Abstract
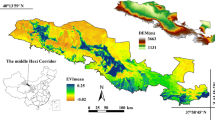
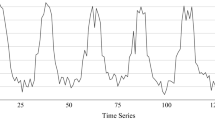
Time-series Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) data have been widely used for large area crop mapping. However, the temporal crop signatures generated from these data were always accompanied by noise. In this study, a denoising method combined with Time series Inverse Distance Weighted (T-IDW) interpolating and Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) was presented. The detail crop planting patterns in Hebei Plain, China were classified using denoised time-series MODIS NDVI data at 250 m resolution. The denoising approach improved original MODIS NDVI product significantly in several periods, which may affect the accuracy of classification. The MODIS NDVI-derived crop map of the Hebei Plain achieved satisfactory classification accuracies through validation with field observation, statistical data and high resolution image. The field investigation accuracy was 85% at pixel level. At county-level, for winter wheat, there is relatively more significant correlation between the estimated area derived from satellite data with noise reduction and the statistical area (R 2 = 0.814, p < 0.01). Moreover, the MODIS-derived crop patterns were highly consistent with the map generated by high resolution Landsat image in the same period. The overall accuracy achieved 91.01%. The results indicate that the method combining T-IDW and DWT can provide a gain in time-series MODIS NDVI data noise reduction and crop classification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achard F E H, Mayaux P, 2001. Tropical forest mapping from coarse spatial resolution satellite data: Production and accuracy assessment issues. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 22(14): 2741–2762. doi: 10.1080/01431160120548
Addison P S, 2002. The Illustrated Wavelet Transform Handbook. Bristol: The Institute of Physics Publishing.
Bartholome E, Belward A, 2005. GLC2000: A new approach to global land cover mapping from Earth observation data. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 26(9): 1959–1977. doi: 10.1080/01431160412331291297
Beck P, Atzberer C, Høgda K et al., 2006. Improved monitoring of vegetation dynamics at very high latitudes: A new method using MODIS NDVI. Remote Sensing of Environment, 100(3): 321–334. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2005.10.021
Boles S, Xiao X, Liu J et al., 2004. Land cover characterization of Temperate East Asia using multi-temporal VEGETATION sensor data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 90(4): 477–489. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2004.01.016
Canisius F, Turral H, Molden D, 2007. Fourier analysis of historical NOAA time series data to estimate bimodal agriculture. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 28(24): 5503–5522. doi: 10.1080/01431160601086043
Cao Zhenguo, Yang Jingxiang, Zhao Wenhai, 2007. Rural Statistical Yearbook of Hebei Province. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 476–522. (in Chinese)
Chawla N, Bowyer K, Hall L et al., 2002. SMOTE: Synthetic minority over-sampling technique. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 16: 321–357. doi: 10.1613/jair.953
Chen J, Jonsson P, Tamura M et al., 2004. A simple method for reconstructing a high-quality NDVI time-series data set based on the Savitzky-Golay filter. Remote Sensing of Environment, 91(3–4): 332–344. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2004.03.014
Didan K, Huete A, 2006. MODIS vegetation index product series collection 5 change summary. Available at: http://landweb.nascom.nasa.gov/QAwww/forPage/MOD13VIC5ChangesDocument062806.pdf.
Friedl M, Mciver D, Hodges J et al., 2002. Global land cover mapping from MODIS: Algorithms and early results. Remote Sensing of Environment, 83(1–2): 287–302. doi: 10.1016/ S0034-4257(02)00078-0
Galford G, Mustard J, Melillo J et al., 2008. Wavelet analysis of MODIS time series to detect expansion and intensification of row-crop agriculture in Brazil. Remote Sensing of Environment, 112(5): 576–587. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2007.05.017
Hird J, Mcdermid G, 2009. Noise reduction of NDVI time series: An empirical comparison of selected techniques. Remote Sensing of Environment, 113(1): 248–258. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2008. 09.003
Homer C, Huang C, Yang L et al., 2004. Development of a 2001 national land-cover database for the United States. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 70(7): 829–840.
Huete A, Justice C, Leeuwen W V, 1999. MODIS vegetation index (MOD13) algorithm theoretical basis document (Version 3). Available at: http://modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/data/atbd/atbdmod13.pdf (accessed 20 March 2009).
