Abstract
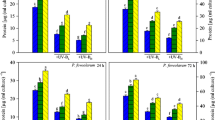
The present investigation is aimed to understand how a bloom-forming cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa adapts to changing climatic conditions. The cyanobacterium was exposed to stresses of UV-B (2 Wm−2) radiation and temperature (45 °C) for desired time intervals. Results showed that both the stresses affect growth and photosynthetic efficiency of M. aeruginosa. More than 50% loss of survival and content of photosynthetic pigments was noted after 4 h treatment of both the above stresses. Such changes were mainly due to the generation of reactive oxygen species which cause damage to proteins, DNA, lipids, and modulation of the membrane stability. An increase in the proline accumulation was noted in the cells which probably negates the harmful effects. In addition, activity of antioxidative enzymes namely, catalase, superoxide dismutase, ascorbate peroxidase, and peroxidase was induced by 1.5–3.0-fold on 3 h of UV-B and temperature treatment indicating their possible role in protection. Interestingly, induction of photoprotective compound, mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs) were also found under UV-B stress which might be an additional strategy of defense mechanism for the survival of the cyanobacterium. Analysis of photoprotective compound revealed shinorine as the main MAA synthesized by the cyanobacterium.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allakhverdiev SI, Los DA, Murata N (2009) Regulatory roles of photosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids in membrane lipids. In: Wada H, Murata N (eds) Lipids in photosynthesis: essential and regulatory functions. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 373–388
Apel K, Hirt H (2004) Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative and signal transduction. Ann Rev Plant Biol 55:373–399
Babele PK, Singh G, Tyagi MB, Sinha RP, Kumar A (2012) Ultraviolet-B radiation effects on cyanobacteria and the role of sunscreen pigments in its protection. Phykos 42:1–13
Backor M, Fahselt D, Wu CT (2004) Free proline content is positively correlated with copper tolerance of the lichen photobiont Trebouxia erici (chlorophyta). Plant Sci 167:151–157
Bais AF, McKenzie RL, Bernhard G, Aucamp PJ, Ilyas M, Madronich S, Tourpalia K (2014) Ozone depletion and climate change: impacts on UV radiation. Photochem Photobiol Sci 14:19–52
Basak M, Sharma M, Chakraborty U (2001) Biochemical responses of Camellia sinensis (L) O. Kuntze to heavy metal stress. J Environ Biol 22:37–41
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Tear ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Camejo D, Jimenez A, Alarcon JJ, Torres W, Gomez JM, Sevilla F (2006) Changes in photosynthetic parameters and antioxidant activities following heat-shock treatment in tomato plants. Funct Plant Biol 33:177–187
Carmichael WW, Azevedo SMFO, An JS, Molica RJR, Jochimsen EM, Lau S, Rinehart KL, Shaw GR, Eaglesham GK (2001) Human fatalities from cyanobacteria: chemical and biological evidence for cyanotoxins. Environ Health Persp 109:663–668
Carreto JI, Carignan MO (2011) Mycosporine-like amino acids: relevant secondary metabolites. Chemical and ecological aspects. Mar Drugs 9:387–446
Ding Y, Song L, Sedmak B (2013) UV-B radiation as a potential selective factor favoring microcystin producing bloom-forming cyanobacteria. PLoS One 8:e73919. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0073919
Foyer CH, Noctor G (2009) Redox regulation in photosynthetic organisms: signaling, acclimation, and practical implications. Antioxid Redox Signal 11:861–905
Gao K, Li P, Watanabe T, Helbling EW (2008) Combined effects of ultraviolet radiation and temperature on morphology, photosynthesis and DNA of Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis (cyanophyta). J Phycol 44:777–786
