Abstract
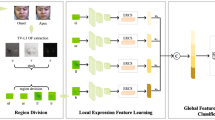
Most existing micro-expression recognition (MER) methods are based on convolutional neural networks (CNN) and could obtain better representations than conventional handcrafted-based methods. Nevertheless, the local receptive field of CNN leads to poor global feature extraction and thus limits the accuracy. In contrast, the vision transformer, an alternative technique, could capture global facial information and perform superiority over CNN in many vision tasks. However, directly applying it to MER may not be as effective as expected since the insufficient data and class-imbalanced characteristics of existing ME datasets could seriously restrict the accuracy. To address these problems, we propose a three-stream vision transformer-based network with sparse sampling and relabeling (SSRLTS-ViT). First, the network learns discriminative ME representations from three optical flow components. Second, a sparse sampling strategy is employed to add the optical flow components computed by the onset and images around the apex into training sets, which can expand the sample capacity and simultaneously guarantee the differences between data. Moreover, we introduce a relabeling mechanism to reassign the training data with correct labels to decrease the impact caused by subjectivity annotations, which can further improve recognition accuracy. Experimental results on two benchmarks show that SSRLTS-ViT outperforms other competing methods by obtaining the UF1 of 0.843 and UAR of 0.853 on the 3-class datasets and the UF1 of 0.795 and UAR of 0.801 on the 5-class datasets, respectively.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used in our paper (SMIC-HS, CASME II, and SAMM) are publicly available.
References
Zhao, G., Pietikainen, M.: Dynamic texture recognition using local binary patterns with an application to facial expressions. IEEE Trans. Patt. Analy. Mach. Intell. 29(6), 915–928 (2007)
Liong, S.-T., See, J., Wong, K., Phan, R.C.-W.: Less is more: Micro-expression recognition from video using apex frame. Signal Process. Image Commun. 62, 82–92 (2018)
Dosovitskiy, A., Beyer, L., Kolesnikov, A., Weissenborn, D., Zhai, X., Unterthiner, T., Dehghani, M., Minderer, M., Heigold, G., Gelly, S., et al.: An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929 (2020)
Carion, N., Massa, F., Synnaeve, G., Usunier, N., Kirillov, A., Zagoruyko, S.: End-to-end object detection with transformers. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 213–229 (2020). Springer
Ma, F., Sun, B., Li, S.: Facial expression recognition with visual transformers and attentional selective fusion. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 1–1 (2021)
Wang, Y., Xu, Z., Wang, X., Shen, C., Cheng, B., Shen, H., Xia, H.: End-to-end video instance segmentation with transformers. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8741–8750 (2021)
Bobojanov, S., Kim, B., Arabboev, M., Begmatov, S.: Comparative analysis of vision transformer models for facial emotion recognition using augmented balanced datasets. Appl. Sci. 13, 12271 (2023)
Zhou, H., Huang, S., Xu, Y.: Inceptr: micro-expression recognition integrating inception-cbam and vision transformer. Multimedia Syst. 29, 1–14 (2023)
Wang, K., Peng, X., Yang, J., Lu, S., Qiao, Y.: Suppressing uncertainties for large-scale facial expression recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6897–6906 (2020)
Peng, M., Wu, Z., Zhang, Z., Chen, T.: From macro to micro expression recognition: Deep learning on small datasets using transfer learning. In: 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), pp. 657–661 (2018). IEEE
Liu, Y., Du, H., Zheng, L., Gedeon, T.: A neural micro-expression recognizer. In: 2019 14th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2019), pp. 1–4 (2019). IEEE
Zhao, S., Tao, H., Zhang, Y., Xu, T., Zhang, K., Hao, Z., Chen, E.: A two-stage 3d cnn based learning method for spontaneous micro-expression recognition. Neurocomputing 448, 276–289 (2021)
Khor, H.-Q., See, J., Phan, R.C.W., Lin, W.: Enriched long-term recurrent convolutional network for facial micro-expression recognition. In: 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), pp. 667–674 (2018). IEEE
Xia, Z., Hong, X., Gao, X., Feng, X., Zhao, G.: Spatiotemporal recurrent convolutional networks for recognizing spontaneous micro-expressions. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 22(3), 626–640 (2019)
Xia, Z., Peng, W., Khor, H.-Q., Feng, X., Zhao, G.: Revealing the invisible with model and data shrinking for composite-database micro-expression recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 8590–8605 (2020)
Gan, Y.S., Liong, S.-T., Yau, W.-C., Huang, Y.-C., Tan, L.-K.: Off-apexnet on micro-expression recognition system. Signal Process Image Commun 74, 129–139 (2019)
Liong, S.-T., Gan, Y.S., See, J., Khor, H.-Q., Huang, Y.-C.: Shallow triple stream three-dimensional cnn (ststnet) for micro-expression recognition. In: 2019 14th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2019), pp. 1–5 (2019). IEEE
Chen, B., Liu, K.-H., Xu, Y., Wu, Q.-Q., Yao, J.-F.: Block division convolutional network with implicit deep features augmentation for micro-expression recognition. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia (2022)
