Abstract
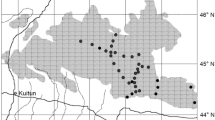
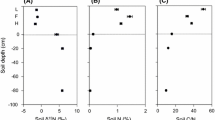
In order to investigate the distribution characteristics of stable carbon isotope ratios (δ 13C) in the desert plant Reaumuria soongorica, the δ 13C values of leaves were measured in 407 individuals of 21 populations. Soil physicochemical properties including soil water content, soil total dissolved solids, soil total nitrogen, soil total phosphorus and soil organic content were also analyzed in order to survey the major factors influencing δ 13C values on spatial variation. Leaves and soil samples were simultaneously collected from the ten major distribution areas in Northwest China at altitudes from 394 m to 1 987 m above sea level, at latitudes from 36°10′N to 44°33′N, and at longitudes from 81°43′E to 106°37′E. These ten areas include Shihezi, Baicheng, Yiwu areas in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region; Anxi, Zhangye, Baiyin, Lanzhou areas in Gansu Province; Shapotou, Yinchuan areas in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region; and Alashan County in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. The results show that the δ 13C value of R. soongorica ranges from −22.77‰ to −29.85‰ with an average of −26.52‰. Foliar d13C values in R. soongorica are not significantly correlated with altitude, latitude or longitude, and a spatial distribution trend of d13C values of R. soongorica is not obvious on a large scale. However, when d13C values of two R. soongorica populations under the same climate conditions are compared, δ 13C values increase obviously from east to west and from north to south. As none of the soil total dissolved solids, soil total nitrogen, soil total phosphorus, and soil organic content shows a uniform trend from east to west and from north to south, we suppose that the small-scaled spatial distribution pattern of δ 13C values of R. soongorica is mainly controlled by the soil water content.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen T, Ma J, Feng H Y, et al (2002). Environmental analysis of stable carbon isotope values in typical desert C3 plants of the Fukang, Xinjiang. Arid Land Geography, 25(4): 342–345 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Craig H (1957). Isotopic standards for carbon and oxygen and correction factors for mass-spectrometric analysis of carbon dioxide. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 12(1–2): 133–149
Farquhar G D, O’Leary M H (1982). On the relationship between carbon isotope discrimination and the intercellular carbon dioxide concentration of leaves. Australian Journal of Plant Physiology, 9: 121–137
Feng H Y, An L Z, Chen T, et al (2003). The relationship between foliar stable carbon isotope composition in Pedicularis L. and environment factors. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 25(1): 88–93 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Feng H Y, An L Z, Wang X L (2000). An effect of environmental factors on plant stable isotope carbon composition. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 17(3): 312–318 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Jiang G M (1996). Application of stable carbon isotope technique in plant physiological ecology research. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 15(2): 49–54 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li X B, Chen J F (1983). Advances in study on plant carbon isotope discrimination and environment change. Advance in Earth Sciences, 13(3): 285–290 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li X B, Chen J F, Zhang P Z, et al (1999). The characteristics of carbon isotope composition of modern plants over Qinghai-Tibet Plateau (NE) and its climatic information. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 17(2): 325–329 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ma J Y, Chen T, Qiang W Y, et al (2005). Correlations between foliar stable carbon isotope composition and environmental factors in desert plant Rearmuria soongorica (Pall.) Maxim.. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 47(9): 1065–1073
Najing Agricultural University (1992). Agricultural Chemical Analysis of Soil. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 20–137 (in Chinese)
O’Leary M H (1988). Carbon isotopes in Photosynthesis (fractionation techniques may reveal new aspects of carbon dynamics in plants). Bioscience, 38: 328–336
Piao H C, Zhu J M, Yu D L, et al (2003). Carbon isotope composition in soil microbial biomass and organic carbon isotope effect. Quaternary Sciences, 23(5): 546–556 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Su B, Han X G, Li L H, et al (2000). Responses of δ 13C value and water use efficiency of plant species to environmental gradients along the grassland zone of Northeast China transect. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 24(6): 648–655 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Su P X, Chen H S, Li Q S (2003). Characteristics of δ 13C values of desert plants and their water utilization efficiency indicated by δ 13C values in the desert of central Hexi Corridor region. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 25(5): 597–602 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Tieszen L L, Senyimba M M, Imbamba S K, et al (1979). The distribution of C3 and C4 grasses and carbon isotope discrimination along an altitudinal and moisture gradient in Kenya. Oecologia, 37: 337–350
Van de Water P K, Leavitt S W, Betancourt J L (2002). Leaf δ13C variability with elevation, slope aspect, and precipitation in the Southwest United States. Oecologia, 132: 332–343
Wang G A (2003). Application of stable carbon isotope for paleoenvironmental research. Quaternary Sciences, 23(5): 471–484 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang G A, Han J M (2001). Relations between δ 13C values of C-3 plants in northwestern China and annual precipitation. Chinese Journal of Geology, 36(4): 494–499 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang G A, Han J M, Liu T S (2003). The carbon isotope composition of C3 herbaceous plants in loess area of Northern China. Science in China (Series D), 46(10): 1069–1076 (in Chinese)
Wang L, Lü H Y, Wu N Q, et al (2003). Altitudinal trends of stable carbon isotope composition for Poeceae in Qinghai-Xizang plateau. Quaternary Sciences, 23(5): 573–580 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang M, Li Y, Huang R Q, et al (2005). The responses of floral carbonate isotopic compositions of the central Qinghai-Tibet Plateau plants to environmental conditions. Journal of Mountain Science, 23(3): 274–279 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu S J, Chen T, Feng H Y, et al (2002). The environmental analysis of spatial differentiation in foliar d13C values in Urumqi up-river region in Xinjiang. Progress in Natural Science, 12(6): 617–620 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang P Y, Zhang Y J (1979). Tamaricaceae. Flora in Reipublicae Populorum Sinarum (Tomus 52). Beijing: Science Press, 142–175 (in Chinese)
Zhao X Y, Wang J, Qian J L (2005). Reconstruction of atmospheric CO2 concentration changes since 1 685 by tree ring δ13C annual series. Quaternary Sciences, 25(5): 545–551 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Quaternary Sciences, 2006, 26(6): 947–954 [译自: 第四纪研究]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, J., Chen, F., Zhang, H. et al. Spatial distribution characteristics of stable carbon isotope compositions in desert plant Reaumuria soongorica (Pall.) Maxim.. Front. Earth Sci. China 1, 150–156 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-007-0019-0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-007-0019-0