Häder DP, Williamson CE, Wangberg SA, Rautio M, Rose KC, Gao K, Helbling EW, Sinha RP, Worrest R (2015) Effects of UV radiation on aquatic ecosystems and interactions with other environmental factors. Photochem Photobiol Sci 14:108–126
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (1999) Free radicals in biology and medicine, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press Inc, New York, p 107
Hare PD, Cress WA (1997) Metabolic implications of stress-induced proline accumulation in plants. Plant Growth Regul 21:79–102
Hargreaves A, Taiwo FA, Duggan O, Kirk SH, Ahmad SI (2007) Near-ultraviolet photolysis of b-phenylpyruvic acid generates free radicals and results in DNA damage. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 89:110–116
He YY, Häder DP (2002) Reactive oxygen species and UV-B: effect on cyanobacteria. Photochem Photobiol Sci 1:729–736
Herman JR (2010) Global increase in UV irradiance during the past 30 years (1979–2008) estimated from satellite data. J Geophys Res 115:D04203. doi:10.1029/2009JD012219
Hu C, Voller G, Submuth R, Dittmann E, Kehr JC (2015) Functional assessment of mycosporine-like amino acids in Microcystis aeruginosa strain PCC 7806. Environ Microbiol 17:1548–1559. doi:10.1111/1462-2920.12577
Johnk KD, Huisman J, Sharples J, Sommeijeri B, Visser PM, Strooms JM (2008) Summer heat waves promote blooms of harmful cyanobacteria. Glob Change Biol 14:495–512
Jones DP (2006) Redefining oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal 81:1865–1879
Kumar A, Tyagi MB, Jha PN (2004) Evidences showing ultraviolet-B radiation-induced damage of DNA in cyanobacteria and its detection by PCR assay. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 318:1025–1030
Kumar J, Babele PK, Singh D, Kumar A (2016) UV-B radiation stress causes alterations in whole cell protein profile and expression of certain genes in the rice phyllospheric bacterium Enterobacter cloacae. Front Microbiol 7:1–14. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2016.01440
Kyungsil C, Pauli S, Marianne P (2004) Oxidative stress tolerance in the filamentous green algae Cladophora glomerata and Enteromorpha ahlneriana. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 298:111–123
Li M, Hu CW, Zhu Q, Chen L, Kong Z, Liu Z (2006) Copper and zinc induction of lipid peroxidation and effects on antioxidant enzyme activities in the microalga Pavlova viridis (Prymnesiophyceae). Chemosphere 62:565–572
Llabres M, Agusti S, Fernandez M, Canepa A, Maurin F, Vidal F, Duarte CM (2013) Impact of elevated UVB radiation on marine biota: a meta-analysis. Glob Ecol Biogeog 22:131–144
Madronich S, McKenzie RL, Bjorn O, Caldwell MM (1998) Changes in biologically active ultraviolet radiation reaching the Earth’s surface. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 46:5–19
Manney GL, Santee ML, Rex M, Livesey NJ, Pitts MC, Veefkind P, Nash ER, Wohltmann I, Lehmann R, Froidevaux L, Poole LR, Schoeberl MR, Haffner DP, Davies J, Dorokhov V, Gernandt H, Johnson B, Kivi R, Kyro E, Larsen N, Levelt PF, Makshtas A, McElroy CT, Nakajima H, Parrondo MC, Tarasick DW, von der Gathen P, Walker KA, Zinoviev NS (2011) Unprecedented arctic ozone loss in 2011. Nature 478:469–475
Marwood CA, Greenberg BM (1996) Effect of supplementary UV-B radiation on chlorophyll synthesis and accumulation of photosystems during chloroplast development in Spirodela oligorrhiza. Photochem Photobiol 64:664–670. doi:10.1111/j.1751-1097.1996.tb03121.x
Mittler R, Finka A, Goloubinoff P (2012) How do plants feel the heat? Trends Biochem Sci 37:118–125
Naudts K, Van den Berge J, Farfan E, Rose P, AbdElgawad H, Ceulemans R, Janssens IA, Asard H, Nijs I (2014) Future climate alleviates stress impact on grassland productivity through altered antioxidant capacity. Env Exp Bot 99:150–158
Pourzand C, Tyrrell RM (1999) Apoptosis, the role of oxidative stress and the example of solar UV radiation. Photochem Photobiol 70:380–390
