Abstract
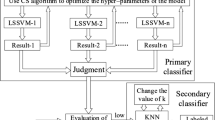
The pre-warning of abnormal energy consumption is important for energy conservation of industrial engineering. However, related studies on the lead smelting industries which usually have a huge energy consumption are rarely reported. Therefore, a pre-warning system was established in this study based on the intelligent prediction of energy consumption and the identification of abnormal energy consumption. A least square support vector regression (LSSVR) model optimized by the adaptive genetic algorithm was developed to predict the energy consumption in the process of lead smelting. A recurrence plots (RP) analysis and a confidence intervals (CI) analysis were conducted to quantitatively confirm the stationary degree of energy consumption and the normal range of energy consumption, respectively, to realize the identification of abnormal energy consumption. It is found the prediction accuracy of LSSVR model can exceed 90% based on the comparison between the actual and predicted data. The energy consumption is considered to be non-stationary if the correlation coefficient between the time series of periodicity and energy consumption is larger than that between the time series of periodicity and Lorenz. Additionally, the lower limit and upper limit of normal energy consumption are obtained.
摘要
异常能耗预警是工业过程节能的重要内容。然而, 对于通常能耗巨大的铅冶炼行业的相关研究 却鲜有报道。因此, 本研究建立了基于智能能耗预测和异常能耗识别的预警系统。采用自适应遗传算 法优化最小二乘支持向量回归(LSSVR)模型, 对铅冶炼过程的能耗进行预测。分别通过递归图 (RP)分 析和置信区间(CI)分析, 定量确定能耗的平稳程度和正常范围, 实现异常能耗的识别。通过比较实际 数据与预测数据, 发现LSSVR 模型的预测精度可达 90%以上。如果周期时间序列与能耗的相关系数 大于周期时间序列与洛伦兹时间序列的相关系数, 则认为能耗是非平稳的。此外, 得到了正常能耗的 上限和下限。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
LIU Gang, LI Meng-si, ZHOU Bing-jie, CHEN Ying-ying, LIAO Sheng-ming. General indicator for techno-economic assessment of renewable energy resources [J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2018, 156: 416–426. DOI: 10.1016/j.enconman.2017.11.054.
LI Yu-qiang, TANG Wei, CHEN Yong, LIU Jiang-wei, LEE Chia-fon F. Potential of acetone-butanol-ethanol (ABE) as a biofuel [J]. Fuel, 2019, 242: 673–686. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.01.063.
CHEN Jing-wei, XU Wen-wen, ZUO Hong-yan, WU Xiao-min, E Jia-qiang, WANG Tao-sheng, ZHANG Feng, LU Na. System development and environmental performance analysis of a solar-driven supercritical water gasification pilot plant for hydrogen production using life cycle assessment approach [J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2019, 184: 60–73. DOI: 10.1016/j.enconman.2019.01.041.
International Energy Agency. World Energy Outlook 2018 [EB/OL]. https://www.iea.org/weo2018/.
MA Wei-wu, XUE Xin-pei, LIU Gang. Techno-economic evaluation for hybrid renewable energy system: Application and merits [J]. Energy, 2018, 159: 385–409. DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2018.06.101.
COURSOL P, MACKEY P J, KAPUSTA J P T, VALENCIA N C. Energy consumption in copper smelting: A new asian horse in the race [J]. JOM, 2015, 67: 1066–1074. DOI: 10.1007/s11837-015-1380-1.
SLOVIKOVSKII V V, GULYAEVA A V. Effective linings for kivcet furnaces [J]. Refractories and Industrial Ceramics, 2014, 54: 350–352. DOI: 10.1007/s11148-014-9609-z.
NIKOLIC S, HOGG B, VOIGT P. ISASMELT™-flexibility in furnace design [M]. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2018. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-95022-8_35.
PEREZ-TELLO M, SANCHEZ-CORRALES V M, PRIETO-SANCHEZ M R, RODRÍGUEZ-HOYOS O. A kinetic model for the oxidation of selenium and tellurium in an industrial kaldo furnace [J]. JOM, 2004, 56: 52–54. DOI: 10.1007/s11837-004-0236-x.
BAI Lu, QIAO Qi, LI Yan-ping, XIE Ming-hui, WAN Si, ZHONG Qing-dao. Substance flow analysis of production process: A case study of a lead smelting process [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2015, 104: 502–512. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.05.020.
RABAH M A, BARAKAT M A. Energy saving and pollution control for short rotary furnace in secondary lead smelters [J]. Renewable Energy, 2001, 23: 561–577. DOI: 10.1016/S0960-1481(00)00134-8.
JIANG Bo, RAVINDRAN B, CHO H. Probability-based prediction and sleep scheduling for energy-efficient target tracking in sensor networks [J]. IPEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2013, 12: 735–747. DOI: 10.1109/TMC.2012.44.
SEEM J E. Pattern recognition algorithm for determining days of the week with similar energy consumption profiles [J]. Energy and Buildings, 2005, 37: 127–139. DOI: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2004.04.004.
FUMO N, RAFE BISWAS M A. Regression analysis for prediction of residential energy consumption [J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2015, 47: 332–343. DOI: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.03.035.
EKONOMOU L. Greek long-term energy consumption prediction using artificial neural networks [J]. Energy, 2010, 35: 512–517. DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2009.10.018.
MA Zhan-yu, LI Hai-long, SUN Qie, WANG Chao, YAN Ai-bing, STARFELT F. Statistical analysis of energy consumption patterns on the heat demand of buildings in district heating systems [J]. Energy and Buildings, 2014, 85: 464–472. DOI: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2014.09.048.
KALOGIROU S A, BOJIC M. Artificial neural networks for the prediction of the energy consumption of a passive solar building [J]. Energy, 2000, 25: 479–491. DOI: 10.1016/S0360-5442(99)00086-9.
