOVA L, ZHUSSUPOVA A. Copper smelter slag treatment by ammonia solution: Leaching process optimization [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(1): 2799–2804. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-017-3694-3.
HEO J H, KIM B S, PARK J H. Effect of CaO addition on iron recovery from copper smelting slags by solid carbon [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2013, 44(6): 1352–1363.
LI Si-wei, PAN Jian, ZHU De-qing, GUO Zheng-qi, XU Ji-wei, CHOU Jian-lei. A novel process to upgrade the copper slag by direct reduction-magnetic separation with the addition of Na2CO3 and CaO [J]. Powder Technology, 2019, 347: 159–169. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2019.02.046.
HEO J H, CHUNG Y S, PARK J H. Recovery of iron and removal of hazardous elements from waste copper slag via a novel aluminothermic smelting reduction (ASR) process [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2016, 137: 777–787.
LI Xiao-bin, WANG Hong-yang, ZHOU Qiu-sheng, QI Tian-gui, LIU Gui-hua, PENG Zhi-hong. Efficient separation of silica and alumina in simulated CFB slag by reduction roasting-alkaline leaching process [J]. Waste Management, 2019, 87: 798–804. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2019.03.020
SHEN Lei-ting, LI Xiao-bin, ZHOU Qiu-sheng, PENG Zhi-hong, LIU Gui-hua, QI Tian-gui, TASKINEN P. Sustainable and efficient leaching of tungsten in ammoniacal ammonium carbonate solution from the sulfuric acid converted product of scheelite [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 197: 690–698. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.06.256.
ROMCHAT C F, KATSUYA M, TAKAHIRO M, TETSUYA N. The selective alkaline leaching of zinc oxide from electric arc furnace dust pre-treated with calcium oxide [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2016, 159: 120–125.
CHEN J H, MI W J, CHEN H Y, LI B, CHOU K C, HOU X M. Iron oxide recovery from fayalite in water vapor at high temperature [J]. Journal of Mining and Metallurgy, Section B: Metallurgy, 2018, 54(1): 1–8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2298/JMMB160926011C.
GYUROV S, MARINKOV N, KOSTOVA Y, RABADJIEVA D, KOVACHEVA D, TZVETKOVA C, GENTSCHEVA G, PENKOV I. Technological scheme for copper slag processing [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2017, 158: 1–7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2016.11.008.
JIAO K X, ZHANG J L, LIU Z J, CHEN C L, LIU F. Circulation and accumulation of harmful elements in blast furnace and their impact on the fuel consumption [J]. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2017, 44(5): 344–350. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/03019233.2016.1210913.
ZHANG Qing-chen, QIU Guan-zhou, XIAO Qi. The effect of coal-kind on coal-based direct reduction of low grade iron ore [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 1997, 28(2): 126–129. (in Chinese)
LI Xiao-bin, WANG Hong-yang, ZHOU Qiu-sheng, QI Tian-gui, LIU Gui-hua, PENG Zhi-hong, WANG Yi-lin. Reaction behavior of kaolinite with ferric oxide during reduction roasting [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2019, 29(1): 186–193. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64927-1.
HAN Bin, TONG Xiong, ZHANG Guo-hao, XIE Xian, LV Hao-zi. Process mineralogy study on a copper slag [J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2015(1): 63–68. (in Chinese)
BARI I. Thermochemical data of pure substances [M]. VCH Verlagsgesellschaft mbH, Germany, 1995.
LUO Jun, LI Guang-hui, JIANG Tao, PENG Zhi-wei, RAO Ming-jun, ZHANG Yuan-bo. Conversion of coal gangue into alumina, tobermorite and TiO2-rich material [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2016, 23: 1883–1889. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-016-3243-5.
CROKER D, LOAN M, HODNETT B. Desilication reactions at digestion conditions: an in situ X-ray diffraction study [J]. Crystal Growth & Design, 2008, 8(12): 4499–4505.
MIHAILOVA I, MEHANDJIEV D. Characterization of fayalite from copper slags [J]. Journal of the University of Chemical Technology and Metallurgy, 2010, 45(3): 317–326.
MING C Q, GREISH Y, El-GHANNAM A. Crystallization behavior of silica-calcium phosphate biocomposites: XRD and FTIR studies [J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine, 2004, 15(11): 1227–1235.
REIG F B, ADELANTADO J V G, MORENO M C M M. FTIR quantitative analysis of calcium carbonate (calcite) and silica (quartz) mixtures using the constant ratio method. Application to geological samples [J]. Talanta, 2002, 58(4): 811–821.
MARINKOV N, MARKOVA-VELICHKOVA M, GYUROV S, KOSTOVA Y, SPASSOVA I, RABADJIEVA D, KOVACHEVA D, PENKOV I, TZVETKOVA C, GENTSCHEVA G. Preparation and characterization of silicagel from silicate solution obtained by autoclave treatment of copper slag [J]. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 2018, 87(2): 331–339. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-018-4741-8.
YAO Cong, FANG Li, GUO Yan-xia, LIU Dan-dan, CHENG Fang-qin. Modulus control of pre-desilication solution by alumina-extracted residues of coal fly ash [J]. Journal of North University of China (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 39(3): 328–333. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(WUT: 2019IVA096) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China; Project(2019M662733) supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation; Project(2018YFC1901502) supported by National Key Research and Development Program of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Hy., Song, Sx. Separation of silicon and iron in copper slag by carbothermic reduction-alkaline leaching process. J. Cent. South Univ. 27, 2249–2258 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4446-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4446-3