Nie, X., Takalkar, M.A., Duan, M., Zhang, H., Xu, M.: Geme: dual-stream multi-task gender-based micro-expression recognition. Neurocomputing 427, 13–28 (2021)
Zhou, H., Huang, S., Li, J., Wang, S.-J.: Dual-atme: dual-branch attention network for micro-expression recognition. Entropy 25, 460 (2023)
Peng, Z., Huang, W., Gu, S., Xie, L., Wang, Y., Jiao, J., Ye, Q.: Conformer: Local features coupling global representations for visual recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.03889 (2021)
Srinivas, A., Lin, T.-Y., Parmar, N., Shlens, J., Abbeel, P., Vaswani, A.: Bottleneck transformers for visual recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 16519–16529 (2021)
Zhang, L., Hong, X., Arandjelović, O., Zhao, G.: Short and long range relation based spatio-temporal transformer for micro-expression recognition. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 13(4), 1973–1985 (2022)
King, D.E.: Dlib-ml: a machine learning toolkit. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 10, 1755–1758 (2009)
Zach, C., Pock, T., Bischof, H.: A duality based approach for realtime tv-l 1 optical flow. In: Joint Pattern Recognition Symposium, pp. 214–223 (2007). Springer
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A.N., Kaiser, Ł, Polosukhin, I.: Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inform. Process. Syst. 30, 12 (2017)
Yan, W.-J., Li, X., Wang, S.-J., Zhao, G., Liu, Y.-J., Chen, Y.-H., Fu, X.: Casme ii: an improved spontaneous micro-expression database and the baseline evaluation. PloS one 9(1), 86041 (2014)
Davison, A.K., Lansley, C., Costen, N., Tan, K., Yap, M.H.: Samm: a spontaneous micro-facial movement dataset. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 9(1), 116–129 (2016)
Li, X., Pfister, T., Huang, X., Zhao, G., Pietikäinen, M.: A spontaneous micro-expression database: Inducement, collection and baseline. In: 2013 10th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (fg), pp. 1–6 (2013). IEEE
See, J., Yap, M.H., Li, J., Hong, X., Wang, S.-J.: Megc 2019-the second facial micro-expressions grand challenge. In: 2019 14th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face Gesture Recognition (FG 2019), pp. 1–5 (2019)
Davison, A.K., Merghani, W., Yap, M.H.: Objective classes for micro-facial expression recognition. J. Imaging 4(10), 119 (2018)
Van Quang, N., Chun, J., Tokuyama, T.: Capsulenet for micro-expression recognition. In: 2019 14th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2019), pp. 1–7 (2019). IEEE
Zhou, L., Mao, Q., Xue, L.: Dual-inception network for cross-database micro-expression recognition. In: 2019 14th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2019), pp. 1–5 (2019). IEEE
Li, H., Sui, M., Zhu, Z., Zhao, F.: Mmnet: Muscle motion-guided network for micro-expression recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.05297 (2022)
Lei, L., Chen, T., Li, S., Li, J.: Micro-expression recognition based on facial graph representation learning and facial action unit fusion. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), pp. 1571–1580 (2021)
Esmaeili, V., Mohassel Feghhi, M., Shahdi, S.O.: A comprehensive survey on facial micro-expression: approaches and databases. Multimedia Tools Appl. 81(28), 40089–40134 (2022)
Esmaeili, V., Shahdi, S.O.: Automatic micro-expression apex spotting using cubic-lbp. Multimedia Tools Appl. 79, 20221–20239 (2020)
Esmaeili, V., Mohassel Feghhi, M., Shahdi, S.O.: Spotting micro-movements in image sequence by introducing intelligent cubic-lbp. IET Image Process. 16(14), 3814–3830 (2022)
Chaudhry, R., Ravichandran, A., Hager, G., Vidal, R.: Histograms of oriented optical flow and binet-cauchy kernels on nonlinear dynamical systems for the recognition of human actions. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1932–1939 (2009). IEEE
Polikovsky, S., Kameda, Y., Ohta, Y.: Facial micro-expressions recognition using high speed camera and 3d-gradient descriptor. In: 3rd International Conference on Imaging for Crime Detection and Prevention (ICDP 2009), pp. 1–6 (2009)
Wang, C., Peng, M., Bi, T., Chen, T.: Micro-attention for micro-expression recognition. Neurocomputing 410, 354–362 (2020)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inform. Process. Syst. 25, 1097–1105 (2012)
Zhao, S., Yin, S., Tang, H., Jin, R., Xu, Y., Xu, T., Chen, E.: Fine-grained micro-expression generation based on thin-plate spline and relative au constraint. In: Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 7150–7154 (2022)
Zhang, Y., Xu, X., Zhao, Y., Wen, Y., Tang, Z., Liu, M.: Facial prior guided micro-expression generation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 27, 303 (2023)
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Key R &D Program of Hunan (2022SK2104), Leading plan for scientific and technological innovation of high-tech industries of Hunan (2022GK4010), National Key R &D Program of China (2021YFF0900600), China Scholarship Council (CSC, No. 202306130012 and 202306130013), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (61672222).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Yin, L., Zhang, H. et al. Facial micro-expression recognition using three-stream vision transformer network with sparse sampling and relabeling. SIViP 18, 3761–3771 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-024-03039-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-024-03039-x