XU Ning, DANG Yao-guo, GONG Yan-de. Novel grey prediction model with nonlinear optimized time response method for forecasting of electricity consumption in China [J]. Energy, 2017, 118: 473–480. DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2016.10.003.
SPOLADORE A, BORELLI D, DEVIA F, MORA F, SCHENONE C. Model for forecasting residential heat demand based on natural gas consumption and energy performance indicators [J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 182: 488–499. DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.08.122.
TSO G K F, YAU K K W. Predicting electricity energy consumption: A comparison of regression analysis, decision tree and neural networks [J]. Energy, 2007, 32: 1761–1768. DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2006.11.010.
LE C V, PANG C K, GAN O P, CHEE X M, ZHANG D H, LUO M, CHAN H L, LEWIS F L. Classification of energy consumption patterns for energy audit and machine scheduling in industrial manufacturing systems [J]. Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control, 2013, 35: 583–592. DOI: 10.1177/0142331212460883.
SANTAMOURIS M, MIHALAKAKOU G, PATARGIAS P, GAITANI N, SFAKIANAKI K, PAPAGLASTRA M, PAVLOU C, DOUKAS P, PRIMIKIRI E, GEROS V, ASSIMAKOPOULOS M N, MITOULA R, ZEREFOS S. Using intelligent clustering techniques to classify the energy performance of school buildings [J]. Energy and Buildings, 2007, 39: 45–51. DOI: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2006.04.018.
YANG Hai-dong, GUO Jian-hua, LIU Guo-sheng. Energy anomaly detection in tire curing by using data integration and forecasting techniques [EB/OL]. [2019-05-14]. http://nopr.niscair.res.in/handle/123456789/14155.
ANGELOS E W S, SAAVEDRA O R, CORTES O A C, SOUZA A N d. Detection and identification of abnormalities in customer consumptions in power distribution systems [J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2011, 26: 2436–2442. DOI: 10.1109/TPWRD.2011.2161621.
FONTUGNE R, ORTIZ J, TREMBLAY N, BORGNAT P, FLANDRIN P, FUKUDA K, CULLER D, ESAKI H. Strip, bind, and search: A method for identifying abnormal energy consumption in buildings [C]// 2013 ACM/IEEE International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks (IPSN). 2013: 129–140. DOI: 10.1145/ 2461381.2461399.
SUYKENS J A K, VANDEWALLE J. Least squares support vector machine classifiers [J]. Neural Processing Letters, 1999, 9: 293–300. DOI: 10.1023/A:1018628609742.
YANG Xiao-wei, TAN Liang-jun, HE Li-fan. A robust least squares support vector machine for regression and classification with noise [J]. Neurocomputing, 2014, 140: 41–52. DOI: 10.1016/j.neucom.2014.03.037.
CHEN Rong, LIANG Chang-yong, HONG Wei-chiang, GU Dong-xiao. Forecasting holiday daily tourist flow based on seasonal support vector regression with adaptive genetic algorithm [J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2015, 26: 435–443. DOI: 10.1016/j.asoc.2014.10.022.
YANG Z, GU X S, LIANG X Y, LING L C. Genetic algorithm-least squares support vector regression based predicting and optimizing model on carbon fiber composite integrated conductivity [J]. Materials & Design, 2010, 31: 1042–1049. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2009.09.057.
YU Le-an, DAI Wei, TANG Ling, WU Jia-qian. A hybrid grid-GA-based LSSVR learning paradigm for crude oil price forecasting [J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2016, 27: 2193–2215. DOI: 10.1007/s00521-015-1999-4.
VALAVANIS D, SPANOUDAKI D, GKILI C, SAZOU D. Using recurrence plots for the analysis of the nonlinear dynamical response of iron passivation-corrosion processes [J]. Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science, 2018, 28: 085708. DOI: 10.1063/1.5025801.
ECKMANN J, KAMPHORST S O, RUELLE D. Recurrence plots of dynamical systems [J]. World Scientific Series on Nonlinear Science Series A, 1995, 16: 441–446.
MARWAN N, CARMEN ROMANO M, THIEL M, KURTHS J. Recurrence plots for the analysis of complex systems [J]. Physics Reports, 2007, 438: 237–329. DOI: 10.1016/j.physrep.2006.11.001.
MARWAN N, WESSEL N, MEYERFELDT U, SCHIRDEWAN A, KURTHS J. Recurrence-plot-based measures of complexity and their application to heart-rate-variability data [J]. Physical Review E, 2002, 66: 026702. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.66.026702.
ADDO P M, BILLIO M, GUEGAN D. Nonlinear dynamics and recurrence plots for detecting financial crisis [J]. The North American Journal of Economics and Finance, 2013, 26: 416–435. DOI: 10.1016/j.najef.2013.02.014.
LAN H, NELSON B L, STAUM J. A confidence interval procedure for expected shortfall risk measurement via two-level simulation [J]. Operations Research, 2010, 58: 1481–1490. DOI: 10.1287/opre.1090.0792.
LEE S, BOLIC M, GROZA V Z, DAJANI H R, RAJAN S. Confidence interval estimation for oscillometric blood pressure measurements using bootstrap approaches [J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2011, 60: 3405–1415. DOI: 10.1109/TIM.2011.2161926.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Foundation item: Project(2015SK1002) supported by Key Projects of Hunan Province Science and Technology Plan, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Hc., Fang, Hr., Meng, L. et al. A pre-warning system of abnormal energy consumption in lead smelting based on LSSVR-RP-CI. J. Cent. South Univ. 26, 2175–2184 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4164-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4164-x
Key words
- lead smelting
- energy consumption
- least square support vector regression (LSSVR)
- recurrence plots (RP)
- confidence intervals (CI)