Jönsson P, Eklundh L, 2002. Seasonality extraction by function- fitting to time series of satellite sensor data. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 40(8): 1824–1832. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2002.802519
Julien Y, Sobrino J A, 2010. Comparison of cloud-reconstruction methods for time series of composite NDVI data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 114(3): 618–625. doi: 10.1016/j.rse. 2009.11.001
Liu C M, Yu J J, Kendy E, 2001. Groundwater exploitation and its impact on the environment in the North China Plain. Water International, 26(2): 265–272. doi: 10.1080/02508060108686913
Lobell D, Asner G, 2004. Cropland distributions from temporal unmixing of MODIS data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 93(3): 412–422. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2004.08.002
Lotsch A, Tian Y, Friedl M et al., 2003. Land cover mapping in support of LAI and FPAR retrievals from EOS-MODIS and MISR: Classification methods and sensitivities to errors. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 24(10): 1997–2016. doi: 10.1080/01431160210154858
Lovell J L, Graetz R D, 2001. Filtering pathfinder AVHRR land NDVI data for Australia. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 22(13): 2649–2654. doi: 10.1080/01431160116874
Lu X, Liu R, Liu J et al., 2007. Removal of noise by wavelet method to generate high quality temporal data of terrestrial MODIS products. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 73(10): 1129–1139.
Lunetta R, Knight J, Ediriwickrema J et al., 2006. Land-cover change detection using multi-temporal MODIS NDVI data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 105(2): 142–154. doi: 10.1016/ j.rse.2006.06.018
Ma M, Veroustraete F, 2006. Reconstructing pathfinder AVHRR land NDVI time-series data for the Northwest of China. Advances in Space Research, 37(4): 835–840. doi: 10.1016/j.asr. 2005.08.037
Mallat S, 1989. A theory for multiresolution signal decomposition: The wavelet representation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 11(7): 674–693. doi: 10. 1109/34.192463
Roerink G J, Menenti M, Verhoef W, 2000. Reconstructing cloud free NDVI composites using Fourier analysis of time series. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 21(9): 1911–1917. doi: 10.1080/014311600209814
Sakamoto T, Yokozawa M, Toritani H et al., 2005. A crop phenology detection method using time-series MODIS data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 96(3–4): 366–374. doi: 10. 1016/j.rse.2005.03.008
Savitzky A, Golay M J E, 1964. Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Analytical Chemistry, 36(8): 1627–1639. doi: 10.1021/ac60214a047
Sellers P, Tucker C, Collatz G et al., 1994. A global 1° by 1° NDVI data set for global studies. Part 2: The generation of global fields of terrestrial biophysical parameters from the NDVI. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 15(17):3519–3545. doi: 10.1080/01431169408954343
Torrence C, Compo G, 1998. A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 79(1):61–78.
USGS (U.S. Geological Survey), 2009. Land processes distributed active archive center (LP DAAC). Available at: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/lpdaac/get_data/data_pool (accessed 20 March 2009).
Viovy N, Arino O, Belward A S, 1992. The best index slope extraction (BISE): A method for reducing noise in NDVI time-series. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 13(8):1585–1590. doi: 10.1080/01431169208904212
Wardlow B, Egbert S, 2008. Large-area crop mapping using time-series MODIS 250 m NDVI data: An assessment for the US Central Great Plains. Remote Sensing of Environment, 112(3): 1096–1116. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2007.07.019
Wardlow B, Egbert S, Kastens J, 2007. Analysis of time-series MODIS 250 m vegetation index data for crop classification in the US Central Great Plains. Remote Sensing of Environment, 108(3): 290–310. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2006.11.021
Wessels K, Fries D R, Dempewolf J et al., 2004. Mapping regional land cover with MODIS data for biological conservation: Examples from the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem, USA and Pará State, Brazil. Remote Sensing of Environment, 92(1): 67–83. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2004.05.002
Wu G, De Leeuw J, Skidmore A et al., 2008. Comparison of MODIS and Landsat TM5 images for mapping tempo-spatial dynamics of Secchi disk depths in Poyang Lake National Nature Reserve, China. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 29(8): 2183–2198. doi: 10.1080/01431160701422254
Xiao X, Braswell B, Zhang Q et al., 2003. Sensitivity of vegetation indices to atmospheric aerosols: Continental-scale observations in Northern Asia. Remote Sensing of Environment, 84(3): 385–392. doi: 10.1016/S0034-4257(02)00129-3
Zhang M W, Zhou Q B, Chen Z X et al., 2008. Crop discrimination in Northern China with double cropping systems using Fourier analysis of time-series MODIS data. International Journal of Applied Earth Observations and Geoinformation, 10(4): 476–485. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2007.11.002
Zhang X, Friedl M, Schaaf C et al., 2003. Monitoring vegetation phenology using MODIS. Remote Sensing of Environment, 84(3): 471–475. doi: 10.1016/S0034-4257(02)00135-9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of Knowledge Innovation Programs of Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. KZCX2-YW-449, KSCX-YW-09), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40971025, 40901030, 50969003)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Lei, Y., Wang, L. et al. Crop classification using MODIS NDVI data denoised by wavelet: A case study in Hebei Plain, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 21, 322–333 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-011-0472-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-011-0472-2