Rastogi RP, Singh SP, Hader DP, Sinha RP (2011) Ultraviolet-B-induced DNA damage and photorepair in the cyanobacterium Anabaena variabilis PCC 7937. Env Exp Bot 74:280–288
Richa Sinha RP (2015) Biochemical characterization of sunscreening mycosporine-like amino acids from two Nostoc species inhabiting diverse habitats. Protoplasma 252:199–208
Rippka R, Deruelles J, Waterbury JB, Herdman M, Stanier RY (1979) Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. J Gen Appl Microbiol 111:1–61
Ruelland E, Zachowski A (2010) How plants sense temperature. Env Exp Bot 69:225–232
Schopf JW (2000) The fossil record: tracing the roots of the cyanobacterial lineage. In: Whitton BA, Potts M (eds) The ecology of cyanobacteria. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 13–35
Shirkey B, Kovarcik DP, Wright DJ, Wilmoth G, Prickett TF, Helm RF, Gregory EM, Potts M (2000) Active Fe-containing superoxide dismutase and abundant sodF mRNA in Nostoc commune (Cyanobacteria) after years of desiccation. J Bacteriol 182:189–197
Singh G, Babele PK, Sinha RP, Tyagi MB, Kumar A (2013) Enzymatic and non-enzymatic defense mechanisms against ultraviolet-B radiation in two Anabaena species. Process Biochem 48:796–802
Van Breusegem F, Dat JF (2006) Reactive oxygen species in plant cell death. Plant Physiol 141:384–390
Wang G, Chen L, Hao Z, Li X, Liu Y (2011) Effects of salinity stress on the photosynthesis of Wolffia arrhiza as probed by the OJIP test. Fresenius Environ Bull 20:432–438
Wendehenne D, Durner J, Klessig DF (2004) Nitric oxide: a new player in plant signaling and defense responses. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:449–455
Wulff A, Mohlin M, Sundback K (2007) Intra-specific variation in the response of the cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena to moderate UV-B radiation. Harmful Algae 6:388–399
Yakes BJ, Handy SM, Kanyuck KM, DeGrasse SL (2015) Improved screening of microcystin genes and toxins in blue-green algal dietary supplements with PCR and a surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Harmful Algae 47:9–16
Yamori W, Hikosaka K, Way DA (2014) Temperature response of photosynthesis in C3, C4, and CAM plants: temperature acclimation and temperature adaptation. Photosynth Res 119:101–117
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the project grant sanctioned to AK by the Department of Science and Technology, Govt. of India, New Delhi (SR/SO/PS-49/09). Thanks are due to IIT-BHU for providing facilities for the characterization of MAAs. PKB is grateful to the UGC, New Delhi, for the award of JRF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Z. Miszalski.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11738_2017_2540_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Fig. S 1. Micrographs of M. aeruginosa (A) phase contrast, and (B) fluorescence microscopy. Fig. S 2. Effects of UV-B radiation and temperature on (A) percent survival, (B) Chl a, and (C) phycocyanin content in M. aeruginosa. Values are means ± S.D.(n = 3) and asterisks indicate significant differences from 0 h (∗P < 0.05).One-way ANOVA was used according to Duncan’s multiple range test (DMRT) at P≤ 0.05. Fig. S 3. Emission spectra of DCF from M. aeruginosa cells at 0 h and after exposure to temperature and UV-B radiation (1 to 4 h) as measured by spectrofluorometer. The excitation wavelength was 485 nm and emission wavelengths were between 500–600 nm. The control (cells without DCFH) shows the basal level of fluorescence due to autooxidation of DCFH (DOCX 696 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babele, P.K., Singh, G., Singh, A. et al. UV-B radiation and temperature stress-induced alterations in metabolic events and defense mechanisms in a bloom-forming cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa . Acta Physiol Plant 39, 248 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-017-2540-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-017-2540-4