Abstract
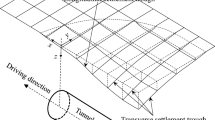
The lining of shield tunnel is usually composed of segments, in which the joints, cracks, and the grouting holes (hereafter called lining deficit) exist. During the long-term running, soils and groundwater may leak from these kinds of lining deficit. The leaking of soil and groundwater causes the long-term ground loss around tunnel and thus results in the settlement of ground surface. This paper aims to analyze the impact of the leakage of groundwater through segments on the long-term settlement of ground surface. The adopted analytical method is based on the theory of groundwater seepage by using numerical simulation. The analyzed results show that settlement of ground surface increases gradually with the increase of the leaked volume of tunnel segments. When the leaked volume was unevenly distributed, differential settlement occurred locally. Comparative analysis by changing the leaked volume was conducted. The results reveal that there is a linear relationship between settlement and leaked volume when the leaked volume was controlled within the allowable limit.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Xu Y S, Shen S L, Du Y J. Geological and hydrogeological environment in Shanghai with geohazards to construction and maintenance of infrastructures. Engineering Geology, 2009, 109(3–4): 241–254
Chai J C, Shen S L, Zhu H H, et al. Land subsidence due to groundwater drawdown in Shanghai. Geotechnique, 2004, 54(3): 143–148
Chai J C, Shen S L, Zhu H H, et al. 1D analysis of land subsidence in Shanghai. Lowland Technology International, 2005, 7(1): 33–41
Xu Y S, Shen S L, Cai Z Y, et al. The state of land subsidence and prediction activities due to groundwater withdrawal in China. Natural Hazards, 2008, 45(1): 123–135
Shanghai Metro Running Management Co Ltd (SMRM). Report of Monitoring on Shanghai Metro Tunnels in 2007. 2007 (in Chinese)
Mair R J, Taylor R N. Bored tunnel in the urban environment. In: Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering. Hamburg, 1997, 2353–2385
Mair R J. Tunnelling and geotechnics: new horizons-46th rankine lecture. Geotechnique, 2008, 58(9): 695–736
Shirlaw J N. Subsidence owing to tunneling II, evaluation of a prediction techniques. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1994, 31(3): 463–466 (discussion)
O’Reilly MP, Mair R J, Alderman G H. Long-term settlements over tunnels: an eleven-year study at Grimsby. In: Proceedings of Conference Tunnelling. London: Institution of Mining and Metallurgy, 1991, 55–64
Shin J H, Addenbrooke T I, Potts D M. A numerical study of the effect of groundwater movement on long-term tunnel behavior. Geotechnique, 2002, 52(6): 391–403
Chen JW and Zhan L X. Deformation measuring of the metro tunnel and deformation data analysis of Shanghai metro line No. 1. Shanghai Geology, 2000, (2): 51–56 (in Chinese)
Wang R L, Zhou X H, Yu Y L. Problem and its treatment during Shanghai metro monitor. In: Proceedings of the 14th Conference of Metro Tunnel Professional Committee. Tunnel and Underground Works Branch of China Civil Engineering Society. 2001, 240–242 (in Chinese)
Wu H N, Hu M D, Xu Y S, et al. Law of influence of segment leakage on long-term tunnel settlement. Chiese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2009, 5(z2): 1608–1611 (in Chinese)
Xia W P. Underground engineering construction in soft clay—civil engineering of Shanghai metro Xujiahui station. Master thesis. Xi an: Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, 2003 (in Chinese)
Liao S M, Liu J H, Wang R L. Shield tunneling and environment protection in Shanghai soft ground. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2009, 24(4): 454–465
Shanghai Urban Construction and Communications Commission. Code for investigation for geotechnical engineering (DGJ 08-37-2002), 2002 (in Chinese)
Bear J. Hydraulics of Groundwater. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1979
Shen S L, Xu Y S, Hong Z S. Estimation of land subsidence based on groundwater flow model. Marine Georesources and Geotechnology, 2006, 24(2): 149–151
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, H., Xu, Y., Shen, Sl. et al. Long-term settlement behavior of ground around shield tunnel due to leakage of water in soft deposit of Shanghai. Front. Archit. Civ. Eng. China 5, 194–198 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-011-0105-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-011-0105-y